Test Information Guide
Field 11: Physics
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
The following reference material will be available to you during the test:
Notes for Physics Test
Not all formulas necessary are listed, nor are all formulas listed used on this test.
In questions on electricity and magnetism, the term current refers to "conventional current" and the use of the right-hand rule is assumed.
All examinees taking the Physics test (field 11) will be provided with an on-screen scientific calculator with functions that include the following: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, square root, percent, sine, cosine, tangent, exponents, and logarithms. You may NOT bring your own calculator to the test.
Nature of Science
Objective 0005
Understand the use of mathematics in physics.
1. The position of an object moving along the x-axis is given by the following equation.
x(t) = t3 – 3t2 + 2t – 5
Which of the following equations gives the velocity of the particle?
- v(t) = 6t – 6
- v(t) = t2 – 3t + 2
- v(t) = 3t2 – 6t + 2
- v(t) =
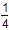 t4 – t3 + t2 – 5t
t4 – t3 + t2 – 5t
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
Correct Response: C.
Force and Motion
Objective 0006
Understand concepts related to motion in one and two dimensions.
2. Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
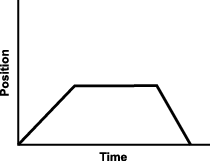
The position versus time of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in the graph above. Which of the following statements best describes the motion of the particle?
- The particle accelerates to a constant velocity and then slows down to a stop.
- The particle travels at a constant speed, stops, and returns to its starting point at a constant speed.
- The particle accelerates to a constant velocity, stops, and then continues at the same velocity.
- The particle has a linear acceleration, attains a constant acceleration, and then decelerates to zero.
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
Correct Response: B.
Objective 0008
Understand characteristics of uniform circular motion, rotational dynamics, and fluid mechanics.
3. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
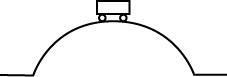
The diagram above shows a 1000 kg car as it moves at 10 m/s over the top of a circular bridge with a radius of 50 m. What is the magnitude of the normal force on the car at the top of the bridge?
- 2,000 N
- 7,800 N
- 9,800 N
- 11,800 N
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
Correct Response: B.
Energy, Momentum, and Heat Transfer
Objective 0009
Understand the concepts of energy, work, and power and the principle of conservation of energy.
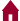
4. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
The graph shows the height on the x axis and position in the y axis. There are four points marked on the graph. The graph starts with position I a low position and high height then decreases quickly to a low height then increases to a plateau at position II then decreases to the lowest height at position III then increases to position IV.
The diagram above shows a frictionless track. A mass is released from point I. At what point does the mass have maximum kinetic energy?
- I
- II
- III
- IV
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
Correct Response: C.
Objective 0011
Understand heat transfer and the principles of thermodynamics.
5. Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
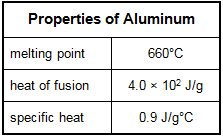
The amount of energy needed to produce 1 mole (27 g) of molten aluminum metal from bauxite ore is 297 kJ. Approximately how much energy could be saved per mole by recycling discarded aluminum (at an initial temperature of 20°C) by melting instead of producing it from bauxite ore?
- 262 kJ
- 271 kJ
- 281 kJ
- 286 kJ
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
Correct Response: B.
Electricity and Magnetism
Objective 0012
Understand principles of electrostatics.
6. Two small spheres are separated by a distance of 0.10 m. One sphere has a charge of 20 μC, and the other has a charge of 40 μC. What is the electrostatic force on each charged sphere?
- 7.2 N
- 80 N
- 720 N
- 800 N
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
Correct Response: C.
Objective 0014
Understand magnetic fields and electromagnetic induction.
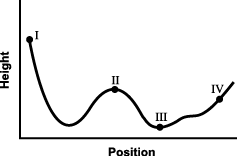
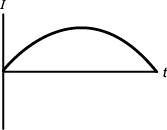
7. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
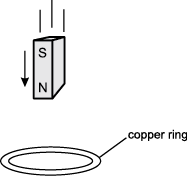
A magnet is passed through a copper ring at a constant speed. If current in the counterclockwise direction, as seen from above, is considered positive, which of the following graphs best represents the current (I) in the ring as a function of time (t)?
graph with current I on the y axis and time t on the x axis the graph starts at the origin decreases into the fourth quadrant where it plateaus then increases back up to the x axis.
graph with current I on the y axis and time t on the x axis the graph starts at the origin increases plateaus then decreases past the x axis into the fourth quadrant where it plateaus then increases back up to the x axis
graph with current I on the y axis and time t on the x axis the graph starts at the origin decreases into the fourth quadrant plateaus then increases past the x axis back into the first quadrant where it plateaus then decreases back down to the x axis
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
Correct Response: C.
Waves, Sound, and Light
Objective 0017
Understand the characteristics of sound waves and the basic principles of acoustics.
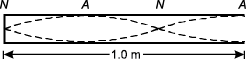
8. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
a pipe one meter in length with an open end on the right side. There are dotted lines in the form of two separate standing waves which cross paths at the points noted by the letter N, the pressure nodes, and are furthest apart at the points noted A, the pressure antinodes. Starting left at the closed end of the pipe, a pressure node is shown, moving to the right there is an antinode, then another node, and finally an antinode at the open end of the pipe.
The diagram above shows a pipe that is open at one end. The dotted lines inside the pipe represent a standing wave associated with an oscillating column of air. The pressure nodes (N) and antinodes (A) are also shown. The length of the pipe is 1.0 m and the speed of sound in air is 330 m/s. What is the frequency of the wave in the pipe?
- 220 Hz
- 250 Hz
- 340 Hz
- 440 Hz
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
Correct Response: B.
Objective 0019
Understand the principles of lenses and mirrors.
9. An object is placed 8.0 cm in front of a thin lens that has a focal length of 6.0 cm. At what distance from the lens will the image of the object be located?
- 2.0 cm
- 3.4 cm
- 7.0 cm
- 24 cm
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
Correct Response: D.
Modern Physics
Objective 0021
Understand the basic principles of quantum theory.
10. Which of the following best explains why macroscopic objects have properties that are more particlelike than wavelike?
- The wavelength of a macroscopic object is too small for diffraction effects to be observed.
- The laws of quantum mechanics are valid only for quantities of the order of Planck's constant.
- The uncertainty principle implies a small value for the position and momentum of macroscopic objects.
- The wave function for a macroscopic object has both a real and an imaginary part.
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
Correct Response: A.