Practice Test: Physics (69)
Suggested Testing Time: 4 hours
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. In addition, this test includes one or more assignments that allow you to handwrite and scan your responses. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
- A scientific calculator and formulas are provided on screen with your actual test.
Question 1.
The half-life of Strontium 90 is 27.7 years. Approximately how long will it take for a sample consisting of 1.0 times 10 to the 6 strontium-90 atoms to decay to 1.0 times 10 to the 3 strontium-90 atoms?
- 30 years
- 110 years
- 280 years
- 730 years
Question 2.
In the Bohr model of the atom, the frequency of an emitted photon due to an electron transition is directly proportional to the:
- orbital radius of the electron about the nucleus.
- acceleration of the electron during the transition.
- electromagnetic force acting on the orbiting electron.
- change in the energy of the electron during the transition.
Question 3.
Which of the following types of radioactive material is of little biological concern, provided it is not inhaled or ingested?
- alpha emitters
- beta emitters
- gamma emitters
- X-ray emitters
Question 4.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Object | Mass (MeV over C squared |
|---|---|
| proton | 938.27 |
| neutron | 939.57 |
| deuterium nucleus | 1875.62 |
A deuterium nucleus is composed of one proton and one neutron. According to the table shown, what is the binding energy of a deuterium nucleus?
- 0.56 MeV
- 1.30 MeV
- 2.22 MeV
- 3.86 MeV
Question 5.
Which of the following statements describes the primary significance of Rutherford's alpha-scattering experiments?
- They developed the concept of the half-life of a radioactive element.
- They created new radioactive isotopes by nuclear bombardment.
- They changed one atomic element into another through nuclear reactions.
- They demonstrated the existence of a small, dense, positively charged atomic nucleus.
Question 6.
A system consists of 3 electrons. The electrons have spin of either 1 half or negative 1 half and energy quantum numbers of either n = 1 or n = 2. Which of the following explains why one electron must have an energy corresponding to n = 2?
- Compton effect
- Meissner effect
- Pauli exclusion principle
- Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Question 7.
Which of the following is a significant advantage of using radioactive tracers in nuclear medicine?
- The radiation passes through the less dense matter such as skin and muscle and is absorbed by denser material such as bone.
- The physiological function of organs can be studied by following the movement of a radioisotope through the organ.
- The radioactive tracers emit high-energy particles that can be used to destroy malignant tumors.
- No ionization energy is released during the use of tracers since the imaging equipment measures the perturbed magnetic field of the water molecules in the body.
Question 8.
The nucleus of a stable xenon atom has 54 protons and 77 neutrons. Which of the following statements best explains why the nucleus remains intact instead of breaking apart due to electrostatic repulsion between the protons?
- The nucleus is so dense that the gravitational force holds it together.
- The weak nuclear force between the nucleons is much greater in magnitude than the electromagnetic force.
- The neutrons act as a shield and block the electromagnetic force from the protons.
- The strong nuclear force between the nucleons is much greater in magnitude than the electromagnetic force.
Question 9.
Which of the following scientific concepts requires the quantization of energy?
- interference of waves
- electrostatic force
- photoelectric effect
- many-body theory
Question 10.
Which of the following experiments led most directly to the quantum theory of light?
- Michelson's and Morley's effort to detect the luminiferous ether
- Röntgen's discovery of the emission of X-rays from a vacuum tube
- Planck's analysis of the spectrum emitted by a blackbody
- Hertz's detection of electromagnetic radiation
Question 11.
A transducer is used to convert mechanical vibrations into electrical waves. The power output of the transducer is of the order of several microwatts. A scientist would like to increase this value so the signal can be recorded to magnetic tape. A circuit based primarily on which of the following components would be most appropriate for this purpose?
- capacitors
- diodes
- transformers
- transistors
Question 12.
An elementary particle moving at 0.99c with respect to the laboratory frame has a half-life of 16μs in the laboratory frame. What is the half-life of the particle in its own frame of reference?
- 0.50 μs
- 2.3 μs
- 4.0 μs
- 15 μs
Question 13.
Which of the following expressions gives the de Broglie wavelength of an electron of mass m and kinetic energy E?
- H over root 2 m E
- h H times root 2 m E
- root (2 E) over m h
- mh m h times root (2 E)
Question 14.
If sigh (x) is a solution to the one-dimensional, time-independent Schrödinger equation, which of the following is proportional to the probability of finding an electron in a region Delta x?
- root sigh of x
- Integral of the absolute value of sigh of x squared d x
- Integral of sigh of x d x
- ih I h times d sigh of x over d x
Question 15.
A car on a highway has an initial speed of 23 m/s. The car accelerates at a constant rate for 10. s to a final speed of 29 m/s. How far does the car travel during this time interval?
- 230 m
- 260 m
- 275 m
- 290 m
Question 16.
A car traveling at +12 m/s slows down and comes to a stop in 20. m. What is the acceleration of the car, assuming it is constant?
- negative 7.2 m/s2
- negative 3.6 m/s2
- negative 0.6 m/s2
- negative 0.3 m/s2
Question 17.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
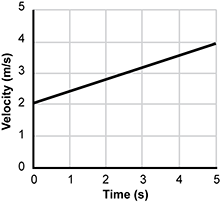
Velocity versus time graph in the first quadrant with velocity in meters per second and time in seconds. The velocity starts at 2 meters per second at t equals zero and increases linearly to 4 meters per second at t equals 5 seconds.
The graph shows the velocity of an object moving in one dimension with respect to time. What is the object's displacement between 0.0 s and 5.0 s?
- 5 m
- 10. m
- 15 m
- 20. m
Question 18.
A ball is launched with an initial vertical velocity of 17.3 m/s and an initial horizontal velocity of 10.0 m/s. If the ball is in the air for 3.00 s, how far has it traveled horizontally from its original position?
- 70.1 m
- 51.9 m
- 35.3 m
- 30.0 m
Question 19.
In a large field, student groups are given 10 notecards, each containing a distance in meters and a cardinal compass direction. If students follow the cards in order, they will successfully travel from the start position to the finish position on the field. A group rearranged its cards so that all cardinal directions were grouped together. Which of the following statements best explains why they were able to reach the correct final position?
- The sum of a large number of vectors added tail to tail trends toward zero.
- Vector addition is independent of the order in which the vectors are added.
- Total displacement is unchanged because north cancels south and east cancels west.
- The average velocity will be the same because students start from rest and end at rest.
Question 20.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
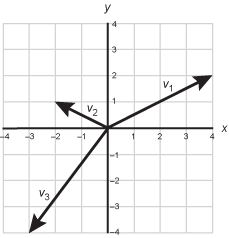
X y coordinate axis showing all 4 quadrants and 3 vectors. The X axis and y axis each go from negative 4 to positive 4. Vector V 1 begins at the origin and ends at the point 4 comma 2. Vector V 2 begins at the origin and ends at the point negative 2 comma 1. Vector V 3 begins at the origin and ends at the point negative 3 comma negative 4.
What is the sum of the three vectors shown above, expressed using the unit vectors i and j?
- negative 1i + ( negative 1j)
- 1i + ( negative 1j)
- negative 1i + 1j
- 1i + 1j
Question 21.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
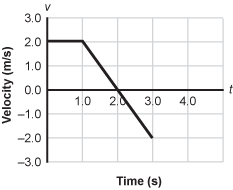
Velocity versus time graph with velocity in meters per second on the vertical axis and time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The velocity begins at 0 comma 2 and is horizontal until t = 1.0 seconds. From t = 1.0 seconds to t = 3.0 seconds, the velocity shows a straight line from 1 comma 2, crosses the time axis at t = 2.0 seconds and continues linearly to 3 comma negative 2.
The graph above shows the velocity of a particle moving in a straight line. At t = 0, the particle is located at x = 0. Which of the following graphs shows the position of the particle with respect to time, x of t ?
-
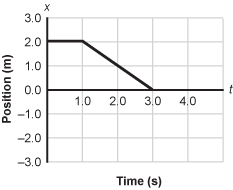
Position versus time graph with Position in meters on the vertical axis and time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The Position begins at 0 comma 2 and is horizontal until t = 1.0 seconds. From t = 1.0 seconds to t = 3.0 seconds, the Position shows a straight line from 1 comma 2, and continues linearly to 3 comma zero.
-
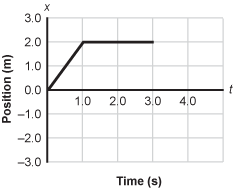
Position versus time graph with Position in meters on the vertical axis and time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The Position begins at 0 comma 0 and increases linearly until t = 1.0 seconds where it reaches the point 1 comma 2. From t = 1.0 seconds to t = 3.0 seconds, the Position shows a horizontal line from 1 comma 2, to 3 comma 2.
-
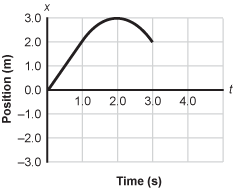
Position versus time graph with Position in meters on the vertical axis and time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The Position begins at 0 comma 0 and increases linearly until t = 1.0 seconds where it reaches the point 1 comma 2. From t = 1.0 seconds to t = 3.0 seconds, the Position shows an inverted parabola. The parabola peaks at 2 comma 3 and ends at 3 comma 2.
-
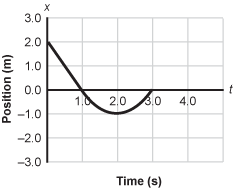
Position versus time graph with Position in meters on the vertical axis and time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The Position begins at 0 comma 2 and decreases linearly until t = 1.0 seconds where it reaches the point 1 comma 0. From t = 1.0 seconds to t = 3.0 seconds, the Position shows an upright parabola. The parabola minimum occurs at 2 comma negative 1 and ends at 3 comma 0.
Question 22.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
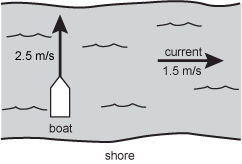
Diagram of a river flowing to the right whose current has a speed of 1.5 meters per second. A boat attempts to travel perpendicular to the current direction, across the river, with a speed of 2.5 meters per second.
A boat that moves in still water with a speed of 2.5 m/s now heads north across a river that has a current of 1.5 m/s east, as shown in the diagram above. What is the boat's velocity relative to an observer on the shore?
- 2.9 m/s at 31° north of east
- 2.9 m/s at 59° north of east
- 4.0 m/s at 31° north of east
- 4.0 m/s at 59° north of east
Question 23.
A 10. kg object is acted on by a net force that makes a 50.° angle with the x-axis. The x-component of the net force is 30. N. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the mass?
- 1.9 m/s2
- 2.3 m/s2
- 3.9 m/s2
- 4.7 m/s2
Question 24.
A 20. N box rests on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between the floor and the box is 0.40, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.38. Which of the following statements describes what will occur if a horizontal force of 75. N is applied to the box?
- The box will not move.
- The box will move at a constant speed.
- The box will move at an increasing speed.
- The box will move at a decreasing speed.
Question 25.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
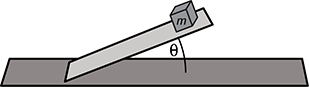
A mass m is on an inclined plane of angle theta as shown in the diagram. Which of the following expressions represents the magnitude of the normal force on the mass?
- mg
- mg sine theta
- mg tangent theta
- mg cosine theta
Question 26.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
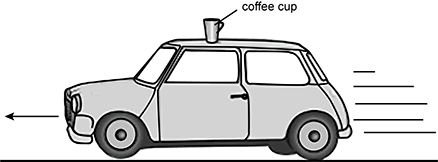
Diagram of a car with a coffee cup on the roof. The car is accelerating in the direction of travel on level ground.
A cup of coffee is on top of a stationary car. The driver of the car accelerates from rest so that the cup falls off the back of the car's roof. Which of the following statements best describes this situation?
- The car provided a force on the cup in the opposite direction of the car's motion.
- The cup's inertia kept it at rest while the car moved forward under it.
- A force equal and opposite to the frictional force from the car pushed the cup.
- The cup's inertia provided an equal and opposite force to the applied force.
Question 27.
Students analyze video of vertically launched projectiles. They notice that the average times for the projectiles to rise to their highest points are consistently shorter than the average times to return to the launching height from the highest point in their trajectories. Which of the following explanations best describes this phenomenon?
- The momentum of the projectiles is diminished by the force of gravity acting over time.
- The drag force from the air always points opposite the direction of motion.
- The force of gravity slows the projectiles faster on the way up.
- The cannon only affects the projectiles while they are going up.
Question 28.
Which of the following is an action-reaction pair for a space station containing astronauts in orbit about Earth?
- the weight of the space station and the centripetal force on the space station
- the weight of the astronauts and the centripetal force on the space station
- the weight of the space station and the gravitational force of the space station on Earth
- the weight of the astronauts and the gravitational force of the space station on the astronauts
Question 29.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
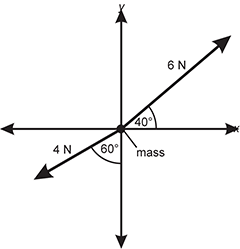
Diagram of 4 quadrants of an x y coordinate axis. A mass is placed at the origin and 2 force vectors originate at the origin. The vector with magnitude 6 Newtons is directed 40 degrees counterclockwise from the positive x axis. The vector with magnitude 4 Newtons is directed 60 degrees clockwise from the negative y axis.
The free-body diagram shows two forces acting on a mass. Which of the following equations represents the vector sum of the forces in newtons, in the x-direction?
- Sigma F x = negative 4 cosine 60 degrees + 6 sine 40 degrees
- Sigma F x = negative 4 sine 60 degrees + 6 sine 40 degrees
- Sigma F x = negative 4 cosine 60 degrees + 6 cosine 40 degrees
- Sigma F x = negative 4 sine 60 degrees + 6 cosine 40 degrees
Question 30.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.

Diagram of a 6.0 kilogram object moving right with a velocity of 10 Meters per second. Another object with mass 0.25 kilograms travels toward the 1st object at unknown velocity, v.
A 6.0 kg mass is moving to the right at 10. m/s. A 0.25 kg mass is fired toward the left at the larger mass, and they stick together after impact. What initial speed v must the smaller mass have to completely stop both masses? (Note: The arrows are not necessarily drawn to scale.)
- 10. m/s
- 15 m/s
- 150 m/s
- 240 m/s
Question 31.
A potter’s wheel accelerates from rest at 2.5 rad/s2 to its optimum working angular speed of 15 rad/s. How much time passes during this acceleration?
- 2.4 s
- 6.0 s
- 38 s
- 45 s
Question 32.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
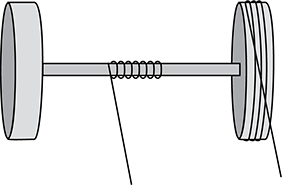
Diagram of two large radius wheels with a small radius axle connecting them coaxially at their centers. A string is wrapped around the axle and another string is wrapped around one of the wheels.
Students are building model cars powered by strings wound around either a fixed axle or wheels. The wheel is set in motion by applying a force on the string, which is wound around either the axle or the wheel as shown in the diagram. The string is a fixed length. Which of the following statements is most accurate when considering placement of the string?
- Wrapping the string on the wheel produces a greater torque.
- Wrapping the string on the axle reduces the moment of inertia.
- Wrapping the string on the wheel means less energy lost to friction.
- Wrapping the string on the axle produces fewer revolutions.
Question 33.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
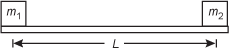
Diagram of a horizontal rod of length L. Mass m 1 is placed on the rod at the left end of the rod. Mass m 2 is placed on the rod at the right end of the rod.
A light rod has masses attached to each end, as shown in the diagram. At what distance from mass M 1 will the rod be balanced in equilibrium?
- L over 2
- M 1 L over (m 1 + m 2)
- M 2 L over (m 1 + m 2)
- L(m1 + m2)/2(m1 + m2) L times (m 1 + m 2) over (2 times (m 1 + m 2))
Question 34.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
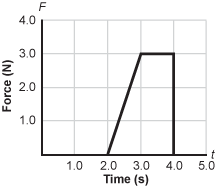
Graph of the 1st quadrant of Force in newtons on the vertical axis versus time in seconds on the horizontal axis. The force is zero from t = 0 to t = 2.0 seconds. The force then increases linearly from 2 comma zero to 3 comma 3. The force is then horizontal from 2 comma 3 to 4 comma 3. The force is then vertical from 4 comma 3 to 4 comma 0. The force is then zero from t = 4.0 to t = 5.0 seconds.
A 2.00 kg mass with an initial speed of 3.00 m/s moving in a straight line in the positive direction is acted on by the force shown in the graph. What is the speed of the mass at t = 5.00 s?
- 2.25 m/s
- 4.50 m/s
- 5.25 m/s
- 10.5 m/s
Question 35.
The angular speed of a star spinning about its axis increases as the star begins to contract to a smaller radius. Which of the following quantities associated with the star must decrease as this occurs?
- moment of inertia
- angular momentum
- rotational kinetic energy
- net external torque
Question 36.
The gravitational force between two masses is 80.0 N. Their centers are separated by a distance of 6.40 times 10 to the sixth power m. What is the force if the distance is changed to 12.8 times 10 to the sixth power m?
- 20.0 N
- 40.0 N
- 160. N
- 320. N
Question 37.
A satellite in a circular orbit travels at a speed v at a distance r above the center of Earth. If the satellite is boosted to a new orbital distance of 2.0r, what will be its speed?
- 0.5v
- 0.7v
- 1.4v
- 2.0v
Question 38.
Which of the following statements describes a property of Coulomb's law that represents a significant difference from Newton's law of universal gravitation?
- The force is conservative and has a scalar potential.
- The force is inversely proportional to distance.
- The force is either attractive or repulsive.
- The force is a three-dimensional vector.
Question 39.
The gravitational force from the Sun changes with distance from the Sun’s center. For distances larger than the Sun’s radius, which of the following quantities changes with distance in the same way as the gravitational force?
- the intensity of light received from the Sun
- the minimum speed needed to escape the Sun’s pull
- the gravitational potential of the Sun
- the orbital period of a planet in a circular orbit around the Sun
Question 40.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
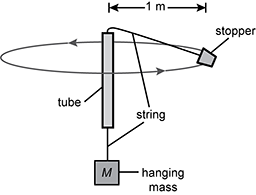
Diagram of a vertical tube with a string passing through the tube. The bottom of the string is attached to a large, hanging mass, M. The top of the string is attached to a small stopper that swings in a horizontal circle of radius 1 meter.
Students use the apparatus shown to rotate a rubber stopper in a horizontal circle of radius 1.0 m at a constant rate so that the mass hanging from the bottom of the string remains stationary. The students repeat this procedure for various masses M, always keeping the radius of the circle at 1.0 m. To analyze the data, the students determine the linear speed, v, of the rubber stopper. How should the students graph the data to get a straight line?
- v versus Mg
- v versus Mg squared
- v squared versus root (M g)
- v squared versus Mg
Question 41.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
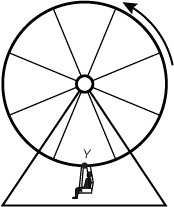
Diagram of a circular Ferris wheel rotating counterclockwise. A passenger is located at the bottom of the wheel, and is labeled Y.
The diagram represents a Ferris wheel rotating at a constant speed. Which of the following vectors represents the acceleration of a person on the wheel at point Y?
Question 42.
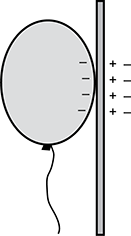
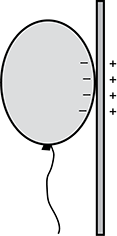
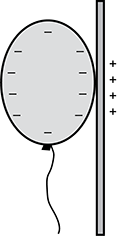
When a person rubs a balloon against their hair, the balloon gains electrons. The balloon is placed against a wall and sticks to it. Which of the following diagrams best represents the charge distributions on the balloon and the wall?
- Diagram of a balloon contacting the wall with negative charges on the side of balloon near the wall. The wall has positive charges near the balloon and negative charges away from the balloon.
- Diagram of a balloon contacting the wall with negative charges on the side of balloon near the wall. The wall has positive charges near the balloon only.
- Diagram of a balloon contacting the wall with negative charges on all sides of the balloon. The wall has positive charges near the balloon only.
- Diagram of a balloon contacting the wall with negative charges on the side of balloon near the wall. The wall has negative charges near the balloon and positive charges away from the balloon.
Question 43.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
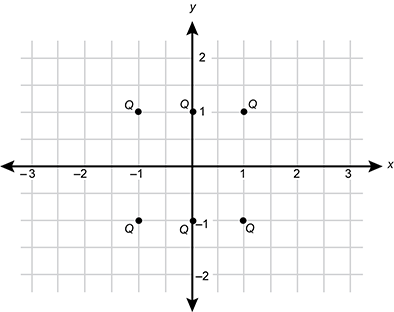
Diagram of a 4 quadrant x y coordinate grid with 6 charges, Q, located at coordinates 1 comma 1, 0 comma 1, negative 1 comma 1, negative 1 comma negative 1, 0 comma negative 1, 1 comma negative one.
Six equal positive charges, each of magnitude Q, are placed at the coordinates shown. In which of the following directions is the net force on a positive test charge placed at the coordinates (2, 0)?
- no direction because the net force is zero
- in the positive-x direction
- in the positive-y direction
- in the positive-x and positive-y directions
Question 44.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
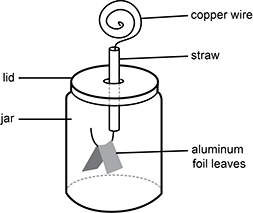
Diagram of an electroscope. A clear glass jar with lid that has a hole in the center. A straw is placed in the hole in the lid. A copper wire extends thru the straw and has a hook at the bottom, inside the jar. Folded aluminum foil leaves are placed on the hook of wire in the jar. The copper wire extends out the top of the straw above the lid.
The diagram shows an electroscope consisting of two conductive aluminum foil leaves inside a glass jar connected to a wire protruding from the top of the jar. When a positively charged object is brought near the wire, the leaves inside the jar separate. Which of the following explanations best accounts for this phenomenon?
- Electrons are pushed down the wire onto the aluminum foil leaves, giving the leaves a net negative charge.
- The aluminum foil leaves are attracted to the positively charged object.
- Electrons flow from the aluminum foil leaves to the copper wire, giving the leaves a net positive charge.
- Equal and opposite charge distributions are induced on the aluminum foil leaves.
Question 45.
A minus 5.0 C charge is accelerated across a potential difference of 5.0 V. How much work is done by the electric field on the charge?
- negative 1.0 J
- 1.0 J
- 10. J
- 25 J
Question 46.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
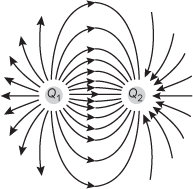
Diagram of 2 small circular charges labeled Q 1 on the left and Q 2 on the right. A series of lines with arrows pointing out, away from Q 1 emanate from the surface of Q 1. Each line bends toward Q 2. The lines bend directly to, and point into, charge Q 2.
Given the electric field lines shown, what are the charge pairs?
- Q 1 positive, Q 2 positive
- Q 1 positive, Q 2 negative
- Q 1 negative, Q 2 positive
- Q 1 negative, Q 2 negative
Question 47.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
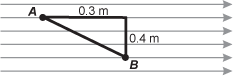
Diagram of several gray, equally spaced, and horizontal lines, each with arrows pointing to the right. Three line segments form a triangle superimposed over the arrows. The horizontal segment of the triangle begins at point A and extends right, 0.3 meters in length. The vertical segment of the triangle extends down from the right end of the horizontal segment and is 0.4 meters in length. The hypotenuse of the triangle is labeled A B.
The diagram shows an electric field of 10 N/C that is constant in magnitude and direction. What is the electrostatic potential between points A and B?
- 3 V
- 4 V
- 5 V
- 7 V
Question 48.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.

Diagram of a rectangular circuit consisting of one loop with a 36 volt battery and a capacitor. The battery is at the top of the rectangular circuit with the positive lead on the left and the negative lead on the right. The capacitor is at the bottom of the loop.
A 36 V battery is in series with a parallel plate capacitor, as shown in the diagram. The plate separation is 0.20 m. The plates are large, so that the electric field is approximately constant between them. What is the magnitude and direction of the field?
- 7.2 N/C to the left
- 7.2 N/C to the right
- 180 N/C to the left
- 180 N/C to the right
Question 49.
A student is investigating factors that affect the strength of an electromagnet. The student proposes the design shown.
Factors: Voltage, number of turns of wire.
Process: Set voltage to 2.0 V, wrap 50 turns of wire around an iron coil. Measure how many paper clips the magnet can pick up. Set voltage to 4.0 V and wrap 30 more turns of wire. Again measure the number of paper clips. Repeat several times.
Which of the following is the most significant problem with this experimental design?
- using increments of 2.0 V instead of 1.0 V
- changing the values of two factors at the same time
- using paper clips to measure the strength of the electromagnet
- not accounting for the resistance of the additional length of wire
Question 50.
Which of the following statements best describes why striking a magnetized iron bar on a solid surface can reduce the strength of the bar's magnetic field?
- The added energy increases the temperature, which increases the resistance of the iron.
- The work done on the bar disrupts the electric surface currents in the iron.
- The impact force creates a secondary field equal and opposite to the internal field.
- The alignment of the magnetic domains is disrupted into random orientations.
Question 51.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
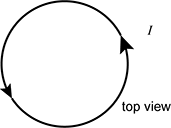
A loop of current-carrying wire sits with its face flat on a tabletop. When looking at the wire from above, the current travels counterclockwise. Which of the following directions best describes the magnetic field it produces at the center of the loop?
- into the page
- out of the page
- toward the top of the page
- toward the bottom of the page
Question 52.
A current-carrying wire sits in a uniform external magnetic field that points into the page. If the current is to the right, which of the following directions corresponds to the force on the wire?
- into the page
- out of the page
- up toward the top of the page
- down toward the bottom of the page
Question 53.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
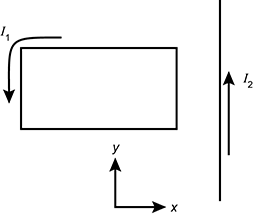
Diagram of a rectangular loop of wire with current, I one, flowing counterclockwise. The loop is to the left of a long vertical wire with current, I two, flowing up, in the positive y direction. A set of axes indicating positive x is to the right and positive y is up.
A rectangular wire frame carrying a current I 1 is placed on a table next to a long wire carrying current I 2 in the positive-y direction, as shown in the diagram. In which direction is the net magnetic force on the frame?
- positive-x
- positive-y
- negative-x
- negative-y
Question 54.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
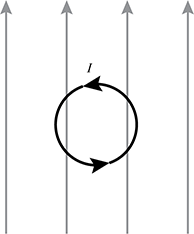
Diagram of circular loop of wire with current, I, flowing counterclockwise. Four equally spaced, parallel Vertical arrows point up.
An initially stationary coil of conducting wire, which is free to move and whose face is parallel to the page, sits in a uniform magnetic field that points upward, as shown. If a counterclockwise current is sent through the coil, which of the following statements best describes the coil's motion?
- The coil will begin to rotate with the top part coming out of the page and the bottom half going into the page.
- The coil will begin to rotate with the top part going into the page and the bottom half coming out of the page.
- The coil will begin to rotate with the right side coming out of the page and the left side going into the page.
- The coil will remain stationary.
Question 55.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
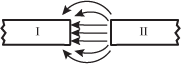
Diagram of the ends of 2 bar magnets lined up horizontally next to each other. The magnet on the left is labeled Roman Numeral 1, the magnet on the right is labeled Roman numeral 2. Magnet 2 has arrows coming out of its left end. Each arrow bends directly to and points into the right end of magnet 1.
The diagram shows the magnetic field between two magnetic poles. Which of the following correctly identifies the poles?
- Roman numeral 1 = S, Roman numeral 2 = S
- Roman numeral 1 = N, Roman numeral 2 = N
- Roman numeral 1 = N, Roman numeral 2 = S
- Roman numeral 1 = S, Roman numeral 2 = N
Question 56.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
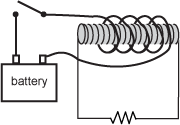
Diagram of a battery with a long wire that wraps around a cylindrical bar several times. The circuit switch containing the battery is open. The cylindrical bar also has a second coil of wire that attaches to a resistor in circuit that is closed.
The diagram shows an iron bar with two insulated coils of wire around the bar. The exterior coil is in series with a battery and a switch. The interior coil is in series with a resistor. The switch is originally open. Which of the following statements describes what happens to the current through the resistor when the switch is closed?
- It will spike to some value and quickly drop to zero.
- It will slowly build up to a constant value.
- It will instantaneously jump to a constant value.
- It will oscillate just above and below a nonzero value.
Question 57.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
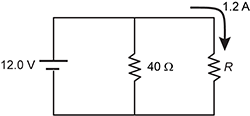
Diagram of a rectangular circuit with 3 vertical wires all connected with horizontal wires at the top and bottom end of each wire. A 12.0 volt battery is in the left wire, a 40 Ohm resistor is in the middle wire, and a resistor of unknown resistance, R, is in the right wire. Current flows clockwise in the right wire, and has a value of 1.2 Amps.
What is the current through the battery?
- 0.30 A
- 1.2 A
- 1.5 A
- 2.4 A
Question 58.
The wall adapter for recharging a cell phone battery draws 20. mA at 115 V. If left plugged in for 24 hours, how much energy will the device dissipate?
- 1.5 times 10 to the power of minus 5 kW•h
- 9.0 times 10 to the power of minus 4 kW•h
- 5.5 times 10 to the power of minus 2 kW•h
- 5.5 times 10 to the power of 1 kW•h
Question 59.
A barefoot person approaches an appliance that is not grounded and has a damaged wire within that connects to the conducting case of the appliance. Which of the following statements best explains whether the person touching the appliance is in danger?
- The person is in danger because they could have current pass through them to the ground.
- The person is not in danger because the damaged wire creates an open circuit that prevents current from passing through.
- The person is in danger because charge will build up on their body even though current does not pass through them.
- The person is not in danger because the charge discharges into the air.
Question 60.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
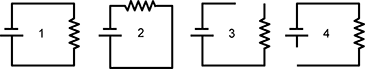
Diagram with 4 square loop circuit diagrams. All circuits have the battery on the left section of each square circuit. Circuit 1 has the resistor on the right section and a complete loop. Circuit 2 has the resistor on the top section and a complete loop. Circuit 3 has the resistor on the right section and a piece of the top section missing from the loop. Circuit 4 has the resistor on the right section and a piece of the left section missing from the loop.
The diagram shows four versions of an electric circuit assembled with identical batteries and identical resistors. Which of the following statements about these circuits is true?
- The electric current flowing through the resistors is equal in circuit 1 and circuit 2.
- The electric current flowing through the resistors is greater in circuit 1 than in circuit 2.
- The electric current flowing through the resistors is nonzero in circuit 3 and circuit 4.
- The electric current flowing through the resistors is smaller in circuit 3 than in circuit 4.
Question 61.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
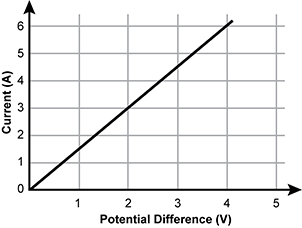
Diagram of a Current versus potential difference graph. Current is measured in amps on the vertical axis and potential difference is measured in volts on the horizontal axis. The Current begins at 0 amps when the potential difference is zero volts, and increases linearly to 6 amps when the potential difference is 4 volts.
The graph shows the current in a conductor for various applied potential differences. Which of the following is the best approximation of the resistance of the conductor?
- 3 halves Ohms
- 6 fifths Ohms
- 3 quarters Ohms
- 2 thirds Ohms
Question 62.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
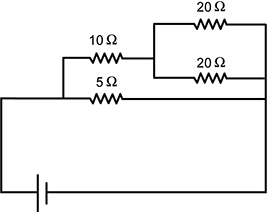
Diagram of a circuit with one battery and 4 resistors. From the positive lead of the battery, the circuit splits into two branches, the bottom branch has a 5 ohm resistor and the top branch has a 10 ohm resistor. The bottom branch then connects directly to the negative lead of the battery. The top branch then splits into two branches, each with 20 ohm resistors and both branches then connect directly to the negative lead of the battery.
Based on the diagram, what is the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown?
- 4 Ω
- 5 Ω
- 40 Ω
- 55 Ω
Question 63.
For an alternating current, the voltage and current oscillate in time. Which of the following equations shows how the root mean square voltage depends on the maximum voltage?
- V R M S = V naught cosine (omega t)
- V naught = V R M S cosine (omega t)
- V R M S = V naught over root 2
- V R M S = root (2 V naught)
Question 64.
A student would like to measure the electric power used by a laptop computer when placed in the low-power mode. Which of the following pairs of meters should be selected for this measurement?
- galvanometer and ammeter
- galvanometer and ohmmeter
- voltmeter and ammeter
- ohmmeter and voltmeter
Question 65.
An elevator with passengers has a total mass of 800. kg and moves a vertical distance of 20. m in 10. s. What is the average power expended in lifting this mass?
- 1.6 times 10 to the 2 W
- 1.6 times 10 to the 3 W
- 1.6 times 10 to the 4 W
- 1.6 times 10 to the 5 W
Question 66.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
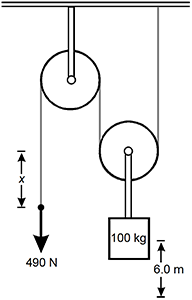
Diagram of a two pully system with a string that winds through each pully and connects to the ceiling. The left pully is anchored to the ceiling and shows the string being pulled down with 490 newtons. The left string moves an unknown distance, x. The right pully has a 100 kilogram mass attached to it and is raised 6.0 meters.
A person applies a force of 490 N over a distance x to lift a 100. kg mass 6.0 m. If the pulley system is 100% efficient, what is x?
- 3.0 m
- 6.0 m
- 8.0 m
- 12 m
Question 67.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
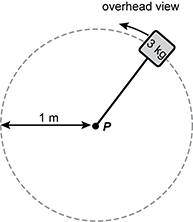
Diagram of a 3 kilogram mass spinning counterclockwise in a horizontal circle of radius 1 meter. The center of the circle is labeled P. A string connects point P to the mass.
A 3.0 kg mass is attached to a 1.0 m string as shown in the diagram and is spun in a horizontal circle with constant angular velocity. The mass makes two complete rotations about the central point P. What is the total work done by gravity on the mass?
- 0.0 N•m
- 2 pie N•m
- 6 pie N•m
- 12 pie N•m
Question 68.
A ball and a brick of the same mass are placed at the top of an inclined plane and released. The ball rolls down without slipping and the brick slides down with negligible friction. Which of the following statements is true regarding the two objects when they arrive at the bottom of the inclined plane?
- The ball's translational speed is greater than the brick's.
- The brick's total kinetic energy is greater than the ball's.
- The ball's total kinetic energy is greater than the brick's.
- The brick's translational speed is greater than the ball's.
Question 69.
A "fast" charger is rated at 3 A and 9 V and takes 30 minutes to charge a device, while another "slow" charger is rated at 2.4 A and 5.2 V and takes 50 minutes to charge the same device. An advertisement claims that the fast charger saves the user time and therefore reduces their energy costs. Which of the following evaluations of the information provided is the most accurate?
- The fast charger does save time and it also requires less energy than the slow charger.
- The fast charger does save time, but it requires about 10 kJ more energy than the slow charger.
- The fast charger does save time, but it requires about 100 kJ more energy than the slow charger.
- The fast charger does save time, but it does not save any energy because both chargers use the same amount of energy.
Question 70.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
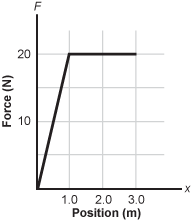
Graph of the first quadrant labeling force in newtons on the vertical axis versus position in meters on the horizontal axis. The force axis runs from zero to 20. The position axis runs from zero to 3.0. The force begins at zero comma zero and increases linearly to 1 comma 20. It then continues horizontally from 1 comma 20 to 3 comma 20.
The graph shows how the force on a mass depends on the position of the mass. What is the change in the kinetic energy of the mass as it moves from x = 0.0 m to x = 3.0 m?
- 0.0 J
- 20 J
- 50 J
- 60 J
Question 71.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
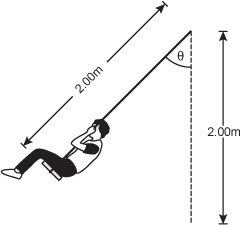
Diagram of a person on a swing. A vertical dashed line is labeled 2.00 meters in length. The person on the swing has swung clockwise from the dashed line, an angle q from the vertical dashed line. The length of the string is labeled 2.00 meters.
The length of each of the ropes on a playground swing is 2.00 m. What is the maximum speed attainable on the swing if the maximum value of theta is 45.0 degrees ?
- 1.41 m/s
- 2.00 m/s
- 3.39 m/s
- 8.85 m/s
Question 72.
A solar panel is 12% efficient at converting sunlight into electrical energy. On average, the sunlight that strikes Earth's surface has an intensity of 250 W/m2. Which of the following is the best estimate for the size of a solar panel needed to provide 1.2 kW of energy to a home?
- 5 m times 8 m
- 6 m times 10 m
- 13 m times 13 m
- 20 m times 20 m
Question 73.
The temperature of an ideal gas at a constant volume is doubled. By what factor does the average speed of the molecules in the gas increase?
- 1
- Root 2
- 2
- 4
Question 74.
In a closed system, a thermodynamic process is reversible if and only if:
- entropy is constant.
- work is done on the system.
- entropy increases.
- no work is done on the system.
Question 75.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
| Substance | Melting Point ( degrees Celsius ) | Heat of Fusion (kJ per kg) | Boiling Point ( degrees Celsius ) | Heat of Vaporization (kJ per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H 2 O | 0.00 | 333 | 100. | 2260 |
| State of H 2 O | Specific Heat (kJ/[kg•°C]) |
|---|---|
| solid H 2 O | 2.10 |
| liquid H 2 O | 4.19 |
| vapor H 2 O | 2.01 |
How much heat is needed to transform 2.00 kg of ice at 0.0 degrees Celsius into liquid water at 55.0 degrees Celsius ?
- 231 kJ
- 461 kJ
- 1130 kJ
- 4980 kJ
Question 76.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Material | Coefficient of Linear Expansion ( Reciprocal degrees Celsius ) |
|---|---|
| aluminum | 25.0 times 10 to the minus 6 |
| copper | 17.0 times 10 to the minus 6 |
A copper rod and an aluminum rod are each 25 cm long at a temperature of 0 degrees Celsius . If both rods are heated to 250 degrees Celsius , what is the difference in their lengths?
- 0.05 cm
- 0.11 cm
- 0.16 cm
- 0.26 cm
Question 77.
A scientist places an ideal gas in a thermally insulated cylinder with a movable piston. The scientist pushes the piston inward, decreasing the volume of the cylinder by half. Which of the following statements explains the result that the scientists should most likely observe?
- The pressure will more than double, since the temperature of the gas has been increased.
- The pressure will not quite double, since the number of gas molecules has been reduced.
- The pressure will more than double, since the internal energy of the gas is unchanged.
- The pressure will not quite double, since no heat can leave the system.
Question 78.
Which of the following methods of energy exchange describes the process by which energy is transmitted from one region of space to another through molecular collisions?
- radiation
- latent heat
- convection
- conduction
Question 79.
Which of the following best describes the microscopic interpretation of the concept of entropy?
- the distribution of energy per degree of freedom of a molecule
- the amount of randomness or disorder in a system
- the average time required for a system to reach equilibrium
- the lowest temperature a quantum mechanical system can reach
Question 80.
Suppose that a giant tunnel could be dug straight through the center of Earth to the far side. Assume that Earth is exactly spherical, and that air resistance is not a factor. If a rock were dropped into the hole on one side of Earth, which of the following statements could be true?
- The rock will exit the hole faster than when it entered.
- The magnitude of the acceleration of the rock is greatest at the center of Earth.
- The rock will continue to fly off into space after traveling through the hole.
- The magnitude of the acceleration of the rock is least at the center of Earth.
Question 81.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
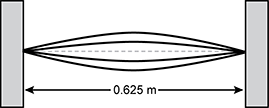
Diagram of a string that is anchored between two walls. The string is shown as having a standing wave that oscillates between having one crest and one trough in the middle of the string. The end points of the string do not oscillate due to being anchored at the wall. The distance between the walls is labeled 0.625 meters.
A string is oscillating in the mode shown at a frequency of 100. Hz. The string has a length of 0.625 m and its ends are fixed. What is the speed of the wave on the string?
- 0.625 m/s
- 3.43 m/s
- 62.5 m/s
- 125 m/s
Question 82.
A transverse wave travels down a rope. Which of the following changes would be most likely to increase the wave's energy?
- decreasing the linear density of the rope
- increasing the amplitude of the wave
- decreasing the frequency of the wave
- increasing the tension on the rope
Question 83.
Radios usually broadcast in A M and FM. Information is embedded on an A M radio broadcast by:
- multiplexing the audio.
- modulating the amplitude.
- amplifying the magnetic field.
- alternating the magnetic field.
Question 84.
Large numbers of radio stations are transmitting their signals at the same time. Radio receivers can be tuned to receive the signal from any single radio station and ignore the rest. Which of the following wave properties enables such tuning?
- phase shift
- amplitude
- frequency
- speed
Question 85.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
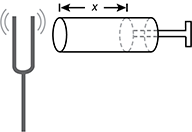
Diagram of a tuning fork vibrating. A cylindrical tube is mounted horizontally with the open end of the tube directed toward the tuning fork. A piston is shown that can adjust the cavity length inside the tube. This cavity length in the tube is labeled x.
Students are using a tuning fork and a cylindrical tube with a piston that can be adjusted for some value, x, as shown in the diagram. When struck, the tuning fork oscillates and creates an audible tone. One step in using this device to measure the wavelength of sound is to adjust the value of x until:
- the frequency of the tone changes.
- the tone from the fork becomes inaudible.
- an oscillating beat frequency is heard.
- the tone produced is loudest in volume.
Question 86.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
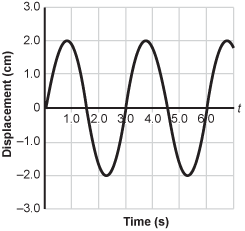
Graph of displacement in centimeters on the vertical axis versus times in seconds on the horizontal axis. The displacement axis runs from negative 3.0 to 3.0 and the time axis runs from zero to 6.0 seconds. The displacement function is sinusoidal and begins at the origin. The function increases to a peak, then decreases to a trough, then increases to cross the axis at 3 comma 0. The function then increases to a peak, then decreases to a trough then increases to cross the axis at 6 comma 0. Peaks occur at displacements of 2.0 centimeters. Troughs occur at displacements of negative 2.0 centimeters.
The graph gives the displacement of a pendulum bob with respect to time. What is the length of the pendulum?
- 0.74 m
- 1.5 m
- 2.2 m
- 3.0 m
Question 87.
A piece of string, fixed at both ends, is struck to produce a wave in the string. Given that mew is the string's linear mass density and T is its tension, which of the following combinations of values will produce the greatest wave speed?
- mew = 0.1 kg/m, T = 0.1 N
- mew = 0.1 kg/m, T = 1.0 N
- mew = 1.0 kg/m, T = 0.1 N
- mew = 1.0 kg/m, T = 1.0 N
Question 88.
A ray of light passes from air (n = 1.0) into a transparent material. The angle of incidence is 40.° and the angle of refraction is 25°. What is the index of refraction of the material?
- 0.66
- 0.85
- 1.2
- 1.5
Question 89.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
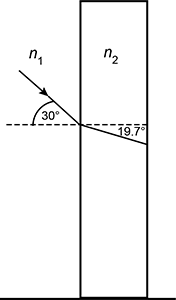
Diagram of a rectangular block of transparent material labeled n two, surrounded by air labeled n one. A dashed line perpendicular to the rectangle is shown and crosses from the air into the material. A ray is shown entering the material. In the air, the ray makes an angle of 30 degrees relative to the dashed line. In the material, the ray makes an angle of 19.7 degrees relative to the dashed line.
The diagram shows laser light in air ( n 1 = 1.00) incident on a slab of transparent material from the left, striking the surface of the material at an angle of 30.0° to the normal. Within the material, the beam refracts at an angle of 19.7° to the normal. Which of the following values is equal to n 2 , the transparent material's index of refraction?
- 0.674
- 1.31
- 1.48
- 1.52
Question 90.
Some sunglasses use polarized lenses. Which of the following statements best describes the benefit of polarized sunglass lenses versus regular tinted lenses?
- Polarized sunglasses block horizontally polarized light as it reflects from a surface.
- Polarized lenses reduce the light from the preferential direction caused by Mie and Rayleigh scattering in the atmosphere.
- Polarized lenses reduce the light intensity by any percentage desired, allowing a more customized selection of light reduction.
- Polarized lenses allow visible light wavelengths through but preferentially block ultraviolet radiation.
Question 91.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
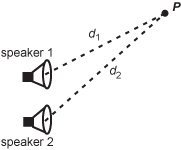
Diagram of two speakers, one directly above the other. The speaker on top is labeled speaker 1, the bottom is labeled speaker 2. Point P is located above and to the right of the set of speakers. A dashed line labeled d 1 goes from speaker 1 to point P. A dashed line labeled d 2 goes from speaker 2 to point P.
The two loudspeakers shown in the diagram are in phase and produce a sound of frequency 680 Hz. The speed of sound is 340 m/s. At point P, no sound is heard. Given that d 1 and d 2 are the distances from P to speaker 1 and speaker 2, respectively, which of the following equations could be true?
- d 2 minus d 1 = 1 quarter m
- d 2 minus d 1 = 1 half m
- d 2 minus d 1 = 2 m
- d 2 minus d 1 = 3 m
Question 92.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
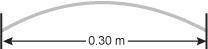
Diagram of a string that is anchored between two walls. The string is shown as having a standing wave that oscillates having one crest in the middle of the string. The end points of the string do not oscillate due to being anchored at the wall. The distance between the walls is labeled 0.30 meters.
The diagram shows a string of length 0.30 m oscillating in its first harmonic. What is the wavelength when the string is oscillating in its third harmonic?
- 0.10 m
- 0.20 m
- 0.45 m
- 0.90 m
Question 93.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
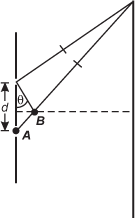
Diagram of a vertical line with two small slits, one above the other cut out of the line. The vertical distance between the slits is labeled d. A vertical screen is some distance to the right of the vertical line. A diagonal line runs up and to the right from the top slit to the top of the screen. A diagonal line also runs up and to the right from the bottom slit to the top of the screen. A small line segment runs from the top slit down and to the right, perpendicular to the line going from the top slit to the screen, and stops at the line connecting the bottom slit to the screen. This point is labeled B and has a horizontal dashed line running from the screen to the vertical line. The perpendicular line from the top slit to point B is labeled as making an angle, q, from the vertical line containing the slits. The distance from point B to the top of the screen is marked as congruent to the line from the top slit to the top of the screen. The bottom slit is marked point A.
The diagram shows the geometry for a double-slit interference pattern produced by light from a laser that is incident on two slits separated by a distance d. For small values of theta , which of the following statements best describes the significance of the length of segment A B in the diagram?
- It is equal to an integral multiple of the wavelength of the incident laser light.
- It is directly proportional to the intensity of a bright region in the pattern.
- It is equal to the distance between any two adjacent bright fringes on the screen.
- It is related to the difference in phase between the two light waves arriving at a point on the screen.
Question 94.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
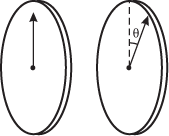
Diagram of two thin, circular discs that are coaxial along a horizontal axis. The discs are oriented vertically. The left disc has a vertical arrow pointing from its center to the top of the disc. The right disc has a dashed line from its center to the top of the disc. The right disk also has an arrow pointing from the center to the top of the disc but is rotated toward the viewer by an angle q from the vertical dashed line.
Light is incident on the first polarizing filter. As the second filter is rotated, at what angles will the intensity of the transmitted light be a minimum?
- 45°, 90°
- 45°, 225°
- 90°, 180°
- 90°, 270°
Question 95.
Which of the following lists shows different types of electromagnetic waves in the order of increasing wavelength?
- gamma rays then visible light then infrared
- X-rays then microwaves then ultraviolet
- infrared then radio waves then gamma rays
- ultraviolet then X-rays then visible light
Question 96.
White light illuminates a thin soap film surrounded by air at a 90° angle. The light is reflected by both surfaces of the film and produces constructive interference for certain wavelengths of light. The film is 120 nm thick. What is the longest wavelength of the light within the soap film for which constructive interference can be produced?
- 60 nm
- 240 nm
- 480 nm
- 560 nm
Question 97.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
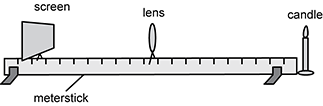
Diagram of a horizontal meterstick. At the right end of the meter stick is a candle. Mounted on the meterstick at the left end is a screen. A convex lens is mounted on the meterstick between the screen and the candle.
Students are using the setup shown in the diagram to examine optical properties of a given thin converging lens. The candle represents the object for the lens and is fixed in place at the end of a stable meterstick. A thin converging lens and a white screen are mounted on the meterstick and are allowed to slide along the length of the meterstick. Which of the following statements describes a possible pair of independent and dependent variables in the experiment using this setup?
- The independent variable is focal length, and the dependent variable is image distance.
- The independent variable is radius of curvature, and the dependent variable is focal length.
- The independent variable is image distance, and the dependent variable is object distance.
- The independent variable is object distance, and the dependent variable is radius of curvature.
Question 98.
Which of the following electric circuits could be used to generate electromagnetic waves of a given frequency f?
- A rectangular circuit loop with an inductor in the left side and a capacitor in the right side of the loop.
- A rectangular circuit loop with a resistor in the left side and an inductor in the right side of the loop.
- A rectangular circuit loop with a resistor in the left side and a diode in the right side of the loop.
- A rectangular circuit loop with a capacitor in the left side and a diode in the right side of the loop.
Question 99.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
Frequency of Electromagnetic Waves Hz
| infrared | 10 to the 12 |
|---|---|
| ultraviolet | 10 to the 15 |
| X-ray | 10 to the 18 |
| gamma | 10 to the 23 |
The table gives the approximate frequency of some electromagnetic waves. Which of following wavelengths should be used for penetrating radiation designed to produce medical images?
- 10 to the negative 3 m
- 10 to the negative 6 m
- 10 to the negative 9 m
- 10 to the negative 12 m
Question 100.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
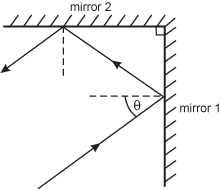
Diagram of two mirrors perpendicular to each other, forming a corner between the mirrors in the upper right of the diagram. The horizontal mirror at the top is labeled mirror 2. The vertical mirror at the right is labeled mirror 1. Dashed lines come out of the middle of each mirror and are each perpendicular to their mirror surface. An arrow heads from the lower left of the diagram diagonally upward toward mirror 1, striking mirror one at the dashed line. This arrow makes an angle, q, relative to the dashed line. The arrow reflects from mirror 1, toward mirror 2, striking mirror two at its dashed line. The arrow then reflects from mirror two and heads away from the mirrors heading down and to the left of the diagram.
The diagram shows two mirrors attached at a right angle. A ray of light is incident on one mirror with an angle of incidence of theta . What is the angle of reflection from the second mirror?
- 1 half theta
- theta
- 90 minus theta
- 180 minus 2 theta
Open-Response Items
The directions shown below represent what you will see on the actual test. For the purposes of this practice test, you will be able to type your written responses in the boxes provided on the answer key.
This section of the test consists of two open-response item assignments. You will be asked to prepare a written response of approximately 150–300 words, or 1–2 pages, for each assignment.
Read the assignments carefully before you begin your responses. Think about how you will organize your responses. You may use the erasable sheet(s) to make notes, write an outline, or otherwise prepare your responses. However, your final response to each assignment must be either:
- typed into the on-screen response box,
- written on a response sheet and scanned using the scanner provided at your workstation, or
- provided using both the on-screen response box (for typed text) and a response sheet (for calculations or drawings) that you will scan using the scanner provided at your workstation.
Instructions for scanning your response sheet(s) are available by clicking the "Scanning Help" button at the top of the screen.
As a whole, your response to each assignment must demonstrate an understanding of the knowledge of the field. In your response to each assignment, you are expected to demonstrate the depth of your understanding of the subject area by applying your knowledge rather than by merely reciting factual information.
Your responses to the assignments will be evaluated based on the following criteria.
- Purpose: the extent to which the response achieves the purpose of the assignment
- Subject Knowledge: appropriateness and accuracy in the application of subject knowledge
- Support: quality and relevance of supporting evidence
- Rationale: soundness of argument and degree of understanding of the subject area
The open-response item assignments are intended to assess subject knowledge. Your responses must be communicated clearly enough to permit valid judgment of the evaluation criteria by scorers. Your responses should be written for an audience of educators in this field. The final version of each response should conform to the conventions of edited American English. Your responses should be your original work, written in your own words, and not copied or paraphrased from some other work.
Be sure to write about the assigned topics. Remember to review your work and make any changes you think will improve your responses.
Any time spent responding to an assignment, including scanning the response sheet(s), is part of your testing time. Monitor your time carefully. When your testing time expires, a pop-up message will appear on-screen indicating the conclusion of your test session. Only response sheets that are scanned before you end your test or before time has expired will be scored. Any response sheet that is not scanned before testing ends will NOT be scored.
Question 101.
Use the information below to complete the assignment that follows.
Standards-Based Objective
Use algebraic expressions and the principle of energy conservation to calculate the change in energy of one part of a system when the change in energy of the other part of the system is known. Identify any transfers among electric, kinetic, and thermal energy and power.
System
An electric car has a mass of 2000 kg and uses a battery as a power source. The car accelerates at a constant rate from 0.0 m/s to 27 m/s in 9.0 s. Assume that the system is 60% efficient.
Assignment
Use your knowledge of physics to develop a response of approximately 150–300 words, or 1–2 pages, in which you use the standards-based objective to analyze the system. In your response:
- describe qualitatively the key energy transfers in this system;
- use formulas to create a mathematical model of this system to calculate the kinetic energy and power of the car, and the energy generated as thermal energy (assume that all dissipated energy is converted to thermal energy); and
- discuss how you could use this model in the classroom to help students make sense of the conservation of energy.
Question 102.
Use the information below to complete the assignment below.
Experimental Design Objective
Design an investigation to explore how a changing magnetic field produces an electric current in a conductor.
Assignment
Use your knowledge of physics to develop a response of approximately 150–300 words, or 1–2 pages, in which you design an investigation as described in the given experimental design objective. In your design:
- form and describe a testable scientific claim that addresses the concept of how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current;
- describe a scientific procedure to investigate the proposed claim, including identifying variables and the data to be collected;
- explain how an analysis of the collected data may provide evidence that supports or refutes the tested claim; and
- discuss how this investigation could be used to help students make sense of how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current (e.g., demonstration, experiment, investigation).