
Practice Test: Bilingual Education (79)
Suggested Testing Time: 3 hours and 15 minutes
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
Question 1.
Chomsky's theory of language acquisition hypothesizes that language is acquired primarily through:
- modeling, imitation, and practice.
- an innate ability to learn grammar.
- access to comprehensible input.
- a process of behavioral reinforcement.
Question 2.
The use of grinder, hoagie, or sub to refer to a sandwich is an example of which of the following types of language variation?
- regionalism
- jargon
- diachronic
- register
Question 3.
In a second-grade bilingual education classroom, the teacher and students often alternate between English and their first languages throughout their school day. Which of the following concepts related to bilingualism does this practice best exemplify?
- code switching
- language transfer
- fossilization
- language interference
Question 4.
Which of the following theories and hypotheses concerning language acquisition is most closely associated with the idea that students' proficiency in their first language positively contributes to learning a second language?
- Krashen's input hypothesis
- Chomsky's theory of universal grammar
- Vygotsky's collaborative learning theory
- Cummins's linguistic interdependence hypothesis
Question 5.
The study of the origin and roots of words is most useful for:
- determining the accurate pronunciation of words.
- identifying false cognates in second language learning.
- understanding the evolution of syntax and grammar rules.
- analyzing the meaning of complex words in academic texts.
Question 6.
A bilingual education student writes the following sentences in their writing journal.
The last weekend, I went to Franklin Park Zoo. I like the zoos because I love the animals.
The student would primarily benefit from instruction in the use of which of the following parts of speech?
- articles
- conjunctions
- nouns
- verbs
Question 7.
A third-grade bilingual education teacher and a bilingual education student have the following exchange.
Teacher: In Chapter One, the main character, Lily, learns that her best friend is moving away at the end of the school year. Lily feels so blue that she doesn't even want to go to summer camp. What advice does Lily's mother give her?
Student: I have question. What it means to "feel blue"?
The student's question is most clearly related to which of the following linguistic concepts?
- semantics
- register
- morphology
- syntax
Question 8.
The adjectives "youthful" and "childish" differ semantically in their:
- referential meaning.
- collocative meaning.
- connotative meaning.
- denotative meaning.
Question 9.
A speaker poses the question "Where is the key?" To understand the meaning of the word key, a listener would benefit from:
- considering the speaker's intonation.
- knowing the context of the conversation.
- reflecting on the origin of the word key.
- analyzing the structure of the sentence.
Question 10.
As part of a lesson on narrative writing, a bilingual education teacher compares the placement of descriptive adjectives in English and in the students' first languages. In this context, the teacher's instructional strategy will most likely advance which of the following goals?
- affirming students' linguistic diversity
- fostering a culturally responsive classroom
- activating students' background knowledge
- promoting students' metalinguistic awareness
Question 11.
Which of the following teacher actions most effectively communicates the message that bilingualism/multilingualism is a valuable asset for bilingual education students?
- urging students to leverage English and their first language during whole-class and small-group discussions
- volunteering to act as a translator for parent-teacher meetings as well as for other school functions
- inviting members of the community to the classroom to share some personal experiences to enrich student learning
- obtaining reading materials for the classroom library that reflect the diverse backgrounds of the students
Question 12.
A bilingual education teacher is planning instruction for a group of bilingual education students to help them recognize the implications of indirect questions in English, such as "Are you working with someone?" (which implies "Do you want to work with me?"). Which of the following language systems does this instruction primarily focus on?
- syntax
- discourse
- pragmatics
- morphology
Question 13.
A bilingual education teacher has students use the target language in a pair activity in which Student A describes an object that Student B cannot see. Student B tries to identify the object by asking for clarifications and making guesses. The students then switch roles and repeat the process with a new object. This activity most effectively promotes students' conversational skills by encouraging them to use:
- negotiation and repair strategies.
- nonverbal clues and key words.
- background knowledge and context clues.
- questioning and restatement strategies.
Question 14.
Students in an eleventh-grade English language arts class read a play in which many of the characters speak a dialect of English that the students are not familiar with. Which of the following activities would most effectively promote students' awareness of and respect for language variations of English prior to reading the play?
- showing a video on language variations of English and having students identify various dialects spoken and where they are spoken
- playing recordings of English speakers from the United States and having students identify the areas the speakers represent
- providing a list of various words and phrases in the English dialect from the play and having students guess their meaning using context clues
- having students read an article on language variations of English and discuss how the dialects evolved out of sociocultural contexts
Question 15.
A high school history teacher regularly incorporates into the curriculum a variety of recordings such as radio broadcasts, oral histories, interviews, and songs in English. This practice most effectively enhances students' academic progress in which of the following areas?
- integrating language domains
- cross-cultural communication
- listening to authentic speech
- interdisciplinary learning
Question 16.
A bilingual education teacher seeks to understand the beliefs, values, and practices of bilingual education students within the context of the students' cultures. The teacher in this scenario is primarily modeling which of the following cultural concepts?
- cultural pluralism
- cultural assimilation
- cultural relativism
- cultural universalism
Question 17.
Use the flowchart below to answer the question that follows.
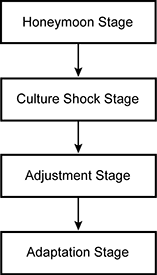
The flowchart consists of four stacked rectangular boxes with an arrow pointing down between each box to indicate a series of four consecutive steps or stages from the top box down to the bottom box. The first box contains the words "Honeymoon Stage." The arrow below the first box points down to the second box, which contains the words "Culture Shock Stage." The arrow below the second box points down to the third box, which contains the words "Adjustment Stage." The arrow below the third box points down to the fourth box, which contains the words "Adaptation Stage."
The flowchart primarily illustrates which of the following processes of cultural contact?
- acculturation
- accommodation
- assimilation
- appropriation
Question 18.
A recently arrived middle school bilingual education student is experiencing some of the effects of cultural fatigue, including frustration, anxiety, and inability to focus during class. Which of the following teacher approaches would be most appropriate in this situation?
- allowing the student to adjust to the new culture in the student's own way
- creating a supportive environment that validates cultural differences
- providing the student with explicit instruction in school cultural norms
- increasing the student's motivation to achieve academically across the curriculum
Question 19.
Use the chart below to answer the question that follows.
| Letter to the Principal | Letter to a Friend |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fourth-grade bilingual education students compare letters written to a friend with letters written to a school principal and record their observations on an anchor chart such as the one shown. This activity primarily promotes students' cultural awareness by:
- teaching the elements of letter writing.
- emphasizing the importance of formal language.
- highlighting specific similarities in written language.
- demonstrating how context influences language use.
Question 20.
High school bilingual education students will write a research paper on how interactions between past societies were affected by geographical factors such as the location of bodies of water, mountains, deserts, and climate. The teacher encourages students to research some societal interactions that took place in their heritage country histories that were influenced by such factors. The teacher's actions primarily demonstrate attention to which of the following instructional goals?
- building on students' cultural identities to enhance their learning
- facilitating positive intercultural communication
- helping students develop cultural competency and problem-solving skills
- using cultural diversity to foster critical thinking
Question 21.
A ninth-grade bilingual education student states, "In my old school, my teacher would teach, and I would pay attention so that I would do well on the test. Here, the students are talking instead of the teacher, and we must learn everything ourselves. How am I going to do well if the teacher isn't telling me what I need to know?" Based on the statement, the bilingual education teacher should primarily engage the student in a discussion about which of the following topics?
- differences in educational environments and teaching approaches
- current academic demands and classroom expectations
- social language norms and appropriate interactions with peers
- high- and low-cognitive-demand learning contexts
Question 22.
A fourth-grade bilingual education teacher plans literacy instruction for a reading group using texts that are culturally relevant to the students. The use of these texts supports students' literacy development by:
- increasing students' awareness of cultural and linguistic diversity through texts.
- helping students understand who they are through relatable characters.
- promoting students' comprehension by linking prior knowledge with the texts.
- exposing students to vocabulary that is culturally and linguistically specific.
Question 23.
Title VII of the Elementary and Secondary Act, known as the Bilingual Education Act (1968), was a significant piece of education legislation because it:
- ensured that school districts have a system for identifying bilingual students.
- mandated implementation of theoretically sound programs for bilingual students.
- required that bilingual students receive instruction primarily in their native language.
- funded the development and implementation of programs for bilingual students.
Question 24.
A ninth-grade bilingual education teacher plans to incorporate more culturally relevant texts in students' literacy instruction. When selecting texts, which of the following questions should the teacher primarily consider to avoid perpetuating cultural stereotypes?
- Are the stories age appropriate for students?
- Do the stories reflect students' experiences?
- Will the stories promote discussion among students?
- Do the stories have characters that are relatable to students?
Question 25.
A bilingual education teacher could most effectively use literary texts that form part of students' cultural heritage in which of the following ways?
- planning instructional activities that integrate elements reflecting students' various home cultures
- solving misunderstandings and classroom behavior problems related to cultural differences
- determining appropriate ways to group students from different cultural backgrounds during instruction
- forming expectations regarding the academic motivation of students from different cultural backgrounds
Question 26.
A recently arrived eighth-grade bilingual education student at the expanding level of English language proficiency is reluctant to speak during whole-group instruction except when the teacher randomly calls on the student to participate. The bilingual education teacher is aware that in the student's home culture teachers tend to assume a more authoritarian role in the classroom while students assume a more passive role. Which of the following approaches would be the most appropriate for the teacher to use to increase the student's class participation?
- pulling the student aside and explaining that participating in class only when called on by the teacher is not an acceptable practice in U.S. schools
- calling on the student during classroom instruction until the student learns that it is preferable to volunteer responses rather than wait to be called on
- engaging the student in partner and small-group activities regularly to help the student become more familiar and comfortable with the new classroom setting
- describing the advantages of the less formal role that teachers play in U.S. classrooms to help convince the student of the benefits of more active classroom participation
Question 27.
A sixth-grade bilingual education teacher leads a class discussion on how nonverbal communication is used in various cultures and contexts. The teacher encourages students to share relevant experiences with the class. The teacher's strategy primarily demonstrates attention to which of the following instructional goals?
- mediating students' cultural differences in communication styles
- facilitating students' understanding of cultural differences
- identifying exceptions to behavioral norms among peers
- supporting students' development of positive cultural identities
Question 28.
A high school bilingual education class includes students from various cultural groups that differ in attitudes toward cooperation, competition, formality, gender roles, risk taking, and other factors. When planning instruction for this class, which of the following approaches should the bilingual education teacher primarily consider?
- developing strategies for helping the students assimilate into the school culture
- establishing appropriate ways to group students from different cultural backgrounds
- modeling and encouraging appreciation for cultural similarities and differences
- maintaining a formal atmosphere to minimize tensions between different cultural groups
Question 29.
A bilingual education teacher encourages students to preview materials and resources in their first language before introducing a new topic in the target language of instruction. The teacher's action is most consistent with which of the following principles of bilingual education?
- making content comprehensible to improve students' English language skills
- leveraging students' first-language skills to teach grade-level concepts
- implementing scaffolding strategies to communicate content-area information
- adapting lessons to account for students' English language proficiency levels
Question 30.
A bilingual education teacher plans an activity in which first-grade students create a personal timeline using photographs, illustrations, and artifacts with support from their families. Students will then share their timelines with the class. This learning activity primarily promotes students' understanding of:
- chronology as it relates to events in the past and present.
- how perspectives are shaped by unique beliefs and attitudes.
- parallels in backgrounds that contribute to a national identity.
- experiences that contribute to the cultural identity of others.
Question 31.
According to Stephen Krashen's theory of second language acquisition, learners acquire a second language by:
- forming habits as the result of encouragement and feedback.
- memorizing grammar rules, vocabulary lists, and verb conjugations.
- studying language structures in a systematic and progressive way.
- constructing understanding through meaningful interactions with others.
Question 32.
An elementary bilingual education teacher reads several writing journal entries made by a second-grade emerging-level bilingual education student. The teacher notes that the student frequently adds -e before words that begin with the letter -s in English. For example, the student writes "eschool" for school, "especial" for special, and "estudy" for study. Which of the following rationales best explains the student's errors?
- The student has fossilized the spelling errors.
- The student is experiencing first language transfer.
- The student is unable to recognize false cognates.
- The student is overgeneralizing an orthographic rule.
Question 33.
A middle school bilingual education teacher frequently hears a student who immigrated to the United States about ten months ago speaking with friends in the hallway and in the cafeteria. In class, however, the student faces challenges with discipline-specific language used in content-area lessons. Which of the following statements best explains why the student is experiencing these challenges?
- Social language skills typically take more time to develop than academic-language skills.
- The student does not possess strong academic language skills in the first language.
- Social interactions are context reduced while academic language is context embedded.
- It takes approximately three to five years to master academic language in the classroom.
Question 34.
A fifth-grade bilingual education science teacher preteaches general academic and domain-specific words and phrases at the beginning of every lesson. The teacher typically prepares a video presentation that builds background knowledge and includes a slide for each new word accompanied by a photograph or illustration. The teacher's actions benefit bilingual education students' language development primarily by:
- providing students with comprehensible input.
- engaging students in metacognitive learning strategies.
- accommodating students' different learning approaches.
- differentiating lessons according to students' academic levels.
Question 35.
A middle school bilingual education teacher wants to create a classroom environment that includes frequent opportunities for meaningful academic conversations. Which of the following strategies would most effectively achieve this goal?
- conducting lectures on academic concepts followed by teacher-led question-and-answer periods
- engaging students in activities in which students apply learned concepts to solve problems
- incorporating more opportunities for students to turn and talk before and after new content concepts are introduced
- having students discuss academic concepts in pairs using structured dialogues and sentence frames
Question 36.
Bilingual education students are reading a novel. Prior to reading the next chapter, the teacher asks them to make a prediction about a character, using a character trait anchor chart and graphic organizers. This activity most effectively promotes the students' reading skills by:
- increasing their motivation to read similar novels.
- developing their ability to draw inferences from a text.
- promoting their understanding of narrative techniques.
- scaffolding their use of reading comprehension strategies.
Question 37.
A developing-level third-grade bilingual education student writes the following sentence in a teacher-student dialogue journal.
Last weekend, I goed to the house of my auntie. I played with her puppy Max outside. I throwed the ball. He bringed it back to me but bited my finger a little.
The errors in the journal entry demonstrate that the writer is most likely:
- experiencing first-language interference.
- unfamiliar with subject-verb agreement rules.
- overgeneralizing a grammatical rule.
- uncertain about narrative verb tenses.
Question 38.
A teacher in a first-grade bilingual education class observes that a student at the emerging level of English language proficiency regularly omits the subject pronoun when speaking and writing in English. The student's omission is an example of:
- diglossia.
- code switching.
- fossilization.
- language transfer.
Question 39.
A bilingual education student writes the following statement.
The mother of my friend is a doctor.
The statement reflects transfer from the student's first language. The most appropriate conclusion to draw about the student's first language is that it:
- does not capitalize proper nouns.
- does not have subject-verb agreement.
- does not alter nouns to show possession.
- does not utilize indefinite articles.
Question 40.
A bilingual education teacher encourages students to demonstrate their language skills in various ways, such as answering open-ended questions, agreeing or disagreeing with specific statements, and following directions in the target language. Which of the following statements provides the primary rationale for this approach?
- The teacher can adapt each student's mode of response based on the student's proficiency in the target language.
- The students can prepare thoughtful and focused responses in the target language prior to the activities.
- The teacher can identify specific skills that should be included in future instruction in the target language.
- The students can compare their level of proficiency in the target language to that of their classmates.
Question 41.
In addition to reviewing newly arrived students' scores on English language proficiency screening tests, a bilingual education teacher gathers information about the students' educational background, including past school performance, as well as level of first-language proficiency, including literacy skills. The teacher's actions primarily demonstrate awareness of which of the following factors involved in teaching bilingual education students?
- the influence of sociocultural, socioeconomic, and sociolinguistic variables on new-language development
- the interaction of age, personality, and learning style and their effects on new-language acquisition
- the interrelatedness of linguistic, cognitive, and academic factors in new-language development
- the importance of creating a culturally responsive classroom environment that fosters new-language acquisition
Question 42.
A seventh-grade bilingual education mathematics teacher posts the task list below for students to follow when they enter the classroom.
5-Minute Warm-up
- Copy the math problem from the board.
- Solve the problem.
- Check your work.
- Compare your answer with a classmate's.
- Talk about how you got your answer.
Bilingual education students at the emerging level of English language proficiency have a goal of learning to follow the procedure. Which of the following activities would most effectively promote these students' successful achievement of the goal?
- identifying key words and phrases in the procedure
- reading aloud the procedure with peer support
- copying the procedure into math journals
- practicing the procedure with a partner
Question 43.
In a tenth-grade U.S. history class, bilingual education students have a goal to understand concepts related to the decline in living standards, extended drought conditions, and poor agricultural practices that characterized the Great Depression. The bilingual education teacher shows the students archived images of the effects of these conditions. The primary rationale for sharing the images with the students is that the images:
- can be grouped into the three identified concept categories.
- provide information that words and statistics in a text may lack.
- demonstrate the importance of visual documentation in history.
- give clues to the programs implemented to restore prosperity.
Question 44.
A fifth-grade bilingual education teacher plans a cross-curricular thematic unit in which systematic, explicit, and sustained language instruction will be delivered in the context of the Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks. The use of thematic units in this context benefits bilingual education students primarily by:
- providing students with opportunities to work on language skills.
- creating a rigorous intellectual environment in which students can take academic risks.
- enhancing students' understanding of cross-disciplinary inquiry.
- promoting students' ability to acquire content knowledge and develop language skills.
Question 45.
A newly hired kindergarten bilingual education teacher inherits a collection of wordless picture books from a predecessor. The new teacher plans to evaluate the books and determine if they are appropriate for student use. When evaluating the books, the teacher should determine whether:
- the message promotes the reader's sense of self and a positive attitude toward others.
- the publication date indicates that the book's theme may lack contemporary relevance.
- the author is popular among many readers in the targeted age group.
- the characters in the books are familiar to the students in the class.
Question 46.
A bilingual education teacher often reads illustrated stories to a second-grade class that includes students with varying English language proficiency levels. Following the read-alouds, the teacher leads brief discussions to check student comprehension. During the discussions, the teacher could most effectively promote students' comprehension by encouraging them to:
- share personal anecdotes related to a story's theme.
- express opinions about characters' behaviors and actions.
- ask and answer clarifying questions about the plot.
- refer back to illustrations that evoke setting and mood.
Question 47.
A fifth-grade bilingual education teacher plans a lesson on analyzing character traits. The teacher will read aloud a short, illustrated narrative text and ask students to pay close attention to what the characters say and do. The students will then try to identify some of the main characters' traits. Which of the following strategies would most effectively promote emerging-level students' achievement of this activity?
- having students discuss with a partner the directions for the task prior to the read-aloud
- giving students a character traits graphic organizer to complete during the read-aloud
- leading students on a picture walk of the text prior to reading aloud
- using visual cues, gestures, and tone of voice while reading aloud
Question 48.
A fourth-grade bilingual education teacher shows a short film about Native American history in New England. Following the film, the teacher asks students to share one interesting fact they learned about Native American history with a partner. The teacher's instructional approach primarily supports bilingual education students' listening and speaking skills by:
- providing a structure for expected responses.
- offering an opportunity to paraphrase information presented.
- promoting accountability during classroom discussions.
- increasing processing times to better organize thoughts.
Question 49.
In a bilingual education kindergarten class, a small group of students is pretending that they are getting ready to be in a play. Two students interrupt each other as they describe a silly scene that the group could perform. Other students try on costume items and choose props in the dress-up area. The teacher's goal is to maximize students' communication experience from this activity. Which of the following strategies would most effectively accomplish this goal?
- recruiting additional students from the class to join the activity or act as audience members for the play
- letting the activity continue naturally and encouraging the students to include speaking parts for all participants
- questioning the students about how the costumes and props they choose help reinforce the roles they have in the play
- assuming a role as a character in the play and modeling how to use gestures and facial expressions to enhance verbal delivery
Question 50.
Use the graphic organizer below to answer the question that follows.
| Discussion Elements | Looks Like | Sounds Like |
|---|---|---|
| active listening |
|
|
| asking questions for clarification |
|
|
| building on the ideas of others |
|
|
| disagreeing appropriately |
|
|
A third-grade bilingual education teacher engages students in a whole-group discussion to identify elements that contribute to academic discussions to promote engagement during weekly literature circles. This activity most effectively supports bilingual education students' development of which of the following skills?
- outlining appropriate language use for given conversational situations
- fostering preparedness for conversations about domain-specific topics
- listing social rules that are expected to be followed during peer interactions
- increasing awareness of behaviors that promote effective conversations
Question 51.
A high school bilingual education teacher is planning to engage expanding-level bilingual education students in team debates. Each team will take a side on a controversial issue and then brainstorm and formulate arguments. The teams will present their arguments and respond to their opponents' arguments. Which of the following teacher strategies would most effectively promote students' academic speaking skills during this activity?
- instructing each student team to appoint a team spokesperson to present and respond to arguments
- providing students with a printed outline to follow as they present and respond to arguments
- providing key words and phrases to students that they can use to persuade or disagree when presenting and responding to arguments
- instructing each student to make note cards that can be read verbatim when presenting and responding to arguments
Question 52.
In a class with bilingual education students who are beginning readers, a bilingual education teacher uses a variety of activities and materials to introduce and reinforce letter recognition, beginning and ending sounds, rhyming words, blends, homonyms, and words with silent letters. This approach primarily demonstrates the teacher's understanding of the importance of:
- focusing instruction on sounds that are not part of students' primary languages and therefore are difficult to decode and produce.
- promoting students' phonological awareness and skills in the context of language experiences.
- building a basic vocabulary foundation for students' social language and academic language development.
- reading aloud to students who may have limited vocabulary and prior knowledge.
Question 53.
A kindergarten bilingual education teacher teaches a lesson on the basic features of print. Before the teacher begins reading an illustrated book aloud, the teacher asks the students some questions about the text. Which of the following questions would be appropriate to ask students at the entering level of language proficiency?
- Can you point to the title?
- Which letters are capitalized in the title?
- What is the title of this book?
- Shake your head "yes" or "no." (Teacher pointing to various lines of the book) Is this the title or is this the title?
Question 54.
Middle school bilingual education students who are at the developing and expanding levels of English language proficiency are getting ready to perform readers theatre. To prepare, they practice reading their lines with a partner. As they read aloud, the teacher circulates around the classroom and provides feedback and support. This activity is primarily effective in promoting bilingual education students' development of:
- vocabulary knowledge.
- visualization.
- fluency.
- comprehension strategies.
Question 55.
In a think-aloud activity with students, a bilingual education teacher introduces a chapter in an illustrated book on mammals in the following way.
"First, I look at the chapter title: 'The Sleepy Sloth.' Next, I look at the two photos of sloths. They're cute! Then I read the subheadings: 'Where Do Sloths Live?', 'How Do Sloths Travel?', and 'Why Are Sloths So Slow?'. Well, judging from the photos, they live in trees. The map on the next page shows Central and South America. I guess that is where sloths live. I'm still curious about how sloths travel and what makes them so slow!"
Which of the following reading comprehension strategies is the teacher primarily demonstrating in this activity?
- predicting
- summarizing
- paraphrasing
- previewing
Question 56.
A first-grade bilingual education teacher works with students at the developing level of English language proficiency. The teacher and students preview an informational text by looking at photographs from the text and reading the titles and subtitles to make a prediction about what the text will be about. This activity most effectively promotes bilingual education students' ability to:
- comprehend the main idea and supporting details of a text.
- read for the purpose of gaining new knowledge.
- build background knowledge to increase comprehension of a text.
- increase understanding of academic and social vocabulary.
Question 57.
An elementary bilingual education teacher is reviewing short stories written and illustrated by bilingual education students. In one story, the student wrote, "I know Maya since I was a little girl," followed by, "Her family visit our new home last year." Based on the language production in the writing sample, which of the following aspects of grammar should the teacher primarily address in differentiating instruction for this student?
- verb tenses
- placement of adjectives
- basic sentence structures
- incorrect or missing articles
Question 58.
A seventh-grade bilingual education teacher presents a weekly mentor sentence to introduce grammatical concepts to bilingual education students. After students have recorded and shared their observations about the mentor sentence, they are instructed to craft a sentence that replicates the structure of the mentor sentence. This instructional approach primarily promotes bilingual education students' writing by:
- scaffolding structure to increase the focus on writing content.
- introducing writing concepts through corrective approaches.
- providing access to content-specific vocabulary while writing.
- reinforcing target skills by modeling effective writing.
Question 59.
Middle school bilingual education students at the bridging level of English language proficiency will write letters to a newspaper editor in response to an op-ed piece. The teacher discusses with students how to structure an argumentative paper and organize paragraphs in a logical progression.
- introducing the claim
- presenting the counterclaim
- providing evidence to support the claim
- summarizing and concluding
The teacher provides students with a copy of an argumentative paper to review, and then leads students in identifying the main function of each paragraph. This activity primarily reflects the teacher's awareness of the value in promoting students' understanding of:
- main elements of various genres of expository writing.
- key characteristics of text structures in writing.
- organizational patterns typically used in journalism.
- rhetorical features commonly used in nonfiction texts.
Question 60.
A third-grade bilingual education teacher plans a unit in which students will use informational texts to research a topic. During the unit, students will use various texts to gather information about their topic and take notes. Which of the following strategies would most effectively promote expanding-level bilingual education students' successful achievement of this activity?
- assigning partners with similar language abilities to research the same topic and exchange information
- showing how photographs and illustrations in a text can give the reader significant information
- modeling how to use a bilingual picture dictionary to identify the meaning of challenging words in the text
- demonstrating how to use nonfiction text features (e.g., table of contents, subtitles) to locate key information
Question 61.
An elementary bilingual education teacher works with students who have a good understanding of basic mathematical operations and concepts. In one activity designed to help students choose appropriate math operations, the teacher contextualizes key vocabulary. Students also learn that some words have different meanings in mathematical contexts, such as table and quarter. This type of instruction most effectively promotes students' ability to:
- use word analysis to make quick calculations.
- translate words into mental images or diagrams.
- understand and solve word problems.
- use auditory cues to solve number problems.
Question 62.
A fourth-grade bilingual education class includes students at the entering and emerging levels of English language proficiency. The teacher differentiates class assignments and assessments so that these students can demonstrate their knowledge of grade-level content-area subjects at their current levels of language development. This practice primarily benefits student learning by:
- lowering students' affective filter.
- adjusting the pace of instruction for students.
- fostering the academic language development of students.
- focusing on content students know instead of their ability to produce the target language.
Question 63.
Bilingual education students in an elementary school science class are beginning a unit on the water cycle. During the unit, students will conduct several experiments. At the beginning of the unit, students have a goal of learning about vocabulary that they will encounter or need while conducting the experiments throughout the unit. Which of the following teacher strategies would most effectively promote students' achievement of their learning goal?
- having students illustrate a word list of content-specific vocabulary typically used in science experiments
- providing students with reading-based instruction in the concepts illustrated by the experiments before they are conducted
- familiarizing students with names of procedures and tools related to simple lab experiments in hands-on experiences
- asking expanding- and bridging-level students to help with the experiments and translate directions during class
Question 64.
An elementary school bilingual education teacher is planning a mathematics project for students who are at various levels of English language proficiency. The students will create informational slides for a class multimedia presentation on geometric figures and their properties. Which of the following teacher strategies would most effectively promote students' successful completion of this project?
- briefly reviewing with students objectives and concepts covered in grade-level appropriate mathematics curricula related to geometry
- providing multiple ways for students to access geometry concepts and materials (e.g., cooperative group activities, concrete models, dynamic geometry software)
- having students complete "do-talk-record" entries in their math journals, in which they write about or draw the properties of geometric figures
- asking students to choose their own individualized tools and resources (e.g., software, illustrated word banks, graphic organizers) for completing the geometry project
Question 65.
At the beginning of the school year, a bilingual education teacher reviews students' W I D A Assessing Comprehension and Communication in English State-to-State for English Language Learners (ACCESS for E L ells registered trademark ) scores. The teacher notes that several students earned low scores in the speaking domain. To improve the students' speaking skills, the teacher will incorporate daily speaking activities into instruction and will monitor students' progress using assessment tools such as rubrics and checklists. The teacher's actions demonstrate an understanding of the importance of which of the following practices related to assessment?
- selecting and designing meaningful, authentic assessments
- using assessment results to plan and adjust instruction for students
- providing feedback to students relative to their performance on speaking tasks
- administering summative assessments that are aligned with state learning standards
Question 66.
Which of the following strategies for assessing the academic progress of bilingual education students would most effectively improve the validity of decisions made based on assessment results?
- modifying accommodations during a formal assessment
- identifying options for standardized assessments
- comparing assessment scores among students
- using multiple measures of assessment
Question 67.
A bilingual education teacher is most likely to utilize an observational assessment tool as a language proficiency measure for which of the following bilingual education students?
- a kindergarten student who has never experienced a formal classroom setting
- a middle school student who has recently transferred from a school in another state before the student's records have arrived
- a fifth-grade student who may qualify for gifted and talented pull-out services
- a high school student who has recently been reclassified as a former English learner F E L and is demonstrating academic challenges
Question 68.
A high school bilingual education mathematics teacher utilizes exit tickets at the end of each lesson. The exit tickets typically consist of one or two problems that are aligned with the grade-level math standard that was taught. The teacher reviews the exit tickets and adjusts the lesson plan for the following day depending upon the results. As described in this scenario, exit tickets exemplify which of the following types of assessments?
- summative assessment
- criterion-referenced assessment
- formative assessment
- performance-based assessment
Question 69.
An elementary school bilingual education teacher assembles a portfolio for each student that includes periodic samples of student work, formal test data, checklists and rubric scores on oral tasks, descriptions of student accomplishments, and summary sheets. Which of the following types of assessment is illustrated by this practice?
- performance-based assessment
- summative assessment
- criterion-referenced assessment
- peer assessment
Question 70.
According to Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education D E S E guidelines, in which of the following scenarios would a home language survey be administered to the parents/guardians of a student?
- A student consistently performs below grade level in English language arts.
- A student is being evaluated for special education services.
- A student decides to take a high school world language class.
- A student is newly enrolled in the seventh grade of a middle school.
Question 71.
Which of the following questions would be most important for a bilingual education teacher to consider when evaluating a language assessment with respect to test validity?
- Does the assessment include reading passages that reflect a wide range of cultural traditions and practices?
- Do the assessment results yield data similar to data from examinees who are at different proficiency levels?
- Do the assessment questions closely align with the knowledge and skills they are intended to measure?
- Does the assessment format reflect the examinees' culturally influenced learning strategies and approaches?
Question 72.
A bilingual education teacher is reviewing a formal, standardized assessment and is concerned that results could vary depending on who scores the assessment. Which of the following topics covered in an assessment manual would address this concern?
- the construct validity of the assessment
- the inter-rater reliability of the assessment
- the population that the assessment was normed on
- the alignment of the assessment to learning standards
Question 73.
In preparation for an upcoming unit assessment, a second-grade bilingual education mathematics teacher reviews the word problem below.
Mary and Tom go on an egg hunt for Easter. Tom collects 21 eggs. Mary collects 27 eggs. How many more eggs does Mary collect than Tom?
Which of the following types of bias is evident in the word problem?
- linguistic
- cultural
- gender
- racial
Question 74.
According to Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education D E S E policy, an English language learner with an identified disability is allowed test accommodations on standardized tests when:
- the test that will be administered will be in a computer-based format.
- DESE has approved a formal request for accommodations from the student's parents/guardians.
- the student's Individualized Education Plan I E P or Section 504 plan lists specific accommodations.
- a significant portion of the student's education took place outside Massachusetts.
Question 75.
Parents/guardians of a bilingual education student attend a special education team meeting. The parents/guardians of the student are fluent in English and decline the services of an interpreter. During the meeting, the student's bilingual education teacher will present the results of the student's language proficiency assessment. Which of the following approaches would best promote the parents'/guardians' understanding of the bilingual education teacher's presentation?
- having an interpreter present during the meeting in case the parents/guardians need clarification in their native language during the presentation
- providing copies of the assessment results in both English and the parents'/guardians' native language for them to review after the meeting
- explaining the results of the student's performance on the assessment and eliminating professional jargon to the extent that it is possible
- asking the parents/guardians during the presentation if they have questions about the student's performance on the assessment
Question 76.
A third-grade bilingual education teacher plans to assess an entering-level bilingual education student's listening skills in English. The teacher has the student listen to an audio recording of a short narrative text. Which of the following strategies would be most appropriate for the teacher to use to assess the student's understanding of the story?
- having the student retell the events of the story sequentially
- instructing the student to reenact important events from the story
- asking the student to draw pictures that portray some of the story's events
- requiring the student to complete a series of multiple-choice questions about the story
Question 77.
A first-grade bilingual education teacher regularly conducts informal assessments of students' oral language development in English. Below is a partial transcript of an exchange between the teacher and an emerging-level bilingual education student.
Teacher: Can you tell me what is happening in this picture?
Student: Huh?
Teacher: What is happening in this picture?
Student: Four students at the table. Sitting.
Teacher: Yes. There are four students sitting at a table. What are they doing?
Student: Art project.
Teacher: Why do you think they are doing an art project?
Student: Cuz the crayons, the construction papers, the scissors, the glue stick.
Which of the following strengths in the student's oral language development is most evident?
- pragmatic competence
- vocabulary knowledge
- discourse competence
- syntactic knowledge
Question 78.
A bilingual education teacher assigns a short nonfiction reading passage to a group of developing-level bilingual education students. The teacher can best assess the students' comprehension of the passage by having the students complete which of the following tasks?
- writing responses to a series of text-dependent questions about the passage
- referring to details in the passage when drawing inferences from the text
- using context clues to determine the meaning of words used in the passage
- identifying the main idea of the passage and some supporting details
Question 79.
A fourth-grade bilingual education teacher is creating a checklist that developing-level bilingual education students can use as a self-assessment tool during the editing stage of the writing process. Which of the following questions would be most appropriate for the teacher to include?
- Does each sentence have a subject and a verb?
- Are pronouns in the proper case (i.e., subjective, objective, and possessive)?
- Do commas and quotation marks appear in dialogues?
- Is there a variety of sentence structures (e.g., simple, compound, complex)?
Question 80.
Which of the following educational models promotes biliteracy and bilingualism as an asset and a goal for students enrolled in the program?
- dual language instruction
- transitional bilingualism
- sheltered English immersion
- pull-out ESL instruction
Question 81.
Two-way immersion T W I programs effectively promote enrolled students' bilingualism and biliteracy primarily by:
- providing grade-level content instruction in the English language learners' primary languages and in English to facilitate rapid transition to an English mainstream classroom.
- teaching academic content and literacy in English utilizing scaffolding strategies to support English language learners' successful grade-level achievement.
- providing content and literacy instruction in English and in the second language of instruction to students who are English language learners and students who are fluent in English.
- teaching literacy in the English language learners' primary languages to support the development of academic language and literacy skills in English.
Question 82.
In Lau versus Nichols, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the right of language minority students to receive equitable education in public schools based on which of the following rationales?
- the illegality of government policies that limit the freedoms granted by the U.S. Constitution
- the right of parents/guardians to advocate for their child's individual educational needs
- the illegality of discrimination in federally funded programs based on race, color, or national origin
- the right of individuals to protect the freedoms provided to them under the U.S. Constitution
Question 83.
The U.S. Supreme Court case Plyler versus Doe impacted education programs by:
- mandating that public schools provide instruction in English and in students' native languages.
- barring public schools from refusing to educate students based on their undocumented immigration status.
- prohibiting public schools from segregating students based on race, color, or national origin.
- requiring that public schools base instruction for language minority students on sound pedagogical instruction.
Question 84.
A student whose home language is English received instruction that included literacy instruction solely in Spanish in kindergarten and first grade. In second grade, instruction in Spanish began to decrease as instruction in English language arts was added. This scenario primarily illustrates which of the following types of programs?
- maintenance bilingual education
- transitional bilingual education
- two-way immersion
- sheltered English immersion
Question 85.
A new bilingual education teacher plans to motivate students to set high expectations for their learning. To achieve this goal, the teacher reads several professional articles about student motivation. Building on the information in the articles, which of the following steps would be the most appropriate for the teacher to take next?
- applying motivational strategies mentioned in the professional literature to determine their effectiveness
- organizing a workshop with colleagues to share their professional experiences related to student motivation
- contacting other teachers in the school district to seek their opinions on the motivational strategies mentioned in the professional literature
- enrolling in an online course for professional development that focuses on strategies for enhancing student motivation
Question 86.
A bilingual education teacher maintains a self-reflection journal in which notes are made daily on the effectiveness of the lessons taught. This journal would primarily benefit a bilingual education teacher in which of the following ways?
- recognizing possible biases on instructional practices
- developing a professional development plan to improve instruction
- identifying professional strengths and growth opportunities on an ongoing basis
- creating a professional development workshop for bilingual education colleagues
Question 87.
A bilingual education teacher participates in a professional development workshop on promoting bilingual education students' content and language learning. Which of the following statements describes the primary benefit of attending this type of professional development activity?
- collaborating with other bilingual education teachers
- developing a professional development plan to improve instruction
- acquiring new knowledge to use in mentoring new teachers
- learning about evidence-based strategies for improving instruction
Question 88.
A teacher asks an experienced bilingual education teacher for suggestions on how to develop effective assessments. Which of the following steps taken by the experienced teacher would most effectively meet the new teacher's needs?
- identifying professional development workshops that the new teacher can attend
- providing the new teacher with various articles in professional journals on assessment
- working collaboratively with the new teacher to design assessments
- sharing copies of assessments that the experienced teacher has previously designed
Question 89.
A bilingual education teacher and a special education teacher will be co-teaching a high school science class. Which of the following steps would be most appropriate for the teachers to take first to ensure a successful co-teaching partnership?
- discussing various co-teaching models and determining the most effective model based on the individual strengths of each teacher
- reviewing the first unit of the curriculum and identifying content and language objectives based on learning targets and standards
- creating a weekly schedule that establishes the days and times during the week when the teachers will meet to co-plan
- meeting with the principal to request an outline of the roles and responsibilities of each teacher
Question 90.
The parents of a fourth-grade bilingual education student ask the bilingual education teacher about digital resources that would support their child's literacy skills. Which of the following resources would be most appropriate for the bilingual education teacher to suggest?
- a video streaming service that features adults reading high-interest texts aloud
- a grade-level E L A textbook with an access code for online literacy games
- a website that records students' voices while they read grade-level texts
- a district-provided online reading program that focuses on fluency and comprehension
Question 91.
A high school bilingual education teacher plans to advocate for more resources for bilingual education students to promote their equitable access to the curriculum. Which of the following actions should the teacher take first?
- identifying colleagues who share a similar concern
- gaining a clear understanding of the policies and state and federal laws regarding this issue
- meeting with the principal to request additional resources
- organizing community events to discuss the impact of a lack of resources on students' academic achievement
Question 92.
A bilingual education teacher plans to help families of bilingual education students feel welcomed at parent-teacher conferences by ensuring effective communication between parents/guardians and teachers. Which of the following approaches would best accomplish this goal?
- arranging for a district interpreter to be available during their conferences
- sending a translated pamphlet home explaining the conference process
- distributing a list of online interpretation tools for teachers to use during conferences
- leading a professional development training on cultural norms regarding communication
Question 93.
A bilingual education teacher plans to partner with parents/guardians of bilingual education students to promote students' progress in the classroom. Which of the following actions would be most effective in achieving this goal?
- asking parents/guardians to attend school committee and school board meetings on a regular basis
- encouraging parents/guardians to contact local legislators to discuss current bilingual education policies
- inviting parents/guardians to visit their child's classroom and to attend and volunteer at school-sponsored events
- having ongoing discussions with parents/guardians to create and monitor shared goals for their child
Question 94.
A bilingual education teacher wants to build partnerships with bilingual education students' communities to promote students' academic achievement. Which of the following approaches would be most effective to achieve this goal?
- recruiting community members to volunteer in the classroom and at various school functions
- inviting community members to make presentations that relate to academic topics that students are studying
- seeking donations from community members to purchase books for the classroom library that reflect students' interests
- arranging for students to serve as community service volunteers at local facilities such as the library, hospital, or animal shelter
Use the information below to answer the two questions that follow.
Middle school bilingual education students at the expanding and bridging levels of English language proficiency are participating in a poetry unit. The students study several poems by diverse writers, such as Pat Mora, Shel Silverstein, Maya Angelou, and Martín Espada. For some poems, the teacher shows students video clips of the authors reciting their poems. For other poems, the teacher leads students in reading the poems or excerpts from the poems aloud as a class. Following the video clip and group reading activities, the teacher asks the students to talk about how the poems made them feel or what the poems made them think about. Then the teacher guides students in a discussion about what they noticed about the language and rhythm of the poems.
Question 95.
The discussions primarily benefit bilingual education students by promoting their ability to accomplish which of the following grade-level tasks?
- reading literary passages with enhanced fluency
- recognizing rhetorical devices (e.g., alliteration, imagery) and tone or point of view
- comparing and contrasting text types and purposes
- applying organizational patterns (e.g., cause-effect, spatial) in their own writing efforts
Question 96.
Which of the following English language arts learning outcomes for students is primarily promoted by the poetry activities?
- Present information and evidence so that listeners and audience members can follow the line of reasoning.
- Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays to express information and enhance understanding of presentations.
- Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and communicative tasks and demonstrate command of English when appropriate.
- Participate in a range of collaborations with partners, building on others' ideas and expressing one's own ideas clearly.
Use the information below to answer the two questions that follow.
To promote the oral language skills of fifth-grade bilingual education students, a bilingual education teacher engages the students in "Agree/Disagree" activities. The teacher presents a controversial statement that can be debated, such as "Homework should not be given to students" or "People learn more from traveling than from reading." Students form small groups based on whether they agree or disagree with the statement. Each group works on its position for a few minutes, and then presents the position along with supporting reasons. Speaking is divided among group members.
Question 97.
Which of the following activities would be most important to carry out prior to the "Agree/Disagree" activities?
- providing students with graphic organizers that include flowcharts to help students write down and connect their ideas
- presenting students with a decision-making model and discussing how to implement each step
- providing students with scaffolds for participating in academic discussions
- conducting a whole-class activity in which students discuss the idea of community and how individuals can make contributions to a common goal
Question 98.
Which of the following scaffolding strategies would most effectively support the participation of students who are at the emerging and developing levels of English language proficiency in the activity?
- providing and reviewing with students a vocabulary bank and sentence frames for expressing opinions and persuasive arguments
- modeling for students how to use graphic organizers and webbing tools to facilitate quick note-taking during group discussions
- showing students video clips of student debates and asking students to role-play a debate related to an upcoming "Agree/Disagree" issue
- arranging for students who exhibit lower levels of English language proficiency to partner with group members who exhibit higher proficiency levels
Use the chart1 below to answer the two questions that follow.
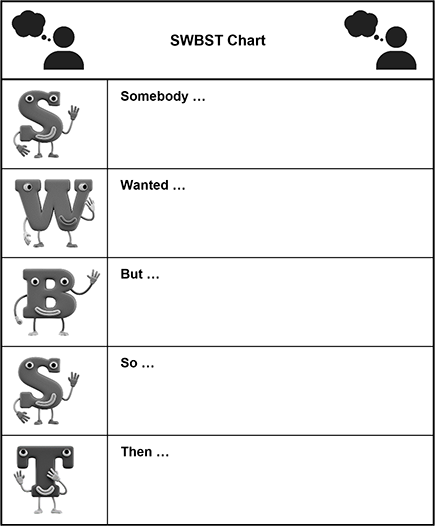
The title of the chart is "SWBST Chart" and appears in the top box. There is a talking icon on each side of the title. The icons are basic representations of a person with a bubble going to their head as in a comic strip to indicate that they are talking or thinking. Below the title, the chart is divided into two columns and five rows. The first column is narrower and contains one cartoony alphabet character per row. The second column is wider and contains one capitalized word per row each followed by three dots. The alphabet characters have eyes, smiles, arms, and legs and are either waving or making gestures indicating that they are thinking or reacting to something they heard or read. In the first row, the alphabet character in the first column is the letter S, and in the second column, the word "Somebody" appears followed by three dots. In the second row, the alphabet character in the first column is the letter W, and in the second column, the word "Wanted" appears followed by three dots. In the third row, the alphabet character in the first column is the letter B, and in the second column, the word "But" appears followed by three dots. In the fourth row, the alphabet character in the first column is the letter S, and in the second column, the word "So" appears followed by three dots. In the fifth row, the alphabet character in the first column is the letter T, and in the second column, the word "Then" appears followed by three dots.
Question 99.
A bilingual education teacher will use the graphic organizer with expanding-level English language learners who have a learning objective of reading and comprehending short stories. Which of the following teacher strategies would most effectively promote students' use of the graphic organizer and understanding of story relationships and connections between events?
- asking the students to read passages from narrative texts to themselves and then retell the passage to a partner using the graphic organizer
- providing the students with academic-language scaffolds (e.g., glossary) to improve their comprehension of dialogue used in narratives
- explicitly teaching the students signal and transition words and other cohesive elements commonly used in narrative text structures
- demonstrating for the students how to make notes or webs of main ideas in narratives that are linked to main supporting details
Question 100.
This type of graphic organizer would be most useful to students who are:
- recalling a character's motivations in a story.
- responding to literary or dramatic elements in a story.
- identifying the organizational pattern used in a story.
- summarizing the main elements in a story.