Practice Test: Middle School Mathematics/Science (77)
Answer Key, Sample Responses, Evaluation Chart, and Score Calculation Tool
Answer Key
Fill in your answers below and then print this answer key to save your work. Alternatively, you can print the answer key first to fill it out offline as you take the practice test. Note that the correct responses will be displayed on the printed answer key, so you may want to cover them until you have completed the practice test and are ready to check your answers.
When you have finished the practice test, click on "show answers" to see how well you did on each objective. In addition, use the Evaluation Chart to determine how many questions within each objective you answered correctly.
You will not receive a score for the practice test, and there is no passing score for the practice test. However, to get a sense of how well you did, use the Score Calculation Tool to better gauge your performance and degree of readiness to take an MTEL test at an operational administration.
NOTE: When you take the actual test, you will receive a score report that provides subarea-level performance, not objective-level performance. Information about test results can be found at Score Report Explanation.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
Related Objectives and Rationale |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C |
Objective 001 Correct Response: C. This claim may be verified with simple examples, such as pi to the 0 power equals 1 and radical 2 squared equals 2. Incorrect Response: A. The sum of an irrational number plus a rational number is irrational. Consider that a non-repeating, nonterminating decimal will remain as such when any terminating or repeating decimal is added to it. Incorrect Response: B. The quotient of an irrational number divided by a rational number is irrational. Suppose that A divided by b formed a rational number, m divided by n. Then it would follow that A equals b times the fraction m over n. That is, A would also be a rational number. This result contradicts the statement that A is an irrational number and so it cannot be true. Incorrect Response: D. The sum of an irrational number plus a rational number is irrational. See the rationale for response A. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2 | B |
Objective 001 Correct Response: B. There are 3 sets of identical groups of x plus 4 shown, or the quantity x plus 4 plus the quantity x plus 4 plus the quantity x plus 4. This may be written as 3 times the quantity x plus 4 by the distributive property of equality. Incorrect Response: A. Since each of the three rods represents x, 3x is the correct term to represent the unknowns in the problem. However, this answer does not distribute the factor of 3 to the ones units shown—there are 12 ones units in the diagram, not 4. Incorrect Response: C. The exponent signifies repeated multiplication of x plus 4. This expression would correspond to the total volume of a cube that has an edge length of x plus 4. This is not what is shown in the diagram. Incorrect Response: D. This response may reflect a misconception that an exponent represents repeated addition (e.g., the multiplication of 4 and 3). The expression 4 cubed denotes 4 times 4 times 4 equals 64 ones units. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 3 | D |
Objective 001 Correct Response: D. Given that K is a multiple of x, then K equals m times x for some whole number m. Similarly, given that K is a factor of y, then Y divided by K equals n for some whole number n. It follows from the substitution of K that Y divided by the product mx equals n implies y equals m times x times n. That is, y is a multiple of x. Incorrect Response: A. Given that K is a factor of y, then Y divided by K equals n for some whole number n. Take the reciprocal of both sides of the equation to see that K divided by y equals 1 divided by n. As such, K divided by y can only be a whole number if K = y. Incorrect Response: B. Given that K is a multiple of x, then K equals m times x for some whole number m. Dividing both sides of this equation by m times x shows that x divided by K equals that unit fraction 1 divided by m: K over the product m times K equals m times x divided by m times k implies 1 over m equals x over k. This means that x divided by k is only a whole number when x = K. Incorrect Response: C. For a proof by counterexample, consider the values K = 4, x = 2, and y = 8. These values are consistent with the information provided. In this case, y is not a factor of x, so the claim that "y is a factor of x" must not always be true. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 4 | D |
Objective 001 Correct Response: D. The expanded form of the number represented as "1 Y 3" is equal to 1 times 100 plus Y times 10 plus 3 times 1. Multiplying the digit Y by 24 corresponds to a partial product of 24 times 10 times Y equals 240 times Y. Incorrect Response: A. 20 times Y does not reflect the contribution of the 4. The correct partial product can be written with the distributive property as The quantity 20 plus 4 times 10 times y. Incorrect Response: B. The tens place value is not expressed with 24 times Y. This response treats the digit Y as though it represented Y units of 1. Incorrect Response: C. This response may represent 4 times 10 times Y. This product does not account for the multiplication between Y and the digit 2 in 24. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 5 | D |
Objective 001 Correct Response: D. Division by 2 will distribute over each of the terms in the parentheses: 2 times 6 to the sixth power divided by 2 plus 10 times 6 to the fourth power divided by 2 plus one half times 6 squared divided by 2 equals six to the sixth power plus 5 times six to the fourth power plus one fourth times 6 squared. Incorrect Response: A. This answer is the result of a misapplication of the distributive property in which the base for each exponential expressing is divided by 2. (It does not hold, for instance, that 6 squared times 18 divided by 2 is equal to 3 squared times 9.) Incorrect Response: B. This response demonstrates a misconception with the division of products in which the exponent for each exponential expression is halved. (It does not hold, for instance, that 6 squared divided by 2 is equal to 6.) Incorrect Response: C. The response 6 cubed plus 5 times 6 squared plus one fourth times 6 could be obtained from multiple errors, such as dividing both the constants and the exponents for each expression by 2. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 6 | C |
Objective 001 Correct Response: C. The value of a number does not change if a pair of inverse operations are applied to it. The pair of equations 4 times 8 equals 32 and 32 divided by 8 equals 4 shows division by 8 reversing the effect of multiplication by 8. Incorrect Response: A. In this response, multiplication occurs with one number and division with its integer opposite. This does not demonstrate the concept of inverse operations. The inverse operation of multiplication by 1 is division by 1, not negative 1. However, even if this were addressed, the concept of inverse operations would not be well illustrated by multiplication and then division by 1. Incorrect Response: B. This response demonstrates properties of zero, not inverse operations. Incorrect Response: D. These equations multiply and divide by different numbers, making them inappropriate to use to illustrate the concept that multiplication and division are inverse operations. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 7 | B |
Objective 002 Correct Response: B. Let a vertical position of 0 represent sea level and negative integers represent the depth of the submarine. In this reference system, the integer negative 375 describes the initial position of the submarine. The expression negative 375 + 183 − 228 represents new position of the submarine after it rises and then dives again. It evaluates to negative 420 feet. If the submarine rises at 30 feet per second, then it reaches the surface in 420 divided by 30 = 14 seconds. Incorrect Response: A. This result can be obtained from the expression negative 375 − 183 + 228 . In this case, the submarine starts at a depth of 375, sinks 183 more feet, and then rises 228 feet. Incorrect Response: C. This result is approximately equal to (375 + 228) divided by 30. Incorrect Response: D. This result can be obtained from the expression 375 + 183 + 228. Because integer signs are not considered, this expression represents a submarine that dives by 183 feet and then by 228 feet. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 8 | D |
Objective 002 Correct Response: D. Let x represent the original price of the television. The price after a 15% discount is 0.85x. The tax is paid on the price after discount, so it can be represented by 0 point 0 6 5 times 0 point 8 5 x. The total price paid including discount and tax is 0 point 8 5 x plus 0 point 0 6 5 times 0 point 8 5 x equals 0 point 8 5 x times the quantity 1 plus 0 point 0 6 5 equals k. Solving for x results in x equals k divided by the product of 0 point 8 5 and the quantity 1 plus 0 point 0 6 5. Incorrect Response: A. This response provides the final cost of the television if K represents its initial amount. K, however, represents the final amount. Incorrect Response: B. This expression attempts to reverse the effects of applying tax and providing a discount but does so incorrectly. Consider the claim that a 6.5% increase can be offset with a 6.5% decrease. The multiplication x times the quantity 1 plus 0 point 0 6 5 times the quantity 1 minus 0 point 0 6 5 does not return x. Because the increase of 6.5% was applied with the multiplication of the quantity 1 plus 0 point 0 6 5, it must be removed with the inverse operation of division by that same amount. The same argument applies to the factor of the quantity 1 plus 0 point 1 5 that is used to compensate for the discount. Incorrect Response: C. This equation is the result of solving the equation 0 point 8 5 x times the quantity 1 minus 0 point 0 6 5 equals K for x. The quantity 1 minus 0 point 0 6 5 treats the tax as if it discounted the original price, which is not correct. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 9 | C |
Objective 002 Correct Response: C. If the GCF of x and y is 3, then x and y can be represented by 3k and 3m, respectively, where k and m are relatively prime (i.e., they share no common factors, otherwise the GCF of x and y would reflect those factors and be greater than 3). Substituting this into 2 over x = 5 over y equals 2 over 3 k = 5 over 3 m. The least common denominator for these fractions is 3km. Given that 3k = x and m = y over 3, the least common denominator can also be written as x times y over 3. Incorrect Response: A. This response corresponds to a least common denominator that is the product of all the quantities shown: 2 times 5 times x times y. Incorrect Response: B. This response incorrectly combines information about the GCF with the denominator values of x and y. Incorrect Response: D. This response corresponds to the reciprocal of 2 times 5 over x times y. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 10 | B |
Objective 002 Correct Response: B. Apply algebraic properties of inequality to test whether A plus c over b plus c is greater than A over b is a true statement. The inequality can be rearranged as b times the quantity A plus c is greater than A times the quantity b plus c through multiplication, expanded as A times b plus b times c is greater than A times b plus a times c by the distributive property, and then further reduced to the simple inequality b is greater than A. This result may be interpreted to mean that A plus c over b plus c is greater than A over b is a true statement when b is greater than A. This must be true because the fraction A over b is a proper fraction greater than zero. Incorrect Response: A. The inequality A minus c over b minus c is greater than A over b can be rearranged as b times the quantity A minus c is greater than A times the quantity b minus c. This expands to A times b minus b times c is greater than A times b minus A times c and simplifies to negative b is greater than negative A, which is also equivalent to b is greater than A. However, this cannot be true because we are given that A over b is a proper fraction greater than 0. Incorrect Response: C. Simplify the left side of the inequality to obtain A over b is greater than A over b, which is a false statement. Incorrect Response: D. Observe that A divided by c over b divided by c is equivalent to A over b. The inequality shown is equivalent to the statement A over b is greater than A over b, which is false. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 11 | C |
Objective 002 Correct Response: C. The problem can be described by the linear equation 5 plus 0 point 7 5 times x equals 31, where x is the time in seconds that the cyclist has coasted down the hill and 5 is the initial speed for the cyclist at time x = 0. Solving the equation for x: 5 plus 3 fourths x equals 31 implies 3 fourths x equals 26 implies x equals 26 divided by 3 fourths implies x equals 26 times 4 thirds implies x equals 104 over 3 equals 34 and 2 thirds. Incorrect Response: A. This response is the result of the computation the quantity 31 minus 5 times 3 fourths, which represents a misinterpretation of the relationships in the problem. Incorrect Response: B. This answer is the result of the computation 31 divided by 3 fourths, which does not take the initial speed of the cyclist into account. Incorrect Response: D. This answer is the result of the computation 36 divided by 3 fourths, which may be the result of using the equation 3 fourths times x minus 5 equals 31. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 12 | C |
Objective 002 Correct Response: C. This response shows 3 times 6 eighths equals 18 over 8 equals 2 and 1 fourth. With these values, A b c equals 2 times 1 times 4 equals 8. Incorrect Response: A. This response shows 3 fifths plus 5 fifths plus 3 fifths equals 11 fifths equals 2 and 1 fifth. With these values, A b c equals 2 times 1 times 5 equals 10. Incorrect Response: B. This response shows 3 times 5 sixths equals 15 sixths equals 2 and one half. With these values, A b c equals 2 times 1 times 2 equals 5. Incorrect Response: D. This response shows 1 fourth plus 3 fourths plus 1 fourth equals 5 fourths equals 1 and 1 fourth. With these values, A b c equals 1 times 1 times 4 equals 4. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 13 | B |
Objective 002 Correct Response: B. The distance between 1 eighth and 3 eighths is 3 eighths minus 1 eighth = 1 fourth unit. This distance is split into 6 segments such that each segment has a length of 1 fourth divided by 6 = 1 twenty-fourth unit. Point D is located 3 segments away from 1 fourth + 3 times 1 twenty-fourth = 1 eighth + 1 eighth = 1 fourth unit. Alternatively, consider that point D is located midway between 1 eighth and 3 eighths, which is 1 fourth. Incorrect Response: A. In this response, Point D is located 3 sevenths of the way from point A to point H. That is, 2 twenty fourths plus 3 sevenths times the quantity 2 thirds minus 2 twenty fourths equals 1 third unit. Incorrect Response: C. In this response, Point D is located 3 fifths of the way from point A to point F. That is, 1 twelfth plus 3 fifths times the quantity one half minus 1 twelfth equals 1 third unit. Incorrect Response: D. In this response, Point D is located 3 fourths of the way from point A to point E. That is, 1 seventh plus 3 fourths times the quantity 3 sevenths minus 1 seventh equals 5 fourteenths unit. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 14 | C |
Objective 003 Correct Response: C. The sequence 0, 4, 9.5, 16.5, 25, 35 increases in a quadratic pattern. This can be seen by the linear increase in the first differences: plus4, plus5.5, plus7, plus8.5, plus10 (i.e., the first differences increase by 1.5 with each term). Continuing this pattern leads to a diameter of 6 miles at day 35 + 11.5 = 46.5, a diameter of 7 miles at day 46.5 + 13 = 59.5, and a diameter of 8 miles at day 59.5 + 14.5 = 74. Incorrect Response: A. This response may be based on the reasoning that the diameter of the spill increases at a constant rate of 4 miles every 25 days. This ratio cannot be doubled to 8 miles every 50 days because the diameter of the spill increases more slowly over time. Incorrect Response: B. This response increases the number of days by 10 with each mile of diameter. This represents the difference between 35 days and 25 days. However, the sequence shows that this difference increases as the diameter grows. Repeated addition of 10 does not account for this dynamic. Incorrect Response: D. This response may be based on the reasoning that the square of diameter is approximately equal to the number of days associated with the previous whole number diameter (i.e., 2 squared equals 4, 3 squared is approximately 9 point 5, 4 squared is approximately 16 point 5…). Continuing this pattern, 9 squared is approximately the number of days it takes for the spill to become 8 miles in diameter. This response does not describe the pattern as accurately as response C. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 15 | B |
Objective 003 Correct Response: B. The value for the first term (when n = 1) is 2 and the sequence decreases by 8 with each new term. The expression that produces 2 for the first term and then decreases by 8 with each additional term is 10 − 8n. Incorrect Response: A. This expression yields 2 minus 8 times 1 equals negative 6 for the first term. It would be correct if the first term corresponded to n = 0 (such as when x = 0 at the y-intercept of a linear equation), but it does not. Incorrect Response: C. This expression yields 8 times 1 minus 2 equals 6 for the first term. Incorrect Response: D. This expression yields 8 times 1 minus 10 equals negative 2 for the first term. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 16 | A |
Objective 003 Correct Response: A. The amount of medication in the patient's bloodstream decreases by 10% each hour, which means that 90% of the medication present at a given moment will still remain in the bloodstream after 1 hour. After the first hour, 100 times 0 point 9 0 equals 90 milligrams remain. After the second hour, 90% of this value remains. This can be expressed as 90 times 0 point 9 0, but it is easier to connect back to the starting value to see the exponential nature of the relationship: 100 times 0 point 9 0 times 0 point 9 0 equals 100 times 0 point 9 0 squared. After t hours, there will be 100 times 0 point 9 0 to the power of t milligrams of medication in the bloodstream. Incorrect Response: B. A linear function changes by a constant rate, so the difference in the amount of medication present in the bloodstream between any two consecutive hours should be the same. This is not what happens. The data below show how a 100 milligram dose of medication will change when only 90% is retained each hour. The difference between any two consecutive hours varies. 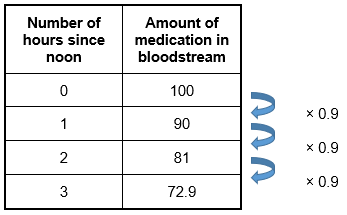 A table with 2 columns and 5 rows. Column 1 head Number of hours since noon. Column 2 head amount of medication in bloodstream. Column 1 row 2 0 column 2 row 2 100. Column 1 row 3 1 column 2 row 3 90. Column 1 row 4 2 column 2 row 4 81. Column 1 row 5 3 column 2 row 5 72.9. Arrows to the right of the table show that data in column 2 changes by times 0.9 for each hour that passes.
A table with 2 columns and 5 rows. Column 1 head Number of hours since noon. Column 2 head amount of medication in bloodstream. Column 1 row 2 0 column 2 row 2 100. Column 1 row 3 1 column 2 row 3 90. Column 1 row 4 2 column 2 row 4 81. Column 1 row 5 3 column 2 row 5 72.9. Arrows to the right of the table show that data in column 2 changes by times 0.9 for each hour that passes.
Incorrect Response: C. A proportional function can be written as f of x equals k times x. In this case, the amount of medication in the bloodstream divided by the number of hours since noon should always produce a constant value. They do not: 90 divided by 1 = 90; 81 divided by 2 = 40.5. Incorrect Response: D. One characteristic of a quadratic function is the difference between two uniformly spaced values will change in a linear pattern. Consider the differences in the pattern below. 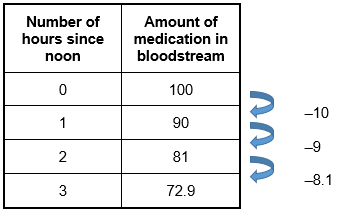 A table with 2 columns and 5 rows. Column 1 head Number of hours since noon. Column 2 head amount of medication in bloodstream. Column 1 row 2 0 column 2 row 2 100. Column 1 row 3 1 column 2 row 3 90. Column 1 row 4 2 column 2 row 4 81. Column 1 row 5 3 column 2 row 5 72.9. Arrows to the right of the table show that data in column 2 changes by minus 10 after the first hour, minus 9 after the second hour, and minus 8.1 after the third hour.
A table with 2 columns and 5 rows. Column 1 head Number of hours since noon. Column 2 head amount of medication in bloodstream. Column 1 row 2 0 column 2 row 2 100. Column 1 row 3 1 column 2 row 3 90. Column 1 row 4 2 column 2 row 4 81. Column 1 row 5 3 column 2 row 5 72.9. Arrows to the right of the table show that data in column 2 changes by minus 10 after the first hour, minus 9 after the second hour, and minus 8.1 after the third hour.
The first difference changes from negative 10 to negative 9 . If this were a linear pattern, the next value should be negative 8, but it is negative 8.1. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 17 | D |
Objective 004 Correct Response: D. The width of the base of the monument can be represented by 12 minus 4x, since 2x is needed for both the top and bottom sections of the stone path surrounding the base. The length can be represented by 20 minus 2x, since x is needed for both the left and right sections of the stone path. The area of the base of the monument is the quantity 12 minus 4 X times the quantity 20 minus 2 X equals 240 minus 24 X minus eighty X plus 8 X squared equals eight x squared minus 104 X plus 240 = 8 times the quantity X squared minus 13 X plus 30. Incorrect Response: A. This expression represents an expansion of the quantity 20 minus 2 X times the quantity 12 minus X. This is the result of halving the width of the path rather than doubling it to account for the two pairs of sides. Incorrect Response: B. This expression follows from the quantity 20 minus X times the quantity 12 minus 2 X. This does not account for the path having two pairs of sides. Incorrect Response: C. This expression represents an expansion of the quantity 20 minus 4 X times the quantity 12 minus 2 X. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 18 | C |
Objective 004 Correct Response: C. Three liters of a 3% acid solution contains 0 point 0 9 liters of acid. The ratio 0 point 0 9 divided by 3 compares the volume of acid to the total volume of this solution. When x liters of 15% acid solution are added to it, the ratio changes to the quantity 0 point 0 9 plus 0 point 1 5 X all divided by 3 plus X. This ratio equals 0 point 1 2 when the correct amount of acid is added: the quantity 0 point 0 9 plus 0 point 1 5 X all divided by 3 plus X equals 0 point 1 2. Apply the distributive property to obtain 0 point 1 5 x plus 0 point 0 9 equals 0 point 1 2 x plus 0 point 3 6. Incorrect Response: A. The equation 0 point 0 9 x plus 0 point 1 5 equals 0 point 1 2 x has several errors. First, the quantity of 15% acid solution is fixed to 1 liter. To this, x liters of 9% acid is mixed in. The situation modeled by this equation answers a different question: "When is the total amount of acid in 1 liter of 15% acid solution and x liters of 9% acid solution the same as x liters of 12% acid solution?" Incorrect Response: B. The equation 0 point 1 5 x plus 0 point 0 9 equals 0 point 1 2 x plus 3 could be the result of incorrectly applying the distributive property to the quantity 0 point 0 9 plus 0 point 1 5 X all divided by 3 plus X equals 0 point 1 2. Incorrect Response: D. As with incorrect response A, this response can be eliminated because the term 0 point 0 9 x would represent adding 9% acid solution to the mixture. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 19 | D |
Objective 004 Correct Response: D. The solution set for the inequality can be found as follows: Original problem: negative 2 thirds times the quantity 3 m minus 2 is less than one half the quantity m plus 1 Apply the distributive property: negative 2 m plus 4 thirds is less than one half m plus 1 half Apply the addition property of inequalities: negative 2 m minus 1 half m is less than one half minus 4 thirds Simplify: negative 5 halves m is less than negative 5 sixths Apply the multiplicative property of inequalities: m is greater than negative 5 sixths times negative 2 fifths Simplify: m is greater than 1 third The graph should have an open circle at 1 third and shading to the right of 1 third. Graph D shows the solution set for the inequality. Incorrect Response: A. One fast way to eliminate this response is by testing a point in the proposed solution set to see whether it satisfies the original inequality. Substituting the point m = negative1 results in the inequality negative 2 thirds times the quantity 3 times negative 1 minus 2 is less than one half times the quantity negative 1 plus 1 implies 10 thirds is less than 0. This is a false statement, so this answer should be eliminated. Incorrect Response: B. One fast way to eliminate this response is by testing a point in the proposed solution set to see whether it satisfies the original inequality. Substituting the point m = 0 results in the inequality negative 2 thirds times the quantity 3 times 0 minus 2 is less than one half times the quantity 0 plus 1 implies 4 thirds is less than one half. This is a false statement, so this answer should be eliminated. Incorrect Response: C. This response could indicate a misconception with the multiplication property of inequalities. Following the steps from the correct response, Original problem: negative 2 thirds times the quantity 3 m minus 2 is less than one half the quantity m plus 1 Apply the distributive property: negative 2 m plus 4 thirds is less than one half m plus 1 half Apply the addition property of inequalities: negative 2 m minus 1 half m is less than one half minus 4 thirds Simplify: negative 5 halves m is less than negative 5 sixths The next step is to multiply both sides of the inequality by negative 2 fifths, so the direction of the inequality must be reversed. The graph in the response could indicate that this change was not applied. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 20 | A |
Objective 005 Correct Response: A. The middle graph shows that can C weighs less than can B, and the left graph shows that can B weighs less than can A. Therefore, can C weighs the least. Incorrect Response: B. The left graph shows that cans A and B do not have the same height. Incorrect Response: C. The middle graph shows that can C is more expensive than can B. Incorrect Response: D. The right graph shows that can C is taller than can A. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 21 | D |
Objective 005 Correct Response: D. The graph of the function f of x plus 5 represents the horizontal translation of the graph of function f of x b units to the left. The function g of x = function f of x plus 5 has a graph that is identical in shape to that of function f of x but is shifted to the left by 5 units. Incorrect Response: A. This response may indicate a misconception in the direction of a shift. If function f of x minus 5 were incorrectly interpreted to mean an upward shift of function f of x by 5 units, then the quantity x plus 5 squared could be interpreted to mean that x squared was shifted down by 5 units. Incorrect Response: B. This response may indicate a misconception in the direction of a shift. Interpreting function f of x plus 5 to mean a shift of function f of x to the right by 5 units would lead to this result. Incorrect Response: C. This response may indicate a misconception either in the direction of a shift or with the order of operations. Subtracting function g of x minus 5 gives the quantity x plus 5 squared minus 5 equals x squared plus 10 x plus 25 minus 5 equals x squared plus 10 x plus 20. This is not equal to function f of x. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 22 | A |
Objective 005 Correct Response: A. The slope of each segment indicates the speed of the car in that segment. The car initially moves quickly and then slows down, speeds up, and slows down again. This is consistent with the description that the car began on the highway, slowed down in traffic, returned to highway speeds, and then slowed down on local roads. The constant slope back to the horizontal axis represents the steady rate home on local roads. Incorrect Response: B. This response shows the distance from home always increases over time. However, the information states that the car returned home. A correct graph must show the car has 0 distance from home at the end of its journey. Incorrect Response: C. This response shows the car returns home from its destination instantly. This is not what happened. Incorrect Response: D. This response is similar to that of response B in that it shows the distance from home always increasing over time; however, the information states that the car returned home. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 23 | D |
Objective 006 Correct Response: D. The ratio of number of students over number of teachers equals x over y equals 20 over 3, so 3 x equals 20 y or y equals 3 twentieths x. The graph of y equals 3 twentieths x is a line through the origin with slope equal to 3 twentieths. Graph D goes through (0, 0) and (100, 15) and has a slope of 15 hundredths equals 3 twentieths. Incorrect Response: A. This graph indicates that 12 teachers on a field trip would chaperone 0 students and that 80 students on a field trip would have 0 chaperones. This is not consistent with the situation. Incorrect Response: B. This graph indicates that 60 teachers on a field trip would chaperone 0 students and that 9 students on a field trip would have 0 chaperones. This is not consistent with the situation. Incorrect Response: C. This graph indicates that 200 teachers would chaperone 30 students, which is likely the result of interpreting the y-values to represent the number of students and the x-values to represent the number of teachers. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 24 | C |
Objective 006 Correct Response: C. Line L moves from negative 2, k plus 8 to 2, k by moving down by 8 units and right by 4 units. Therefore, the slope of the line is negative 2. The x-intercept of the line occurs where the value of the y-coordinate is 0. If the line starts from the point negative 2, k plus 8, then it reaches its x-intercept by moving down by k plus 8 and to the right by half this distance. Its final position is negative 2 plus 1 half k plus 8, and this expression is equivalent to 1 half the quantity k plus 4. Incorrect Response: A. This expression represents the location of the y-intercept. The line moves 2 units to the right and 4 units down from the point negative 2, k plus 8 to reach its y-intercept of 0, k plus 4. Incorrect Response: B. This expression may be the result of the reasoning described in the rationale for response A along with a sign error. Incorrect Response: D. This expression may be the result of the reasoning described in the rationale for response C along with a sign error. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 25 | C |
Objective 006 Correct Response: C. The slopes of parallel lines are equal. The slope of 3 x plus a y equals b can be found by solving the equation for y in terms of x: 3 x plus a y equals b implies a y equals negative 3 x plus b implies y equals negative 3 over a times x plus b over a. Using point-slope form, y minus y 1 equals m times the quantity x minus x 1, slope m = negative 3 over A and point X 1, y 1 equals negative 4, 0 yields y equals negative 3 over a times the quantity x plus 4 for the equation of line p. Incorrect Response: A. The slope of a line written in the standard form A x plus b y equals c is negative A over b. This response could be the result of calculating the slope of the first equation as A divided by b. Incorrect Response: B. This could be the result of combining the error described in response A and by misapplying the distributive property. Incorrect Response: D. This could be the result of a distributive property error while applying the point-slope equation. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 26 | B |
Objective 006 Correct Response: B. A family of lines is a set of lines that have something in common with each other. The set of lines shown in the graph all contain the point (2, negative 3). The point-slope form of a linear equation is y minus y 1 equals m times the quantity x minus x 1, where m is the slope of the line and x 1, y 1 is a point on the line. In this case, the slope of the lines is the parameter k, and the point is (2, negative 3). The equation for the family of lines is y minus negative 3 equals k times the quantity x minus 2, or y plus 3 equals k times the quantity x minus 2. Incorrect Response: A. The equation y plus 3 equals k x minus 2 can be rearranged as y equals k x minus 5. If this were true, then by the point-slope formula, the common point of intersection for the lines would be located at (0, negative 5). Incorrect Response: C. The equation y equals k x plus 2 minus 3 simplifies as y plus 1 equals k x. If this were true, then the common point of intersection for the lines would be located at (0, negative 1). Incorrect Response: D. The equation y equals k times the quantity x plus 2 minus 3 can be rearranged as y plus 3 equals k times the quantity x plus 2. If this were true, then the common point of intersection for the lines would be located at (negative 2, negative 3). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 27 | A |
Objective 007 Correct Response: A. Let x represent the length of one side of the square pen and x squared the area of the pen. Increasing the length of one side by 4 meters and the other side by 2 meters creates a rectangle with length x plus 4 and width x plus 2. The new area, x plus 4 times x plus 2, is three times the old area, 3 x squared. Solving the equation x plus 4 times x plus 2 equals 3 x squared will yield the value of x. First, distribute to multiply the binomials: x squared plus 4 x plus 2 x plus 8 equals 3 x squared. Then combine like terms and use the addition property of equality to set the equation equal to 0: 2 x squared minus 6 x minus 8 equals 0. Use the multiplication property of equality to simplify the equation by a factor of 2: x squared minus 3 x minus 4 equals 0. Incorrect Response: B. This equation represents the expansion of x plus 4 times x plus 2 equals 0. The area of the rectangular pen is not zero. Incorrect Response: C. This equation may represent the sum of the new and expanded pens: x squared plus the quantity x plus 4 times the quantity x plus 2 equals 0. Incorrect Response: D. This equation may come from the equation 2 x plus 4 equals 3 x squared. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 28 | A |
Objective 007 Correct Response: A. Substitute c, representing the y-intercept, into the equation to get y equals x squared plus b x minus 36. The information given states that (3, 0) is also a point. Substitute this into the equation to determine the unknown value of b: 0 equals 3 squared plus b times 3 minus 36 implies 3 b equals 27 implies b equals 9. Obtain the other root by factoring the y equals x squared plus 9 x minus 36 as y equals the quantity x minus 3 times the quantity x plus 12. The other root is located at (negative 12, 0). Incorrect Response: B. A sign error, such as one developed from substituting c = 36 into the equation could lead to this response. For example, 0 equals 3 squared plus b times 3 plus 36 implies 3 b equals negative 27 implies b equals negative 9. Incorrect Response: C. This response could represent the value obtained for bx when (3, 0) is substituted into the equation y equals x squared plus b x minus 36: 0 equals 3 squared plus 3 times 3 minus 36. Incorrect Response: D. A sign error, such as one developed from factoring y equals x squared plus 9 x minus 36 as y equals the quantity x plus 3 times the quantity x minus 12 could lead to this response. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 29 | C |
Objective 008 Correct Response: C. The base of the cone is a circle. The net of the lateral surface of a cone is represented as a 60 degrees sector of a circle 10 centimeters in radius. It follows that the curved edge of the cone has a length of 1 sixth times 2 pi times 10 equals 10 pi divided by 3. This distance fully wraps around the circle at the base. To find the radius of that circle, set its circumference equal to the length of the curved edge of the lateral side and solve for r: 10 pi divided by 3 equals 2 pi r implies r equals 10 sixths which equals 5 thirds. The area of the circle is then pi times 5 thirds squared equals 25 ninths pi. Incorrect Response: A. This answer is the result of not applying the square to both the numerator and the denominator in the final step of the solution shown for response C. Incorrect Response: B. This response is the result of misinterpreting the radius of the circle to be 5 sixths, and then applying the power of 2 only to the numerator in the final step of the solution process shown for response C. Incorrect Response: D. Making an error when solving for r in the solution shown for response C could lead to r = 5 sixths, which results in an answer of 25 pi divided by 36. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 30 | A |
Objective 008 Correct Response: A. The ratio for the smaller cube is surface area divided by volume equals 6 x squared divided by x cubed. The ratio for the larger cube is surface area divided by volume equals 6 times 4 x squared divided by 4x cubed equals 16 times 6 x squared divided by 64 x cubed equals 1 fourth times 6x squared divided by x cubed. In general, scaling the linear dimensions of a shape by k increases its surface area by a factor of k squared and its volume by a factor of k cubed. The ratio of these two values is k. Incorrect Response: B. This response may indicate a misconception with the relationship between a linear dimension of a shape and its surface area and volume. Incorrect Response: C. This response may indicate a misconception with the relationship between a linear dimension of a shape and its surface area and volume. Incorrect Response: D. This response represents the reciprocal of the correct ratio. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 31 | D |
Objective 008 Correct Response: D. When limited to a precision of 2 decimal places, the maximum overestimation possible in the edge of a cube is 10.49 inches. This leads to a maximum error in volume of 10 point 49 cubed minus 10 cubed. Incorrect Response: A. This represents the cube of the difference between the two side lengths. This does not represent the difference in the volumes of the two cubes. Incorrect Response: B. At a precision of 0.01 inches, the greatest overestimate for the volume occurs when using 10 inches for a cube that has a true edge length of 9.5 inches and the greatest underestimate when the true edge length is 10.49 inches. In both cases, the error is relative to using the rounded value of 10 inches and not to each other. This misconception is further compounded with reasoning described in the rationale for response A. Incorrect Response: C. A cube with an edge length of 9.5 inches is the smallest cube that would round up to an edge length of 10 inches. A cube of 9.4 inches would round to 9 inches, not 10, and so this calculation does not apply to this situation. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 32 | A |
Objective 009 Correct Response: A. When solving geometric proofs, one can assume that points that appear to be collinear in a diagram are collinear. Thus, the assumption that can be made regarding the figure shown is that point A is on segment D C. Incorrect Response: B. This is true if triangle A B C is equilateral, but there is no evidence in the diagram to support this claim. Incorrect Response: C. There is no information provided in the diagram that supports that segment B D is perpendicular to segment A C. Incorrect Response: D. There is no evidence to support this, such as congruency between alternate interior angles, in the image provided. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 33 | D |
Objective 009 Correct Response: D. Consider the following diagram. 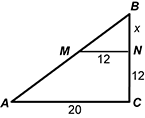 Right triangle A b c with line segment m n intersecting the vertical side and the opposite side to create a smaller triangle m b n. Side a c is 20, m n is 12, c n is 12, and n b is x.
Right triangle A b c with line segment m n intersecting the vertical side and the opposite side to create a smaller triangle m b n. Side a c is 20, m n is 12, c n is 12, and n b is x.
Triangles A B C and M B N are similar by the triangle proportionality theorem (i.e., the corresponding sides are parallel because M N is parallel to A C and intersects the sides of triangle A B C). This establishes the proportion x over 12 equals x plus 12 over 20 and the equation 12 times the quantity x plus 12 equals 20 x. Determine x from the equation 12 x plus 144 equals 20 x implies 8 x equals 144 implies x equals 18. The length of side segment C B is 18 plus 12 = 30. Incorrect Response: A. This response may represent a misconception about similarity. If the triangles were considered to be related by subtraction, then 20 minus 12 = 8 and 12 minus 8 = 4; segment C N = 12 + 4. However, similar triangles are related by multiplicative scale factors and not the subtraction shown here. Incorrect Response: B. This represents the length of segment N B. It must be added to the length of segment C N to obtain the length of segment C B. Incorrect Response: C. This response may be based on an incorrect claim that segment A C and segment C B are congruent. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 34 | A |
Objective 009 Correct Response: A. Using the diagram and the information given about the diagram, the following can be proven: 2 columns and 8 rows
The statement that is a true deduction based on the given information is segment D X is congruent to segment B X. Incorrect Response: B. Kite A B C D could satisfy the given information, which would mean that it is not necessarily true that both diagonals are perpendicular bisectors of each other. This means that segment A X does not have to be congruent to segment C X. Incorrect Response: C. This statement is only true when A B C D is a square. Since a square is not the only shape to satisfy the given criteria, this statement is not necessarily true. Incorrect Response: D. This statement is only true when segment A D is parallel to segment B C. If the figure is a kite, then these segments are not parallel. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 35 | C |
Objective 010 Correct Response: C. The section marked D in the Venn diagram represents the quadrilaterals that have diagonals that are perpendicular bisectors of each other but are not congruent. A rhombus has perpendicular diagonals that bisect each other. Incorrect Response: A. The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular, but only one diagonal must be bisected. Incorrect Response: B. The diagonals of a rectangle are congruent, but not necessarily perpendicular. Incorrect Response: D. The diagonals of a parallelogram are not necessarily perpendicular. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 36 | B |
Objective 010 Correct Response: B. The volume of the cube is v equals 2 r cubed equals 8 r cubed equals 64 cubic inches. Divide 8 r cubed equals 64 by 8 to obtain r cubed equals 8. The value of r is the cube root of 8, which is 2. This is the radius of the sphere, which has a volume of v equals 4 thirds pi r cubed equals 4 thirds pi times 2 cubed equals 32 pi over 3. The value of π is little more than the value of 3pi divided by 3 is approximately 1.04, so the approximation of the volume as 33 cubic inches is reasonable. Incorrect Response: A. This response is the result of using the reciprocal of 4 thirds in the calculation for the volume of the sphere: v equals 3 fourths times pi times 2 cubed equals 6 pi which is approximately 19. Incorrect Response: C. This could be obtained by overestimating the value of pi over 3 in the equation. Incorrect Response: D. Using 4 pi r squared for volume gives 4 pi times 2 squared equals 16 pi, which is approximately equal to this answer. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 37 | B |
Objective 010 Correct Response: B. The top section of the rotated figure will be a hemisphere with radius z. The volume of the hemisphere is 1 half times 4 thirds times pi times z cubed equals 2 thirds pi times z cubed. The bottom section of the solid will be a cylinder with radius z and height 2 z. The volume of the cylinder is pi times z squared times 2 z equals 2 pi z cubed. The volume of the rotated figure is 2 thirds times pi times z cubed plus 2 pi z cubed equals 2 thirds pi z cubed plus 6 thirds pi z cubed equals 8 pi z cubed over 3. Incorrect Response: A. This is the result of quartering the volume of the hemisphere instead of halving it. This leads to a volume for the hemisphere of 1 third times pi times z cubed, which results in a total volume calculation of 1 third pi z cubed plus 2 pi z cubed equals 7 pi z cubed divided by 3. Incorrect Response: C. Forgetting to multiply the formula for the volume of a sphere by 1 half will result in the calculation of 4 thirds times pi times z cubed for the volume of the hemisphere, which leads to the result 4 thirds pi z cubed plus 2 pi z cubed equals 10 pi z cubed divided by 3. Incorrect Response: D. If the 1 half is removed from the volume calculation for the hemisphere, and the radius of the hemisphere is interpreted to be 2 z, then the volume of the hemisphere is calculated as 8 thirds times pi times z cubed. This will result in the total volume calculation of 8 thirds pi z cubed plus 2 pi z cubed equals 14 pi z cubed divided by 3. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 38 | D |
Objective 011 Correct Response: D. A circle that circumscribes a triangle has a center at the intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle. The slope of side segment A B is 8 minus 4 over 8 minus 0 equals one half, making the slope of a perpendicular line to segment A B = negative 2. The midpoint of segment A B equals 8 plus 0 over 2, 8 plus 4 over 2 equals the point 4 6. The equation of the perpendicular bisector of segment A B is y equals negative 2 x plus 14. The slope of side segment B C is 0 minus 4 over 2 minus 0 equals negative 2, making the slope of a perpendicular line to segment B C = 1 half. The midpoint of segment B C equals 2 plus 0 over 2, 0 plus 4 over 2 equals the point 1 2. The equation of the perpendicular bisector of segment B C is y equals 1 half x plus 1 point 5. The intersection of the perpendicular bisectors can be found by solving negative 2 x plus 14 equals 1 half x plus 1 point 5 implies 2 point 5 x equals 12 point 5 x implies x equals 5 and y equals negative 2 times 5 plus 14 equals 4. The radius of the circle is the distance from (5, 4) to one of the vertices of the triangle. Using the vertex (0, 4), r equals the square root of the quantity 5 minus 0 squared plus 4 minus 4 squared equals 5 and the area of the circle is 5 squared times pi equals 25 pi. Incorrect Response: A. This may be the result of interpreting B C to be the diameter of the circle: B C equals the square root of the quantity 4 minus 0 squared plus the quantity 0 minus 2 squared equals radical 20 equals 2 times radical 5. If this is the diameter of the circle, then the area is interpreted as pi times d over 2 squared equals pi times radical 5 squared equals 5 pi. Incorrect Response: B. This answer may be the result of finding the circumference of the circle instead of the area. Incorrect Response: C. This response may be the result of interpreting the segment A B to be the diameter of the circle: A B equals the square root of the quantity 8 minus 0 squared plus the quantity 8 minus 4 squared equals radical 80 equals 4 times radical 5. If this is assumed to be the diameter of the circle, then the area is interpreted as pi times d over 2 squared equals pi times 2 radical 5 squared equals 20 pi. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 39 | C |
Objective 011 Correct Response: C. Consider the median from point A to side B C: The midpoint of B C is 14 plus 4 over 2, 0 plus 12 over 2 equals the point 9 6. Since point A is the origin, the median from A to B C is included in the line 4 equals 2 thirds x implies x equals 6. The center of mass (the intersection of the medians) must be a point on this line. Using substitution with y equals 4 (from the information given in the problem): 4 equals 2 thirds x implies x equals 6. Incorrect Response: A. This response may stem from writing the equation of the line as y equals 9 sixths x then substituting y equals 4 to get x equals 8 thirds. Incorrect Response: B. This response may be the result of using a y-coordinate of 5 instead of 4 in the equation y equals 3 halves x. Incorrect Response: D. This response may be the result of the misconception that the center of mass must be a point on the line x equals 7, since that line is the perpendicular bisector of side A B. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 40 | A |
Objective 011 Correct Response: A. D E equals 2 since E is the midpoint of segment D C. G F equals 2 and angle A G F is a right angle since it is supplemental to angle D G F, which is right for rectangles. segment A F must be the hypotenuse of triangle A G F since it is opposite the right angle, which makes A G equals 2 since it is the other leg in isosceles triangle A G F. A is given as (1, 1), therefore G is (1, 3) and D G equals 5, so the area of the rectangle is 2 times 5 equals 10. Incorrect Response: B. This response may be the result of interpreting point G to be located at (1, 2), which would lead to an area of 2 times 6 for the rectangle. Incorrect Response: C. This answer may be the result of misinterpreting height of the rectangle to be 7 by comparing the y-values between points A and D. Incorrect Response: D. This response may be the result of calculating the area of trapezoid A B C D: 1 half times the quantity 7 plus 3 times 4 equals 20. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 41 | C |
Objective 012 Correct Response: C. A bar graph is most appropriate for this situation because the data are comparing a single measure, the total sales, across six different brands. The total sales for each individual brand could be represented by the height of a bar, and the display would allow for easy visual comparisons of the total sales between each brand. Incorrect Response: A. The most appropriate display for this set of data would be a circle graph or pie chart, since the goal is to show the percentages as parts of a whole. Incorrect Response: B. The most appropriate display for this data set would be a scatter plot. This display would make it easiest to make observations about correlation between the variables. Incorrect Response: D. The most appropriate display to show the change in a single variable over time is a line graph, so a bar graph is less appropriate for this situation than for the situation in response C. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 42 | A |
Objective 012 Correct Response: A. The scores for the three seasons can be converted to a list: 7, 7, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 13, 14, 14, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 22, 25, 25, 28, 28, 29, 29, 32, 35, 35, 38, 40, 42, 42, 44 The median is the center value when the data set is ordered, which falls between 20 and 22 in this set, so the median is 21. The interquartile range is the difference between the first and third quartile. The first quartile, Q 1, is the median for the lower half of the data, and the third quartile, Q 3, is the median for the upper half of the data. Q 1 equals 13, Q 3 equals 32, so the interquartile range is the difference between those values, 32 minus 13 equals 19. Incorrect Response: B. This answer may be the result of miscalculating the median as 23, perhaps identifying the median between 22 and 25 and rounding or if copying the data into a list, making a copying error. Incorrect Response: C. This answer may be the result of misinterpreting the interquartile range as the range. The interquartile range is the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile, but the range is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value, in this case, 44 minus 7 equals 37. Incorrect Response: D. This answer may be the result of both errors from responses B and C. The median was determined incorrectly, and the interquartile range was misinterpreted for the range in this response. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 43 | C |
Objective 012 Correct Response: C. The median for the data set is 4, and it remains 4 after 15 is added to the data set at the far right. (Generally, the median is less affected by outliers than the mean.) Incorrect Response: A. The maximum changes from 8 to 15 once the value of 15 is included in the data set. The difference between those values is 7, which represents a more significant change than either the mean or the median. Incorrect Response: B. The mean for the original data set is the sum of all values in the data set divided by 15 equals 52 over 15 which is approximately 3 point 5. After the inclusion of 15, the mean is the sum of all values in the data set plus 15 divided by 16 equals 67 over 16 which is approximately 4 point 2. (Generally, outliers influence the mean more than the median.) Incorrect Response: D. The range for the original data set is 8 (8 minus 0), and it becomes 15 (15 minus 0) once the value of 15 is included in the data set. The change in the range is 7, which is greater than the change in the median and the mean. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 44 | A |
Objective 012 Correct Response: A. For a normal distribution, the data are symmetrical about the mean with approximately 68% of the data existing within one standard deviation from the mean, 95% of the data existing within two standard deviations from the mean, and approximately 99% of the data existing within 3 standard deviations from the mean. The situation in the question is referring to the data that are greater than 1 standard deviation from the mean. Using the symmetry and percentage descriptions from a normal distribution, this implies that approximately 16% of the students have heights that fall in this range: 0 point 1 6 times 50,000 equals 8,000. Incorrect Response: B. This answer could have come from misinterpreting the meaning of 68% of data existing within one standard deviation of the mean and incidentally summing the percentages at both ends of the normal distribution. This number represents the number of students with heights that are at least 173 centimeters and the number of students with heights that are no greater than 163 centimeters: 0 point 1 6 times 2 times 50,000 equals 0 point 3 2 times 50,000. Incorrect Response: C. This value represents the number of students who are within 1 standard deviation from the mean. These students have heights between 163 centimeters and 173 centimeters: 0 point 6 8 times 50,000 equals 34,000. Incorrect Response: D. This response likely stems from a misinterpretation of the data that are specified in the question. This value represents the number of students who are no taller than 173 centimeters. It is the complement of the data set from what is specified in the question: 0 point 8 4 times 50,000 equals 42,000. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 45 | C |
Objective 012 Correct Response: C. Without knowing the demographics of the communications collected, this is a potential concern that could misrepresent the constituency. There is not enough information provided to know that the sample is random, so there is no way to guarantee that it is representative of the entire constituency. (The bias that can exist in a survey where the participants are volunteers is the same source of bias that may exist in this context.) Incorrect Response: A. Generally, a larger sample is a better representation than a smaller sample, but only if the sample is random. There is no guarantee that the sample is random in this situation, so the results may be disproportionately impacted by a specific group, which could make the data an invalid representation of all constituents. Incorrect Response: B. Even though access promotes broad participation, it does not ensure that an ideologically diverse group of people exercise the right to vote. The constituents who did vote may have been part of a specific, highly motivated group, which could have skewed the data. Access does not ensure that the sample is random. Incorrect Response: D. The outcome of the bill should be the result of the opinions of the constituents, so this is not an accurate assessment of potential bias in the results. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 46 | C |
Objective 013 Correct Response: C. The data can be represented with a Venn diagram, where C = the set of students who saw the comedy movie and A = the set of students who saw the animated movie. The intersection of both sets, which is the percentage of students who saw both movies, is 14%. 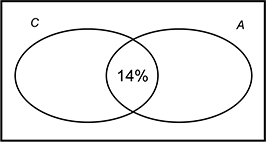 A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled as 14 percent.
A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled as 14 percent.
Since 55% of students saw the comedy movie, and this includes the 14% who saw both, then 55 minus 14 or 41% of students saw only the comedy movie. Likewise, the 28% of students who saw the animated movie includes the 14% who saw both. So, 28 minus 14 or 14% saw only the animated movie. 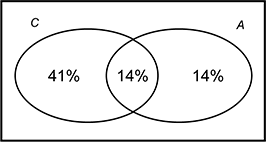 A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled 14 percent, the region that represents only C is labeled 41 percent, and the region that represents only A is labeled as 14 percent.
A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled 14 percent, the region that represents only C is labeled 41 percent, and the region that represents only A is labeled as 14 percent.
Since the Venn Diagram includes 100% of the students, the percent of students who saw neither movie must be 100 minus the sum of the percentages within the sets or 100 minus the quantity 41 plus 14 plus 14 equals 100 minus 69 equals 31. 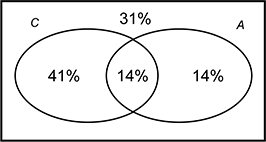 A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled 14 percent, the region that represents only C is labeled 41 percent, and the region that represents only A is labeled as 14 percent. The region outside of both circles is labeled as 31 percent.
A venn diagram with circles labeled C and A that are partially overlapping. The overlapping region is labeled 14 percent, the region that represents only C is labeled 41 percent, and the region that represents only A is labeled as 14 percent. The region outside of both circles is labeled as 31 percent.
Incorrect Response: A. This response may be the result of adding the 55% and 28% in the question without considering how the overlap affects those percentages. Then, 100 minus 87 produces 13%. Incorrect Response: B. This response may be the difference between the percentage of students who saw neither movie and the percentage of students who saw both movies, or 31 minus 14 equals 17 percent. Incorrect Response: D. This response is the percentage of students who saw only the comedy movie. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 47 | B |
Objective 013 Correct Response: B. Probabilities can be assigned to each of the first three branches of the tree diagram using the fact that there are 12 markers total in the box. Information regarding what fraction of each marker is dry can be used to assign probabilities to the second set of branches. 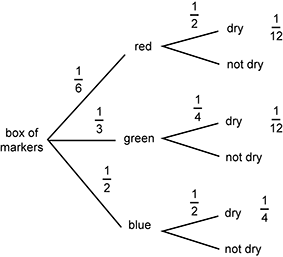 The tree diagram is shown from the question with probabilities labeling the branches. On the first level, red, green, and blue are labeled 1 sixth, 1 third, and 1 half, respectively. On the second level. Which represents dry or not dry for each color, the probabilities are as follows:
The tree diagram is shown from the question with probabilities labeling the branches. On the first level, red, green, and blue are labeled 1 sixth, 1 third, and 1 half, respectively. On the second level. Which represents dry or not dry for each color, the probabilities are as follows:
Red dry 1 half Green dry 1 fourth Blue dry 1 half To the right of each pair of branches at the final level of the diagram are the following probabilities: 1 twelfth, 1 twelfth, 1 fourth. The product of the probabilities along the branches in each path shows the probability that a given marker meets both criteria (e.g., is green and dry = 1 twelfth). To find the probability that a randomly selected marker is dry, we must add the probabilities for each path that represents a dry marker. The sum of the possibilities for drawing a dry red, dry green, or dry blue marker is 1 twelfth plus 1 twelfth plus 1 fourth equals 5 twelfths. Incorrect Response: A. This result could be due to a misinterpretation of the meaning of the first three branches in the tree diagram. Incorrect Response: C. This result could be a misinterpretation of the probability specified in the question. This is the probability that a randomly selected marker will be blue. Incorrect Response: D. This result could be a calculation of the complement for the probability specified in the question. This is the probability that a randomly selected marker is not dry. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 48 | A |
Objective 013 Correct Response: A. The probability of selecting the first red number cube from the bag is 2 thirds, and the probability of selecting a second red number cube is 1 half, since the number cubes are drawn without replacement. The probability of selecting two red number cubes from the bag is then 2 thirds times 1 half equals 1 third. Once the two red number cubes are selected, there are 2 possible ways to roll a resulting sum of 3: (1, 2) or (2, 1). There are 6 times 6 or 36 total possibilities for rolling two number cubes, so the probability of rolling a sum of 3 is 2 thirty-sixths equals 1 eighteenth. The probability of selecting two red dice and rolling a sum of three is 1 third times 1 eighteenth equals 1 fifty-fourth. Incorrect Response: B. This answer may be the result of interpreting the probability of choosing two red number cubes as 1 half, and correctly calculating the probability of rolling a sum of three. This would lead to calculating the probability of selecting two red number cubes and rolling a sum of three as 1 half times 2 thirty-sixths equals 1 thirty-sixth. Incorrect Response: C. This answer may be the result of errors related to the formation of the sample space, or it may be the result of incorrectly adding probabilities for different events in the problem. Incorrect Response: D. This answer may be the result of calculating the probability of rolling a sum of 3 on two number cubes without considering the probability that the two chosen number cubes are red 2 thirty-sixths equals 1 eighteenth. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 49 | C |
Objective 013 Correct Response: C. If we define the number of green grapes originally in the bag to be x, then the number of green grapes in the bag after 5 are removed is equal to x minus 5 and the total number of grapes in the bag is x minus 5 plus 25 equals x plus 20. We can then say that x minus 5 divided by x plus 20 is less than 0.25 implies x minus 5 is less than 0.25 times the quantity x plus 20 implies x minus 5 is less than 0.25 x plus 5 implies 0.75 x is less than 10 implies that x is less than 13 point 3 repeating. Since x must be less than 13 point 3 repeating, and we are assuming there are only whole grapes in the bag, the greatest number of green grapes possible at the start is 13. This means that there could have been as many as 13 plus 25 equals 38 grapes in the bag originally. Incorrect Response: A. This response is the result of finding the correct answer, 38, but then adding the value of 5 back to it. The solution process outlined in the correct response finds the total number of grapes before 5 are removed, so adding 5 to that value is unnecessary. Incorrect Response: B. The same solution process from the correct response is used, but the result is rounded up to the nearest whole value, which could lead to the answer of 14 plus 25 or 39. Incorrect Response: D. This may be the result of solving the original inequality, which leads to an answer of x is less than 6 point 6 repeating, which could lead to the answer 25 plus 6 equals 31. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 50 | B |
Objective 013 Correct Response: B. There is a one-to-one correspondence between the sample spaces for the range of numbers from 1through 26 and the set of letters from Ato Z . This simulation samples from each set in the same manner, and each of the 100 sets can be easily compared to the criteria to check for at least one vowel. Incorrect Response: A. The question does not specify that each of the random five letter samplings must be words, so this simulation does not accurately describe the scenario. Incorrect Response: C. This simulation assumes that there is an equal probability of choosing a vowel or a consonant when randomly choosing a letter of the alphabet, which is not true. Incorrect Response: D. The simulation described does not allow for the repetition of letters within a five-letter sample, which is not consistent with the scenario in the question. Additionally, the simulation involves drawing samples until "only one vowel" is drawn, rather than at least one vowel. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 51 | A |
Objective 014 Shape and dimensions of the levee (Correct Response A) will affect how it functions in preventing flooding. On the other hand, cost (Incorrect Response B) and transportation (Incorrect Response C) of the materials have a smaller effect on the levees' ability to be breached, compared to its design and components. The devices' ability to support vehicles on the adjacent road (Incorrect Response D) is an important factor to consider; however, this question focuses more on problems that may arise from the effects of vehicles than how the levee will function to prevent flooding in the area. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 52 | C |
Objective 014 Since the warning system has already been developed, the modeling and testing of prototypes (Correct Response C) must be the next step in the engineering design process. Defining the problem (Incorrect Response A), brainstorming a solution (Incorrect Response B), and researching criteria and constraints (Incorrect Response D) are steps that occur before the development of a prototype; therefore, they are not considered during the finalization part of this process. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 53 | B |
Objective 014 The first action to take when evaluating a bridge design is calculating the necessary strength of the components based on its extreme load capacity (Correct Response B). The engineer's design must not only be able to withstand everyday traffic but also be prepared for the events of extreme stress that might arise while the bridge is functional, to protect people, property, and infrastructure within the area. Comparing tensile strength (Incorrect Response A) and selecting materials (Incorrect Response C) are parts of the engineering process that generally occur before the evaluation step and primarily occur during either the research or building a prototype stages. Testing to determine if the bridge has the ability to hold a variety of loads (Incorrect Response D) is important and must occur, but not necessarily before evaluation can begin. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 54 | A |
Objective 014 To test the effectiveness of each mechanical arm, the students must determine its maximum capacity. Evaluating the limitations of the different prototypes is the best method for determining which design best achieves the goal of the project (Correct Response A). Calculating the durability of the materials (Incorrect Response B), moving the arm to perform various tasks (Incorrect Response C), and timing how long the arm can hold on to an object (Incorrect Response D) are important components to consider in the overall design. However, these tests focus on either prototype quality or other criteria in relation to functionality without specifically evaluating them against the goal of creating a device that can grasp and lift objects. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 55 | D |
Objective 014 Steel has greater strength and sturdiness (Correct Response D) in comparison to the other materials that are commonly used to construct patio furniture. Even though steel can be resistant to corrosion (Incorrect Response A), other material, such as plastic, can also withstand outdoor conditions. Steel has the capability to be offered in a wide array of shapes and colors (Incorrect Response B), but the other materials can also be painted, tinted, and shaped. Lastly, comfort (Incorrect Response C) is a subjective measure that depends more on the shape of the chair rather than on its composition. Steel and aluminum can be an exception as they often become hot to the touch when left out in the sun. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 56 | B |
Objective 015 Torque is a measure of rotational force. Of the options available, only the wrench (Correct Response B) is primarily used to cause an object to rotate on its axis. A mallet (Incorrect Response A) can be categorized as a third-class lever. In this type of simple machine, the force applied moves in the same direction as the force produced. A block and tackle device (Incorrect Response C) is also a simple machine, but the force applied is in the opposite direction as the force produced. A rivet gun (Incorrect Response D) does not fit easily into the different categories of simple machines, but it functions like the mallet in that the force is linear, not rotational. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 57 | B |
Objective 015 Diamond-dust drill bits are used to drill holes in tile, porcelain, glass, or stone because diamonds are the hardest natural material. Hardness depends on the molecular structure of the material, and diamonds are particularly hard due to their lattice arrangement of carbon atoms double bonded to other carbon atoms (Correct Response B). Other properties, such as friction coefficient (Incorrect Response A), durability (Incorrect Response C), and melting point (Incorrect Response D), are more important to other physical or chemical changes that occur within structures of materials. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 58 | A |
Objective 015 Hot-dip galvanization is an example of conditioning processes in manufacturing (Correct Response A) because the step consists of coating a product in order to improve its characteristics by changing its properties to become more resistant to oxidation and corrosion, compared to primary processes that focus on shaping and sizing a product from raw material. Finishing (Incorrect Response B) is the process of altering the surface of a product, such as cleaning, painting, or removal of defects. Unlike conditioning, the primary focus of this step is appearance or extension of product life during the final stages of completion of the product, rather than modifying its internal properties to a specified criteria of functionality of the final product. Assembling (Incorrect Response C) is the step in the manufacturing process that constructs the parts of the product into a whole unit through various fastening or jointing techniques. And forming (Incorrect Response D) is the process of shaping, bending, or stretching the product into a desired shape and does not add or remove material compared to the galvanization process that occurs in this scenario. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 59 | D |
Objective 015 The fourth line in the table (Correct Response D) best matches the tool with the correct safety procedure because any time a person is handling any type of nail gun the tool needs to be pointing away to prevent accidental discharge. A handheld chisel (Incorrect Response A) is generally constructed out of one or two components. Since this equipment is quite solid, securing loose parts before use is not required. There are no guards on a handheld wrench (Incorrect Response B). Lastly, when using an electrical belt sander (Incorrect Response C) the tool does not need to be sharpened before use because there are no sharp edges. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 60 | D |
Objective 016 The role of embedded electronic microcontrollers (Correct Response D) is to measure the exhaust gasses produced by combustion engines. This information allows the users or mechanics to adjust the engine in order to increase efficiency and reduce emissions. The laws of thermodynamics have not changed in recent years, compared to major advancements in technology (Incorrect Response A). The extraction of fuels (Incorrect Response B) has not changed much or as dramatically in the last 40 years and has no bearing on the efficiency of the engine, as octane fuels are still being used in the combustion process. Any advancement in aerodynamics (Incorrect Response C) primarily effects vehicle efficiency as a whole, rather than the efficiency of an engine that is protected within the vehicle. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 61 | B |
Objective 016 Cell-phone technology relies on radio waves moving through the air to communicate; therefore, it does not require the extensive ground infrastructure (Correct Response B) that landline telephones, which transmit signals through fibers, rely on. Cell phones do have the capability to provide functionality of computers, radios, or television (Incorrect Response A), as well as the ability to transmit text, images, and videos (Incorrect Response C), but these features are not responsible for their spread into previously unconnected regions. The ability to interchange software components (Incorrect Response D) depends on the make and model of the phone and has little relevance to where the cell phone is being used. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 62 | A |
Objective 016 In order for the airlines to determine which flights will be available at particular dates and times, the system needs to know the fleet's passenger capacity (Correct Response A). The system updates each time a seat is taken, allowing the airlines to use this information to chart which dates and times the planes fill the most often and compare that to the destinations that are the most popular. The number of flights to be scheduled in a day (Incorrect Response B) is important for air traffic controllers but does not inform the airlines which planes and routes are highest in demand. Net profits earned each day (Incorrect Response C) and price per seat on a flight (Incorrect Response D) depend upon what the airlines decide to charge. Airlines may consider supply and demand data in their calculations, but it is not a requirement when setting the costs of services and goods. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 63 | A |
Objective 016 A processing device in a technical system is a chip within a computer component, used to understand and perform instructions based on incoming and outgoing data from operational systems or hardware. A microcontroller (Correct Response A) is the processor because it uses the incoming photo data to instruct the device to turn on or stay off within a set amount of time. The power supply (Incorrect Response B) functions to give energy to the system. photo re zis tors (Incorrect Response C) are a component used to affect photo resistance of any input luminosity information. And the lightbulb (Incorrect Response D) is the outgoing component that turns on or off based on the microcontroller; without the connection, the bulb would neither turn on nor stay off by itself. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 64 | B |
Objective 017 The equation used to calculate the orbital velocity of a celestial body revolving around another body is V, for a circular orbit, is equal to 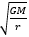 . G is equal to gravitational constant, M is the mass of the body at its center, and r is the radius of its orbit. Therefore, changes to gravitational force and change in radial distance between the two bodies are the best factors used to explain the difference in their orbital velocity (Correct Response B). Changes in density (Incorrect Response A), tilt of orbit (Incorrect Response C), and length of orbital path (Incorrect Response D) have effects on the planets, but they are not used to determine their velocity. . G is equal to gravitational constant, M is the mass of the body at its center, and r is the radius of its orbit. Therefore, changes to gravitational force and change in radial distance between the two bodies are the best factors used to explain the difference in their orbital velocity (Correct Response B). Changes in density (Incorrect Response A), tilt of orbit (Incorrect Response C), and length of orbital path (Incorrect Response D) have effects on the planets, but they are not used to determine their velocity.
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 65 | A |
Objective 017 A total lunar eclipse does not occur every month during the full moon phase because the Moon's orbital plane is tilted at an incline relative to Earth's plane of motion around the Sun (Correct Response A). A lunar eclipse occurs when all the bodies are aligned in the same plane and the Moon enters the shadow cast by the Earth. A lunar eclipse only appears to a viewer on the side of Earth that is currently experiencing night (Incorrect Response B). The distance between the Earth and the Sun has little effect on the probability of an eclipse (Incorrect Response C). Earth is larger than the Moon, so the shadow will completely cover the Moon when they are in the proper alignment (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 66 | D |
Objective 018 The oldest recorded fossils known today are prokaryote microorganisms, similar to bacteria or archaea. Eventually during the Proterozoic eon, eukaryotic cells evolved, leaving fossilized remains. All of these types of organisms lacked the hard body parts (Correct Response D), like bones and shells, that are resistant to decay and are more likely to fossilize. Having a large population size (Incorrect Response A) or body size (Incorrect Response C) can increase the chance of some members leaving behind fossil remnants, but the organisms are much more likely to fossilize if they have structures that more readily mineralize. Particularly during the Proterozoic eon, life on Earth thrived in shallow seas, where fossilization is more likely to occur than on land (Incorrect Response B). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 67 | A |
Objective 018 Growing salt crystals best models the process of chemical sedimentary rock formation. The crystals form as the salt precipitates out of a supersaturated solution, which is a process that is very similar to how inorganic limestones (Correct Response A), such as oolitic limestones, stalactites, and stalagmites, form. Sandstone (Incorrect Response B) is formed by the cementation of sediments, grains, or fragments under the pressure of other layers of sediment and rock. Metamorphic granite (Incorrect Response C) is formed from its parent rock being subjected to high pressure and heat deep within the earth. Basalt (Incorrect Response D) is formed from the cooling of lava over a short period of time. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 68 | C |
Objective 018 Chemical weathering occurs when there are changes made to the molecular structure of a rock or mineral. Water can act as a weak acid, breaking apart the calcium carbonate of the limestone (Correct Response C). Mechanical weathering leaves the molecular structure of the material intact but may cause the material to move (Incorrect Responses A and D) or break into smaller pieces (Incorrect Response B). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 69 | D |
Objective 019 The Coriolis effect is driven by the differences in the amount of solar radiation combined with the rotation of the Earth on its axis. These two phenomena work together to cause masses of moving air to deflect right or left depending on their latitude. The prevailing direction of the wind causes the oceans to form circular gyres as the water continues to move and be deflected (Correct Response D). The transfer of heat from the tropics to the poles (Incorrect Response A) is a result of wind circulation and ocean gyres but is not the source for their deflection or formation. The movement of tides (Incorrect Response B) originates from forces related to the gravitational relationship between the Earth, Moon, and Sun. The evaporation of surface water (Incorrect Response C) occurs when solar radiation reaches the top of the water body and causes the liquid to turn into water vapor into the atmosphere. It can affect weather conditions but has nothing to do with deflection of winds and formation of ocean gyres. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 70 | B |
Objective 019 The ozone layer is a component of the stratosphere, which is the layer that extends from 10 kilometers to 50 kilometers above the Earth's surface (Correct Response B). Air samples from altitudes below 10 kilometers (Incorrect Response A) or higher than 50 kilometers (Incorrect Responses C and D) would not give any indication of the health of the ozone layer. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 71 | D |
Objective 019 Onshore breezes occur on warm summer afternoons because the land heats more rapidly than the water. The warm air over the land rises, and the cooler air over the water moves in to take its place (Correct Response D). Trade winds (Incorrect Response A) and jet streams (Incorrect Response C), on the other hand, are a result of the differences in heat energy at various latitudes. The variation in their strength is more affected by the tilt of the Earth than what is at the Earth's surface. Spring tornadoes (Incorrect Response B) result from the interactions of large, unstable air masses, rather than from the local, surface-level heating differences. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 72 | D |
Objective 019 If there is a deep warm layer of air and only a thin, extremely cold layer of air, then the precipitation will not have time to freeze as it travels towards the surface. It will, however, freeze upon impact (Correct Response D). Snow pellets (Incorrect Response A) will fall if the layer of cold air is deeper, since the precipitation will have a chance to freeze while still in the atmosphere. Wet snow (Incorrect Response B) occurs when there is a thin layer of warm air near the surface, while sleet (Incorrect Response C) requires a shallow warm layer situated above a surface-level cold layer. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 73 | B |
Objective 019 The difference between Doppler radar and traditional radar is that Doppler radar can use the Doppler effect to determine not only the presence of precipitation but its velocity as well (Correct Response B). The snow water equivalent (Incorrect Response A), total precipitation (Incorrect Response C), and precipitation intensity (Incorrect Response D) can all be directly measured or calculated using both traditional and Doppler radar. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 74 | B |
Objective 020 The western part of the United States experiences greater tectonic activity compared to the eastern United States, due to the faulting and deformation that results from the interactions between the Pacific and North American plate (Correct Response B). Although some western states may have drier and hotter climates (Incorrect Response A), the surface temperatures only have a small effect on the temperatures of the water deep below the surface. The thickness of the crust (Incorrect Response C) and amount of vegetation (Incorrect Response D) vary across the continent and minimally affect the groundwater temperatures. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 75 | C |
Objective 020 A positive climate feedback loop is where a change to one part of the system causes changes that amplify or increase the initial conditions. In this case, something causing an increase in global temperatures will trigger a series of events that causes global temperatures to continue to increase. This type of feedback loop is best exemplified through melting permafrost (Correct Response C). Melting of permafrost due to warming global temperatures will release more gases into the atmosphere, which contributes to the greenhouse effect, resulting in even warmer temperatures. Increased snowfall (Incorrect Response A), decomposing vegetation (Incorrect Response C), and slowing of thermohaline circulation (Incorrect Response D) represent negative climate feedback loops because these factors decrease the rate of change to the initial conditions. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 76 | D |
Objective 020 Percolating water through active charcoal is most effective at removing toxins because charcoal has the ability to absorb and trap contaminates as the water passes through it (Correct Response D). Boiling water (Incorrect Response A) and exposing it to UV light (Incorrect Response C) are primarily used to disinfect and eliminate microbiological pathogens, but they do not physically remove other particles or chemicals that are harmful if consumed. While traces of ozone ( O 3 ) present with oxygen are highly effective at killing biological contaminants and can react with certain heavy metals causing them to precipitate out, if an additional filtration step is not added those materials will still be present in the water (Incorrect Response B). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 77 | C |
Objective 021 Meiosis is a cell division process that results in four haploid daughter cells, while mitosis produces two diploid cells (Correct Response C). The number of cells produced by each process is swapped in Incorrect Response A. The daughter cells produced through cell division (Incorrect Response B) may vary in size, but this is not a defining characteristic between these two processes. Both daughter cells of mitosis and meiosis contain a complete set of organelles and the structures needed in order to function properly (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 78 | B |
Objective 021 There are six defined characteristics of life: the ability to reproduce (Correct Response B), the ability to use energy, the ability to grow and change, having stable internal conditions, being organized, and being composed of at least one cell. It is possible that life does not need to possess carbon-containing molecules (Incorrect Response A). There are also many organisms that are at or colder than their surrounding temperatures (Incorrect Response C). All living things are organized but are not necessarily highly ordered (Incorrect Response D), as exemplified by organisms such as amoebas. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 79 | C |
Objective 021 Structure X is the nucleus, which contains the genetic material of the cell (Correct Response C). The cellular membrane, which is the barrier of the cell, controls ion exchange (Incorrect Response A). The vacuoles of the cell, shown here as circles or ovals near the cell membrane, store nutrients of the cell (Incorrect Response B). Cellular waste products are broken down by lysosomes, which carry enzymes for that function (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 80 | C |
Objective 021 Fermentation is an anaerobic process, or one that is performed without oxygen, while cellular respiration is an aerobic process, which means that it requires oxygen to be performed (Correct Response C). All different sized cells can undergo either process (Incorrect Response A). Although aerobic processes produce more ATP, which can be used for the cell's energy needs, it takes time to switch between anaerobic and aerobic processes (Incorrect Response B). Light availability, or even lack of light, does not necessarily initiate fermentative processes (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 81 | A |
Objective 022 The data in the table indicates a slow growth of one or two birds a day and then jumps to double in size overnight, which is shown in the graph in Correct Response A. This is not a linear relationship, as seen in the graph in Incorrect Response B, and population is increasing over time rather than decreasing, which is depicted in the graphs in Incorrect Responses C and D. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 82 | D |
Objective 022 Ecological succession is the gradual development of a complex ecosystem as a site moves through several stages of plant and animal communities (Correct Response D). Evolution (Incorrect Response A) is a change that happens within a species, not on an ecosystem scale. Biological magnification (Incorrect Response B) does occur at the ecosystem level, but it is referring to the increasing concentration of a contaminant, such as mercury, as it moves through the trophic pyramid. Exponential growth (Incorrect Response C) refers to a mathematic model. It could apply to an increase in the number of species or biomass in the field, but it does not explain the change in species presence over time. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 83 | C |
Objective 023 The stigma is adapted for receiving pollen because during the pollination process, the grains transfer from the anther to the sticky stem of a stigma (Correct Response C). The petal (Incorrect Response A) functions to attract pollinators, the anther (Incorrect Response B) is the organ that produces the pollen, and the ovary (Incorrect Response D) of a flowering plant is where seed development and fertilization occur. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 84 | B |
Objective 023 The phenotypic ratio can be found by building a Punnett square with one parent as big B little b and one parent as little B little B , as shown.
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 85 | B |
Objective 023 When DNA is replicating under normal conditions, A pairs with T, while C and G pair (Correct Response B). Incorrect Response A does not use this complementary rule and instead assumes that the complementary DNA strand is the same as the original sequence. Incorrect Response C represents a strand of complimentary RNA, while Incorrect Response D incorrectly pairs A and C, while T and G pair. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 86 | C |
Objective 024 A variant gene can remain in a population, even if it poses no advantage, because these genes can be recessive and are not expressed (Correct Response C). Genetic drift (Incorrect Response A), mutations (Incorrect Response B), and natural selection (Incorrect Response D) may explain the existence of a variant gene, but these scenarios affect the communities through favoring an advantage or disadvantage of gene expression. Also, this does not explain why these phenotypes are not expressed in the majority of individuals. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 87 | C |
Objective 024 Unique mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA indicate that these organelles must have, at one time, been individual prokaryotes. Over time, these prokaryotes would have formed a symbiosis that eventually became a dependency (Correct Response C). The formation of organic molecules was vital to the emergence of life, but this process does not directly explain why these organelles have their own DNA (Incorrect Response A). The emergence of oxygen in the atmosphere was the result of the waste product of photosynthetic organisms, which allowed for aerobic organisms to evolve (Incorrect Response B). However, if these organisms had chloroplasts, they would not necessarily need their own DNA. While there is much support for life arising in the oceans, this does not impact whether DNA is needed for an organelle to function (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 88 | D |
Objective 024 The theory of evolution states that: (1) the trait being selected for must have more than one allele, (2) that trait must be inherited, (3) there are more offspring under selection than can survive, and (4) different alleles confer different survival rates. With this in mind, the population of insects has a gene that is being selected for (the resistance allele) and it has selective pressure on it (those without the allele succumb to the pesticide) (Correct Response D). A hare's coat turning colors is the result of environmental changes, but there is no difference in trait shown across the population (Incorrect Response A). Becoming more skilled at hunting is an acquired, not inherited, trait (Incorrect Response B). The root system is not placed in context of how the rest of the population is surviving (Incorrect Response C). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 89 | A |
Objective 025 "Pure substance" is a term used to describe chemical elements and compounds, substances with a fixed structure down to the atomic level that can be described with a single chemical formula, such as alcohol (Correct Response A). Milk (Incorrect Response B) contains both water- and fat-soluble compounds, as well as water itself. Gasoline (Incorrect Response C) is a mixture of hydrocarbons, each with its own chemical formula. Blood (Incorrect Response D) is a water-based solution of organic molecules that also contains a variety of living cells. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 90 | C |
Objective 025 Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that can form between the oxygen atom in one water molecule and a hydrogen atom in another water molecule. These forces are relatively strong compared to other molecules of similar molecular weights and are responsible for some properties of water, including surface tension (Correct Response C). The size of atoms (Incorrect Response A) can be a proxy for the strength of dispersion forces, another intermolecular force, but the size of the atoms in a water molecule is unremarkable. The solvent properties of water (Incorrect Response B) are produced by the molecule's ability to attack solute particles. The specific heat capacity of water (Incorrect Response D) is another effect of hydrogen bonding. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 91 | C |
Objective 025 The reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide produces a solution of sodium chloride (Correct Response C). In Incorrect Responses A and B, a chemical reaction occurs so that a reactant will not be produced. The reactant oxygen atoms (Incorrect Response D) become part of the water produced in the products and so are unavailable. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 92 | D |
Objective 026 A dependent variable in a scientific investigation is a measured effect of what is being tested or changed within the study. In this scenario, the amount of heat conserved is the independent variable because it is the effect that occurs when a different insolation material is applied to each iteration of the design (Correct Response D). The insulated material (Incorrect Response A) is the independent variable because it is the aspect of the experimental set up that the researcher is intentionally changing and is trying to test. The time (Incorrect Response B) and volume (Incorrect Response C) are the controls because they remain the same for each trial to create the same conditions across the experiment to produce comparable results. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 93 | D |
Objective 026 Holding volume and temperature constant, there is a direct relationship between the amount of gas and its pressure. Decreasing the amount of gas in the chamber decreases the pressure (Correct Response D). Holding volume and the amount of gas constant, there is a direct relationship between the temperature of a gas and its pressure. Increasing the temperature of the gas in the chamber increases the pressure (Incorrect Response A). Increasing the amount of gas in the chamber increases its pressure (Incorrect Response B). Holding the amount of gas and its temperature constant, there is an inverse relationship between the volume of a gas and its pressure. Decreasing the volume of a gas would increase its pressure (Incorrect Response C). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 94 | B |
Objective 027 The object with the greatest potential energy is object B (Correct Response B). Using the formula provided, the result of multiplying the three values together is equal to P E = 5 times 9.8 times 3 = 147 meters per second squared . Substituting the appropriate variables for objects A, C, and D within the same formula, the answers are 68.3 meters per second squared , 98 meters per second squared , 49 meters per second squared respectively. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 95 | D |
Objective 028 The truck starts to move in reverse direction at 12 seconds because the displacement is a negative, based on its original position at zero (Correct Response D). The truck has not stopped moving at 24 seconds but has a zero displacement from its origin (Incorrect Response A). The truck is moving in a reverse, not a forward, direction at 36 seconds (Incorrect Response B). The slope of 0 at 6 seconds indicates that the truck is not moving and therefore is not accelerating (Incorrect Response C). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 96 | A |
Objective 028 Work is the product of force applied to an object and its traveled distance. Since force is dependent on the mass and acceleration of an object, then the largest dog would be expected to demonstrate the most amount of work when climbing the same set of stairs, assuming a similar rate of acceleration (Correct Response A). The fastest dog (Incorrect Response B) and the slowest dog (Incorrect Response D) are traveling the same distance, but their mass is unknown. The smallest dog (Incorrect Response C) should apply the least amount of work because it has the lowest mass. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 97 | B |
Objective 028 This classroom demonstration has two people pulling on opposite sides of a rope. This best represents net forces because the students can observe what happens if the people use the same force on each side or what happens if another person pulls with more force than the other (Correct Response B). Since this activity does not focus on the thermodynamic changes that may occur, it is not likely to be helpful for demonstrating entropy (Incorrect Response A). Energy transfers (Incorrect Response C) are occurring during the rope pull, but they are not immediately apparent. Additionally, there are no outward changes to the matter in the demonstration, so it is unlikely to help students visualize the conservation of matter (Incorrect Response D). |
|||||||||||||||||
| 98 | B |
Objective 028 At constant velocity, the acceleration of the box must be zero. Therefore, all horizontal forces must balance each other and all vertical forces must balance each other. Forces 2 and 3 must be equal in magnitude to produce balance vertically, and forces 1 and 4 (Correct Response B) must also be equal to produce balance horizontally. Forces 1 and 3 (Incorrect Response A), forces 2 and 4 (Incorrect Response C), and forces 3 and 4 (Incorrect Response D) are not required to balance because each pair of forces is perpendicular to each other. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 99 | A |
Objective 029 White light consists of many colors of light, and each color of light depends on its wavelength, lambda . Refraction occurs when light passes from one material into another if the materials have different indices of refraction, n. The speed of light in the material is given by c divided by n , where c = speed of light in a vacuum. Thus, a material with large refractive index will decrease the speed of light. Additionally, the speed, v = lambda f , also depends on the wavelength of light. As a result, different wavelengths, or colors, of light will have different speeds and therefore refract different amounts within a material. This dispersion of white light produces colors that refract different amounts and spread out into a full spectrum (Correct Response A). Amplitude (Incorrect Response B) is not affected by the transition from one material to another, nor does an amplitude change affect the color of light. Changes in reflection (Incorrect Response C) do not cause this phenomenon since prisms allow light to pass through them and refract. Light may become polarized entering a material (Incorrect Response D), but polarization does not cause color dispersion into a full spectrum of colors. |
|||||||||||||||||
| 100 | B |
Objective 029 Parallel circuit branches connected to one voltage source will have the same voltage applied across the branch. The voltage of the source and the internal resistance of any light will not be affected by a light in a different branch burning out. Since the working lights will have the same internal resistance with the same voltage applied, by Ohm's Law— I equals V over R —each branch will draw the same current (Correct Response B). Response A is misinterpreting the circuit to be a series circuit of light bulbs and incorrectly states that a burned bulb still completes a circuit and allows charge to flow. Response C is incorrect because it violates Ohm's Law for any parallel branch. Response D is describing the charge drawn from the battery to correctly decrease, but the charge drawn by each individual branch containing a working bulb will remain the same. |
|||||||||||||||||
| Total Correct: | Review your results against the test objectives. | ||||||||||||||||||
Open Responses, Sample Responses, and Analyses
| Question Number |
Your Response Read about how your responses are scored and how to evaluate your practice responses |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
Open Response Item Assignment #1 For each assignment, you may type your written response on the assigned topic in the box provided. Note: The actual test allows you to handwrite your responses on separate response sheets to be scanned for upload to the test. For this practice test, you may handwrite each response on 1–2 sheets of paper. |
|||||||||||
| First Sample Weak Response |
First Sample Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 1. See my tree below. 2. To make one device, 1st stage has an 80% chance of being good or 4 fifths. If it makes the 2nd stage, it has a 75% chance of being good or 3 fourths. So good ones are 4 fifths times 3 fourths equals 3 fifths chance of being created. Therefore, produce 5 devices and you should get 3 good devices. 3. Produce your own 3 devices – you make more profit. 4. If the factory burns down, then you have to buy Stage 1 and Stage 2 parts from the supplier and make less profit.
The first vertex, labeled 1 device, has two branches. The bottom branch is labeled Stage 1, 20 percent defective, discard, and this branch is terminal. The top branch is labeled Stage 1, 80 percent usable, and two branches extend from it. The top branch is labeled Stage 2, 75 percent usable, and the bottom branch is labeled stage 2, 25 percent defective, discard. Both of these second-level branches are terminal. |
|||||||||||
| First Weak Response Analysis |
Analysis of First Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 Purpose: The purpose of the assignment is limited, although each part is partially addressed. In Part 1, the tree diagram does demonstrate an understanding of the situation but does not include all pertinent information. Part 2 is adequate, but Part 3 just provides an answer with no reasoning. Part 4 names only one influence. Subject Matter Knowledge: The response demonstrates a limited understanding of the topic. In Part 1, there is knowledge of how to draw a tree diagram and gives basic information pertaining to this situation. In Part 2, the response demonstrates an understanding of how to use probability to find the number of usable devices and in Part 3 arrives at a conclusion. Part 4 identifies an influence, though an unlikely one. Support: The support for this response is limited. Part 1 provides a tree diagram but would be improved by including information about the cost at each stage or the loss at each stage. Part 2 shows work but does not explain why this process is being used or why the conclusion reached is valid. Part 3 gives an unsubstantiated conclusion. No work is shown to compare the cost of the company making their own versus buying devices from another company. The response ignores all information about cost, profit, and losses, which are needed to explain their decision. Part 4 identifies one influence when the prompt asks for "influences." An adequate response would include at least two and more likely three influences with an explanation of what effect each would have on the recommendation. Rationale: The response reflects a limited understanding of the topic and much of the reasoning is lacking. Reasons and recommendations are given without sufficient justification. The response shows some understanding of the topic, but there is not enough support or explanation for how answers and conclusions are derived. If any analysis was done, it is not shown. |
|||||||||||
| Second Sample Weak Response |
Second Sample Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 1. I chose to change the 80%, 20%, 75%, and 25% into reduced fractions and used that information to create my production tree (see below). 2. From the tree diagram and the denominator of the fractions for Stage 1 it appears that if you start by making 5 devices, one of them will not pass inspection at end of Stage 1 leaving only 4 going onto Stage 2. At the end of Stage 2 one of the 4 will not pass inspection leaving only 3 good ones to be sold. You need to make 5 to get 3 good ones. 3. Should the company outsource production if they only want 3 units? It will cost 9,000 dollars in total for the 3 from the outside company. The manufacturing company charges 3,500 dollars for each good unit so only makes 500 dollars per unit. Total of 1,500 dollars profit If first 3 units are perfect, selling price of 3,500 dollars minus production cost 1,200 dollars is 2,500 dollars profit each unit. Manufacture the units yourself! Better profit. 4. If the company could no longer get some of raw materials needed for production at the present price, the costs at Stage 1 and/or Stage 2 would increase which cuts into profits. The only person who can run the Stage 2 machinery had a medical emergency and will be out several weeks until another person can be trained on the equipment.
The first vertex is labeled Start production of 5. One branch labeled Stage 1 extends from this vertex. The top branch of the second label is labeled 1 bad. It is a terminal branch. The bottom branch of the second level is labeled 4 go to Stage 2. Two branches extend from the end of its arrowhead. The top branch is labeled 1 bad. It is a terminal branch. The bottom branch is labeled 3 ready to sell, and this is a terminal branch. |
|||||||||||
| Second Weak Response Analysis |
Analysis of Second Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 Purpose: All parts of the prompt are addressed. Part 1 includes a tree diagram but does not answer with a tree for one device only. Part 2 has a correct answer but there is no justification for the numbers shown. Part 3 addresses the profit for outsourcing the device but incorrectly responds to the profit if made in-house. Part 4 identifies two influences and some justification for each. Subject Matter Knowledge: The response reflects a limited and possibly inaccurate application of the subject matter. Part 1 misinterprets the wording of the question by making a tree for five devices instead one device. Part 2 uses the tree to arrive at the conclusion that five are needed, but the analysis is not clearly shown. Part 3 shows a partial understanding of the situation. The response accurately finds the profit if the devices are outsourced. The response does not analyze profits and losses when produced in-house. An assumption is made that the first three devices made were acceptable for sale, giving maximum profit, and ignoring the probability that at least two in every five will be defective, causing a reduction in profit. Part 4 names two reasonable influences and justifies why they could affect the recommendation. Support: The response shows very limited support. In Part 1, the diagram lacks pertinent information about cost or loss in each branch of the tree and has little explanation of how the numbers used in the diagram were found. It mentions changing percentages to fractions but does not show it or justify why it was done. Part 2 uses the numbers from the tree but again never clearly shows how they were found or why they were chosen. Part 3 shows good support for the profit if the device is outsourced but uses faulty reasoning in analyzing the profit if the company decides to make the device in-house. The cost of making the two possible defective devices is ignored and the effects on the total profit. Part 4 names only two influences but does explain why the recommendation might change. Rationale: The response shows some understanding of the topic but ignores the wording of Part 1 of the prompt, which clearly states to make a tree for one device. Throughout this response, clarifying detail is missing, making the response difficult to follow and understand. The thinking used to arrive at conclusions is not shown, and without it, there is no way to know if the reasoning is correct. |
|||||||||||
| First Sample Strong Response |
First Sample Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 1. (See tree diagram.) Summarize net profit/loss: 3 fourths of 0.8 or Three fourths of four fifths pass final inspection or 3 fourths times 4 fifths equals 3 fifths can be sold at 3,500 dollars. 2 fifths of devices are thrown away: 1 fifth times 0 point 2 at stage 1 for a 700 dollars loss per device and 1 fifth left paren 1 fourth of 4 fifths right paren at stage 2 for a 1,200 dollars loss per device.
A note at the top of the diagram says each Initially each device costs 700 dollars. The first vertex is labeled $700 per device, and two branches extend from this vertex to the first level of the tree, labeled stage 1. A terminal branch labeled zero point 2 extends downward and right. Its vertex is labeled Fail, lose that 700 dollars. An arrow points from that vertex label to a note that says throw away. The other first level branch extends downward and left, and it is labeled zero point 8. Its node is labeled Pass, need 500 dollars more each to finish, 700 plus 500, total cost after this step. Two branches extend from this vertex into the second level of the tree, labeled stage 2. One branch is labeled 0 point 75, and the label at its terminal vertex reads pass, each cost 1200 dollars. The other is labeled 0 point 25 and the label at its terminal vertex reads fail, lose that 1200 dollars. An arrow points from that label to a note that says throw away. 2. 3 fourths of 0.8 pass stage 2 which is 3 fourths of 4 fifths which is the same as 3 fourths times 4 fifths equals 3 fifths pass so 3 out of 5 devices made pass inspection and can be sold. So at least 5 attempts to get 3 to sell. 3. Three devices passing inspection costs 3 times 1,200 dollars for them and 700 dollars lost at stage 1 for one device and 1,200 dollars lost at stage 2 for another device. 3600 + 700 + 1200 = 5,500 dollars total to make 3 good devices that can be sold. If the other company charges 9000 dollars for 3 devices, they should make the devices for themselves and save 9000 minus 5500 equals 3,500 dollars. If they sell each device for 3,500 dollars, 3 would make 10,500 dollars minus 5500 equals 5000 dollars profit on 3 devices. 4. Things that could influence the prediction/outcome would include upfront costs (buy equipment, train workers, supply chain issues, change in costs of materials) or machine malfunctioning so expected percentages are not as expected. |
|||||||||||
| First Strong Response Analysis |
Analysis of First Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 Purpose: The purpose of the assignment is fully achieved. All parts are addressed completely with work shown and thinking explained. In Part 1, a tree diagram shows relevant information at each branch. In Part 2, the ratios are provided, and the steps are clear and easy to follow for the processes needed for production. The thinking for arriving at the conclusion that five are needed in order to have three to sell is explained. The work shown and explained in the analysis of Part 3 is complete. Many influences are identified in Part 4. Subject Matter Knowledge: There is substantial and accurate application of knowledge. In Part 1, the tree diagram is clear and concise, providing all the information needed. The work demonstrated in Parts 2 and 3 shows understanding of the situation and step-by-step calculations to arrive at the solutions, with explanation of the steps used to make the appropriate decisions. In Part 4, the influences given are appropriate and could affect the manufacturing process. Support: There is high-quality support for each part of the response with step-by-step work shown and reasons given for each step so that it is easy to understand how each decision was made. Part 1 shows a well-drawn tree with each branch labeled appropriately with manufacturing cost or possible loss. In Part 2, the work needed is clearly shown and explained to arrive at the conclusion of five devices needed. In Part 3, step-by-step analysis of outsourcing as opposed to in-house production leads to a well-justified conclusion. Part 4 lists many influences that can affect the recommendation given. Rationale: The response is an ably reasoned analysis of the problem. The steps shown and reasoning used in each part make it easy to follow and understand why they are needed. The response integrates all four parts of the problem into a well-explained analysis of the situation. |
|||||||||||
| Second Sample Strong Response |
Second Sample Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 See tree diagram below. The probability of creating a successful device is 4 fifths times 3 fourths or 3 fifths left paren 60 percent right paren. Therefore, make the following equation with x standing for the number of devices which need to be produced, 3 fifths probability of success and 3 the number of good devices requested: 3 fifths x equals 3 Solve for x. x equals 3 times 5 thirds which makes x = 5. It should only take 5 tries to get 3 good devices according to theorical probability. To determine whether the company should outsource manufacturing, calculate expected profit of in-house vs outsourced manufacturing. If the company wants to produce 3 sellable devices, they should produce 5 devices. 3 of them will be sellable and cost the company 1,200 dollars each to produce. One will fail quality testing at the end of stage 1, costing the company 700 dollars. One will pass stage 1 testing but fail quality testing after stage 2, costing the company 1,200 dollars. So, the 5 devices' total cost is 3 times 1,200 dollars plus 1 times 700 dollars plus 1 times 1200 dollars. Therefore, total cost equals 3600 plus 700 plus 1200 equals 5,500 dollars. The company will sell the 3 good ones for 3,500 dollars each, for a total of 10,500 dollars. Their profit is total sales minus manufacturing costs – in this case, 10,500 minus 5,500 equals 5,000 dollars. If the company outsources manufacturing, their cost is 9,000 dollars. They still have the same total sales income, so 10,500 minus 9,000 equals 1,500 dollars profit. The company should manufacture its own devices since it will make more profit by producing 5 devices and possibly having 2 that are unusable. Influences that could cause variations: the manufacturing equipment requires repair and is shut down for several days; the materials needed to create the device are not available, but the external manufacturer has them; or employee attendance is not reliable, which means the machine needs to be stopped until they return to work.
The initial node is labeled single device. One terminal branch, labeled bad, 20 percent, one-fifth chance, extends from the initial node. A note appears at the arrowhead of this branch. It reads branch 2, 700 dollars cost, 700 loss. The other first-level branch is labeled good, 80 percent, four-fifths chance. It extends to a node that is labeled 700 cost. Two terminal branches extend outward from this node. The first second-level branch is labeled bad, 25 percent, one-fourth chance. A note appears at the arrowhead of this branch. It reads branch 3, 500 dollars cost, 1200 loss. The other second-level branch is labeled good, 75 percent, three fourths chance. It ends at the following note: branch 1, 500 dollars cost, profit 3500 dollars minus 1200 dollars equals 2300 dollars. |
|||||||||||
| Second Strong Response Analysis |
Analysis of Second Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #1 Purpose: The purpose of the assignment is fully achieved. In Part 1, a tree diagram was created and labeled with all pertinent information. Part 2 shows step-by-step work to arrive at the answers needed, including explanations for what was done and why it needed to be done. Part 3 thoroughly analyzes the cost of production versus outsourcing the three devices. Work is shown and explained in a way that leads to the decision. In Part 4, several influences are given that could change the recommendations. Subject Matter Knowledge: The response shows a clear understanding of the topic. Each part is ably reasoned showing the thinking involved and reasoning used. In Part 1, a complete tree diagram is created. Work shown to arrive at answers in Parts 2 and 3 is clear and easy to follow and explained fully. Influences given are appropriate and show an understanding of the real-world situation. Support: All parts of this response are supported. Each part responds to the question, showing step-by-step work and explanation for why the steps were included and why the conclusions were drawn. Rationale: This is an ably reasoned, comprehensive response to the prompt. The response shows good understanding of the topic, giving reasons for the calculations and providing analysis. The response is easy to follow and supports and defends the analysis well. |
|||||||||||
| 102 |
Open-Response Item Assignment #2 For each assignment, you may type your written response on the assigned topic in the box provided. Note: The actual test allows you to handwrite your responses on separate response sheets to be scanned for upload to the test. For this practice test, you may handwrite each response on 1–2 sheets of paper. |
|||||||||||
| First Sample Weak Response |
First Sample Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 Mendel studied pea plants. He demonstrated that a tall plant crossed with a short plant would create a tall plant. This means that genes are a key concept in pea plant growth. The tall gene dominates the short one. The combination of a tall and short gene is called heterozygous. If both genes are the same, either short or tall, it is called homozygous. The dominant trait of a heterozygous combination will always be the one expressed. Refer to the diagram where T (upper case) is the dominant gene for height and t (lower case) is the recessive one. The environmental factors are meaningless in this case. Mendel proved this. This could be the second key concept. A Punnett square key to table below big T big T = Tall big T little T = Tall big T little T = Tall little T little T = Short
|
|||||||||||
| First Weak Response Analysis |
Analysis of First Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 This is an example of a weak response because it is characterized by the following: Purpose: The candidate, while having an adequate knowledge of Mendel's work with pea plants, fails to adequately address the relationship between environmental factors and genetic ones. Instead, that relationship is dismissed due to a limited understanding of the overall significance of Mendel's work, focusing on only one isolated aspect of it. This could have been scored as adequate, if the candidate had taken more time to explain this relationship. The prompt asked for an understanding of the cause-and-effect relationship that exists between the two concepts. The candidate neglected to address this part of the instructions. This response is scored as limited, albeit on the higher side of that rating, because there was this shortcoming. Therefore, in this case, the purpose of the assignment was not fully achieved. Subject Matter Knowledge: The subject matter knowledge is limited because, while there is an adequate understanding of Mendel's experiments with peas, there is nearly no concession to the additional role of the environment in the growth of plants. Support: The example used is limited to only what the candidate appears to know, the one isolated aspect of Mendel’s work. Rationale: The rationale is limited, making a case for only half of the relationship between the two concepts. |
|||||||||||
| Second Sample Weak Response |
Second Sample Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 The potential height of a pea plant is genetic. Reaching this potential depends on environmental factors, such as the amount of sunlight, the nutrient value of the soil, and the amount of water available to the roots. Temperature of the soil and of the air are also factors. What is unclear, of course, is epigenetic factors. For instance, are certain genes turned on or off due to environmental factors? |
|||||||||||
| Second Weak Response Analysis |
Analysis of Second Weak Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 This is an example of a weak response because it is characterized by the following: Purpose: Response is limited for several reasons, including the glaring lack of a graph, formula, and/or diagram as instructed by the second bullet of the prompt. Subject Matter Knowledge: The response reflects adequate knowledge of the subject matter, but it is delivered in a manner that marks it as incomplete due to the lack of sufficient detail. Support: In order to have made the response adequate, it is necessary to include more relevant examples showing better support for the stated knowledge. Rationale: A rationale needs to provide sufficient understanding of the dual factors of environment and genetics rather than present a question introducing a new concept. |
|||||||||||
| First Sample Strong Response |
First Sample Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 Key concepts related to the environmental and genetic factors that influence the growth of pea plants would be that (1) pea plants' growth is regulated by both of these factors with (2) genetics being the basis for the expected outcome and the environment holding the trump card that decides whether that outcome is realized. All living things are governed by the concept of optimum conditions. Plant growth is a typical example. Plants require sunlight, water, proper temperature, proper soil p H , proper amounts of the key nutrients of phosphorous, nitrogen, and potassium as well as micronutrients such as iron, zinc, manganese, copper, etc. For each of these factors, there is a curve of optimum value. Too much or too little of something vital, and the plant's growth will not reach its full potential (see diagram). That potential is set by the genetics that the plant possesses. When Gregor Mendel did his landmark studies of the expression of traits in pea plants, one of the traits he examined was height. He determined that a gene existed that would make a pea plant taller versus an alternate one that would leave it shorter. If a pea plant inherited the tall gene, which was dominant, it would express itself during the plant's life cycle by growing taller than other pea plants that did not possess this gene. However, Mendel had to be careful to treat all of his plants equally. If he failed to water or fertilize the potentially tall plant as well as he did the potentially shorter one, he might have ended up with two plants of equal height instead of one taller and one shorter. Regardless of the genetics, if the environment is not favorable, the expression of genes will be negatively affected.
A diagram of environmental factors versus the ratio of growth is shown. There are five zones along the environmental factors being rated from low to high. The lowest zone is the zone of intolerance, followed by the zone of physiological stress and the zone of optimum in the middle with minimal stress. However, as the environmental factor progresses higher, there is a zone of physiological stress and a zone of intolerance at the highest environmental factor. To illustrate this, overlaid over the zones is a bell curve with the ratio of growth highest in the middle of the zone of optimum and the trendline quickly tapering down to either side to intersect the x-axis at the boundary between each zone of physiological stress and zone of intolerance. |
|||||||||||
| First Strong Response Analysis |
Analysis of First Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 This is an example of a strong response because it is characterized by the following: Purpose: The candidate focused on the need to tie environmental factors to genetic factors in regards to the growth of peas. There is a clear understanding that growth is the interplay between these two things. Whether the candidate wished to stress the importance of genetics over environment or vice versa is not important. The role of these factors is an active debate in science with evidence for the overarching importance of each. This candidate's response is thorough, having fulfilled the purpose by addressing all three bullets of the prompt. Subject Matter Knowledge: The response demonstrates subject matter knowledge through its integration of principles that govern gene expression together with the range of tolerance effect for key environmental factors. Support: The response demonstrates support for that knowledge through the use of high-quality relevant examples such as citing Mendel as the discoverer of the principle of dominance and recessiveness as well as providing the diagram showing the range of tolerance. Rationale: The response demonstrates a thorough rationale by employing a sound argument to show the effect that environmental factors have on the expression of genes. |
|||||||||||
| Second Sample Strong Response |
Second Sample Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 The growth of a pea plant is affected by different environmental and genetic factors. The most important factor is the genetic information inherited from both of its parents, which controls most of its features, such as color, shape, resistance towards certain diseases, etc. Though less often, genetic mutation does occur from time to time, resulting in changes in the plant's appearances and genetic information as well. Environment also plays an important part in here. For example, the type of climate (sunlight exposure, average temperature, precipitation, seasonal changes) and the type of soil it grows in are both important to the growth of a pea plant. Negative environmental factors, such as pollution of various kinds, will have an effect on the plant's growth as well. Although genetics determine the key features of a plant, environment will have a huge impact on the plant's growth in a way that throughout time, plants will adapt to its environment and develop certain features that might be passed onto its future generations. In that way, environmental factors will ultimately affect the plant's genetic information and have a more profound impact on its growth and reproduction. See scanned diagram for an example of how environmental conditions affect the growth habits of a single species of plant that grows in our region.
A diagram is shown of the growth habits of black spruce on a mountain in New Hampshire. It has a caption that reads “The same species of plant responding to different environmental conditions in its growth habits.” An incline is shown from 1,000 feet to 5,000 feet with different sized trees dotting the incline. At 1,000 feet, the black spruce are 30 to 40 feet tall. Around 3,000 feet, they are 10 to 15 feet tall. Around 4,000 feet, they are small shrubs and at 5,000 feet above sea level, they are sprawling and only grow in rock crevices. |
|||||||||||
| Second Strong Response Analysis |
Analysis of Second Strong Response to Open-Response Item Assignment #2 This is an example of a strong response because it is characterized by the following: Purpose: This is a thorough response because it addresses all aspects of the prompt and has therefore fulfilled the purpose of the assignment. Subject Matter Knowledge: Relating the dimensions of genetic and environmental factors to the growth of pea plants reflects thorough subject matter knowledge: genetic information inherited from both of its parents, environment... climate, type of soil. Support: High-quality relevant examples for the types of traits controlled by genetics (color, shape, resistance towards certain diseases) and kinds of environmental factors (sunlight exposure, average temperature, precipitation, seasonal changes) support the subject matter knowledge. Rationale: The response employs a sound rationale by providing a graphical illustration of how these environmental factors can override genetics in the growth habits of a single species of plant. |
|||||||||||
| Review the Performance Characteristics and Score Scale for Written Performance Assignments. | ||||||||||||
Multiple Choice Question
Practice Test Evaluation Chart
In the evaluation chart that follows, the multiple-choice questions are arranged in numerical order and by test objective. Check your responses against the correct responses provided to determine how many questions within each objective you answered correctly.
Subarea 1 : Number System and Quantity
Objective 0001: Apply the structure and properties of number systems.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | C | |
| 2 | B | |
| 3 | D | |
| 4 | D | |
| 5 | D | |
| 6 | C |
out of 6
Objective 0002: Use rational numbers, ratios, and proportional relationships.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | B | |
| 8 | D | |
| 9 | C | |
| 10 | B | |
| 11 | C | |
| 12 | C | |
| 13 | B |
out of 7
Subarea 1 (Objectives 0001–0002) Total out of 13
Subarea 2 : Algebra, Functions, and Modeling
Objective 0003: Use patterns to model and solve problems.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 14 | C | |
| 15 | B | |
| 16 | A |
out of 3
Objective 0004: Apply algebraic techniques to expressions and equations.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | D | |
| 18 | C | |
| 19 | D |
out of 3
Objective 0005: Demonstrate knowledge of relations and functions.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | A | |
| 21 | D | |
| 22 | A |
out of 3
Objective 0006: Apply the properties of linear relations and functions.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | D | |
| 24 | C | |
| 25 | C | |
| 26 | B |
out of 4
Objective 0007: Apply the principles and properties of nonlinear relations and functions.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 27 | A | |
| 28 | A |
out of 2
Subarea 2 (Objectives 0003–0007) Total out of 15
Subarea 3 : Geometry and Measurement
Objective 0008: Apply principles, concepts, and procedures related to measurement.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 29 | C | |
| 30 | A | |
| 31 | D |
out of 3
Objective 0009: Apply the principles of Euclidean geometry and proof.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 32 | A | |
| 33 | D | |
| 34 | A |
out of 3
Objective 0010: Apply properties of two- and three-dimensional figures.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | C | |
| 36 | B | |
| 37 | B |
out of 3
Objective 0011: Apply the principles and properties of coordinate and transformational geometries.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 38 | D | |
| 39 | C | |
| 40 | A |
out of 3
Subarea 3 (Objectives 0008–0011) Total out of 12
Subarea 4 : Statistics and Probability
Objective 0012: Understand the principles, techniques, and applications of statistics.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 41 | C | |
| 42 | A | |
| 43 | C | |
| 44 | A | |
| 45 | C |
out of 5
Objective 0013: Understand the principles of probability.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 46 | C | |
| 47 | B | |
| 48 | A | |
| 49 | C | |
| 50 | B |
out of 5
Subarea 4 (Objectives 0012–0013) Total out of 10
Subarea 5 : Technology / Engineering
Objective 0014: Apply knowledge of engineering design.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 51 | A | |
| 52 | C | |
| 53 | B | |
| 54 | A | |
| 55 | D |
out of 5
Objective 0015: Demonstrate knowledge of tools, materials, and manufacturing.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 56 | B | |
| 57 | B | |
| 58 | A | |
| 59 | D |
out of 4
Objective 0016: Demonstrate knowledge of technological systems.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | D | |
| 61 | B | |
| 62 | A | |
| 63 | A |
out of 4
Subarea 5 (Objectives 0014–0016) Total out of 13
Subarea 6 : Earth and Space Science
Objective 0017: Demonstrate knowledge of the components of the solar system and universe and their interactions.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 64 | B | |
| 65 | A |
out of 2
Objective 0018: Apply knowledge of Earth's geosphere, geologic history, and processes.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 66 | D | |
| 67 | A | |
| 68 | C |
out of 3
Objective 0019: Demonstrate knowledge of Earth's hydrosphere, atmosphere, weather, and climate.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 69 | D | |
| 70 | B | |
| 71 | D | |
| 72 | D | |
| 73 | B |
out of 5
Objective 0020: Demonstrate knowledge of natural resources, natural hazards, and human impacts on the environment.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 74 | B | |
| 75 | C | |
| 76 | D |
out of 3
Subarea 6 (Objectives 0017–0020) Total out of 13
Subarea 7 : Life Science
Objective 0021: Demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics and processes of living organisms.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 77 | C | |
| 78 | B | |
| 79 | C | |
| 80 | C |
out of 4
Objective 0022: Apply knowledge of the characteristics of populations, communities, ecosystems, and biomes.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 81 | A | |
| 82 | D |
out of 2
Objective 0023: Apply principles related to the inheritance of characteristics.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 83 | C | |
| 84 | B | |
| 85 | B |
out of 3
Objective 0024: Demonstrate knowledge of principles related to the theory of biological evolution.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 86 | C | |
| 87 | C | |
| 88 | D |
out of 3
Subarea 7 (Objectives 0021–0024) Total out of 12
Subarea 8 : Physical Science
Objective 0025: Apply knowledge of the structure and properties of matter.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 89 | A | |
| 90 | C | |
| 91 | C |
out of 3
Objective 0026: Apply knowledge of the states of matter, particle motion, and heat.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 92 | D | |
| 93 | D |
out of 2
Objective 0027: Apply knowledge of different forms of energy and the conservation of energy.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 94 | B |
out of 1
Objective 0028: Apply knowledge of the concepts of force, motion, work, and power.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 95 | D | |
| 96 | A | |
| 97 | B | |
| 98 | B |
out of 4
Objective 0029: Apply knowledge of the characteristics and properties of waves, electricity, magnetism, and electromagnetism.
| Question Number | Your Response | Correct Response |
|---|---|---|
| 99 | A | |
| 100 | B |
out of 2
Subarea 8 (Objectives 0025–0029) Total out of 12
Practice Test Score Calculation
The practice test score calculation is provided so that you may better gauge your performance and degree of readiness to take an MTEL test at an operational administration. Although the results of this practice test may be used as one indicator of potential strengths and weaknesses in your knowledge of the content on the official test, it is not possible to predict precisely how you might score on an official MTEL test.
The Sample Responses and Analyses for the open-response items may help you determine whether your responses are more similar to the strong or weak samples. The Scoring Rubric can also assist in estimating a score for your open responses. You may also wish to ask a mentor or teacher to help evaluate your responses to the open-response questions prior to calculating your total estimated score.
How to Calculate Your Practice Test Score
Review the directions in the sample below and then use the blank practice test score calculation worksheet to calculate your estimated score.
Multiple-Choice Section
| Enter the total number of multiple-choice questions you answered correctly: | 66 | ||
| Use Table 1 below to convert that number to the score and write your score in Box A: | A: | 196 |
Open-Response Section
| Enter the number of points (1 to 4) for your first open-response question: | 3 | ||
| Enter the number of points (1 to 4) for your second open-response question: | 3 | ||
| Add those two numbers (Number of open-response question points): | 6 | ||
| Use Table 2 below to convert that number to the score and write your score in Box B: | B: | 50 |
Total Practice Test Score (Estimated MTEL Score)
| Add the numbers in Boxes A and B for an estimate of your MTEL score: | A + B = | 246 |
Practice Test Score Calculation Worksheet: Middle School Mathematics (65)
Table 1:
| Number of Multiple-Choice Questions Correct | Estimated MTEL Score |
|---|---|
| 0 to 25 | 134 |
| 26 to 30 | 141 |
| 31 to 35 | 148 |
| 36 to 40 | 155 |
| 41 to 45 | 162 |
| 46 to 50 | 169 |
| 51 to 55 | 176 |
| 56 to 60 | 182 |
| 61 to 65 | 189 |
| 66 to 70 | 196 |
| 71 to 75 | 203 |
| 76 to 80 | 210 |
| 81 to 85 | 217 |
| 86 to 90 | 224 |
| 91 to 95 | 230 |
| 96 to 100 | 237 |
Table 2:
| Number of Open-Response Question Points | Estimated MTEL Score |
|---|---|
| 2 | 31 |
| 3 | 36 |
| 4 | 41 |
| 5 | 46 |
| 6 | 50 |
| 7 | 55 |
| 8 | 60 |
Use the form below to calculate your estimated practice test score.
Multiple-Choice Section
| Enter the total number of multiple-choice questions you answered correctly: | |||
| Use Table 1 above to convert that number to the score and write your score in Box A: | A: |
Open-Response Section
| Enter the number of points (1 to 4) for your first open-response question: | |||
| Enter the number of points (1 to 4) for your second open-response question: | |||
| Add those two numbers (Number of open-response question points): | |||
| Use Table 2 above to convert that number to the score and write your score in Box B: | B: |
Total Practice Test Score (Estimated MTEL Score)
| Add the numbers in Boxes A and B for an estimate of your MTEL score: | A + B = |
 = 5
= 5 =
= 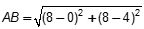 =
=