
Practice Test: Early Childhood (72)
Suggested Testing Time: 4 hours
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
Question 1.
Which of the following statements best explains the primary benefit of reading aloud to young children as part of a home routine?
- Reading aloud expands children's auditory processing, which can contribute to their phonological awareness.
- Reading aloud models descriptive vocabulary and more formal grammatical structures to children.
- Reading aloud provides direct instruction to teach children high-frequency or subject-related vocabulary words.
- Reading aloud expands children's working memory to support their recall of syntactically complex sentences.
Question 2.
Which of the following teacher practices would most directly support the social-emotional development of children who have experienced adverse circumstances?
- providing children with opportunities to practice what they are learning
- creating classroom environments that are organized with clear expectations
- designing learning activities that are highly motivating and based on interests
- establishing relationships that are responsive and sensitive to children's needs
Question 3.
Which of the following instructional approaches would best promote children's generalization of newly acquired knowledge across environments?
- collaborating with grade-level educators to co-plan lessons
- recognizing how families contribute to children's development
- offering repeated opportunities to practice new skills
- designing learning activities that promote choice making
Question 4.
Which of the following actions by a preschool teacher would best support children's motivation to learn?
- offering a variety of items to children that support the development of fine-motor skills
- structuring the daily schedule loosely to provide children with ample play time with minimal active adult support
- creating class environments that foster children's sense of belonging and personal agency
- scripting adult-directed learning activities for children focusing exclusively on academic learning standards
Question 5.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A preschool teacher prepares a list of necessary materials after designing weekly learning centers that encourage children to engage in purposeful play. The teacher's list of materials for one week is shown below.
| Shadow Play | Constructing Structures | Cooking |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The teacher's instructional approach most directly promotes children's learning and development in which of the following areas?
- behavior, history and social science concepts, and self-awareness
- adaptive behavior skills, reading and writing skills, and auditory processing
- emotional regulation, fine- and gross-motor skills, and working memory
- problem solving, science and mathematics concepts, and social communication
Question 6.
A first-grade teacher creates a "Storytelling Theater" activity in which students use props, such as cash registers and tickets, to retell through dramatic play a story that the teacher read aloud. As part of the activity, students construct costumes, paint backdrops, and arrange the pretend stage. The teacher's approach integrates thematic play with comprehending narratives, negotiating play scripts, and:
- thinking abstractly to solve complex problems.
- demonstrating body and spatial awareness.
- using materials in creative and innovative ways.
- applying and making sense of new information.
Question 7.
A parent of an incoming prekindergarten child reports, "Gia naps for two hours every day, so how will she get through the full school day without a nap?" Which of the following teacher responses would most appropriately address the parent's concern?
- "Research indicates that naps interfere with children's overall sleep quality, so it is not recommended that they nap during the day."
- "We help preschoolers get through the day without a nap by engaging them in exciting and fun activities, such as climbing on the play structure and painting."
- "Your child can nap when they appear fussy or sleepy, but otherwise naps are not a part of the daily class routine."
- "Many preschoolers need naps and rest is important to their development, so we have a scheduled rest time when children can sleep or engage in a quiet activity."
Question 8.
Which of the following modifications to the school environment would promote the independence and mobility of a student who ambulates using a power wheelchair?
- offering seating by the door to promote easy access in and out of the classroom
- ensuring that hallways and classroom pathways are free from clutter and barriers
- recommending adult supervision to promote safe decision making in the classroom
- creating a classroom break area to encourage rests and minimize physical fatigue
Question 9.
Which of the following actions should a teacher take first when planning for differentiated learning experiences?
- selecting a curriculum that offers repeated practice opportunities
- creating a progress-monitoring strategy to measure progress
- identifying the skills and concepts that students must achieve
- determining the unique learning style of each student
Question 10.
A prekindergarten teacher uses systematic and strategic observation to assess the physical, sensory, social, emotional, cognitive, and linguistic development of a child. The teacher is most likely to use information obtained from the observations for which of the following purposes?
- determining whether the child requires intervention to support academic readiness
- comparing the child's learning gains to that of grade-level peers
- referencing milestones to quantify the child's acquisition of concepts
- providing data about the child's skill gains across authentic contexts
Question 11.
Which of the following factors is most important for a preschool teacher to consider when assessing the development of children?
- Children are more likely to demonstrate their developmental skills in the home than in a classroom setting.
- Norm-referenced measures provide the most reliable and valid information regarding the development of children.
- Children develop unevenly across domains and inconsistently demonstrate newly acquired skills in different contexts.
- Collecting a variety of authentic work samples is the most effective method for measuring children's development.
Question 12.
Children engage in a whole-group discussion to identify similarities and differences between two different cultural versions of a popular folktale read aloud. This activity would promote children's development of which of the following literacy skills?
- including story elements such as the setting when retelling stories
- engaging in higher-order thinking to comprehend and analyze texts
- making inferences about character actions based on personality traits
- identifying recurring themes to determine the life lesson of each story
Question 13.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A prekindergarten teacher engages a child in conversation while playing. An excerpt of their conversation is shown below.
Teacher: Where do you want me to put Clover, your fuzzy teddy bear?
Child: Clover will go on top of the chair! (Child gestures to the chair.)
Teacher: Okay! What do you think Clover wants to eat?
Child: Strawberries! Put the strawberries on the plate for Clover.
Teacher: Sure! Where are the strawberries? Are they under the sink?
Child: Under the sink? No! They are in the bowl by the sink.
Teacher: I see them now. Okay, Clover. Here are your strawberries.
Which of the following language strengths does the child demonstrate in this exchange?
- producing compound and complex sentences
- executing two-step and multistep directions
- understanding and using spatial concepts
- answering abstract and choice questions
Question 14.
While reading stories aloud, a kindergarten teacher frequently asks children open-ended questions such as, "If that happened to you, how would that make you feel?" Asking open-ended questions while children listen to texts aloud is likely to support their:
- active listening and engagement with the text to derive meaning.
- understanding of content-specific vocabulary words.
- use of learned words and phrases from texts in conversations.
- identification of characters and major events in stories.
Question 15.
While outside, first-grade students work with partners to illustrate, label, and discuss the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits of a plant. This activity is likely to support the vocabulary learning of students in which of the following ways?
- giving students a list of content-specific vocabulary words that should be included in their work samples
- using meaningful contexts to promote students' recall and use of content-specific vocabulary words
- encouraging students to engage in conversation with peers using content-specific vocabulary words
- providing students with meaningful feedback on their use of content-specific vocabulary words
Question 16.
Which of the following factors has the greatest influence on young children's vocabulary knowledge and use?
- explicit instruction in content-area words
- access to books in the home environment
- application of word-learning strategies
- experiences with oral and written language
Question 17.
Which of the following statements best explains the relationship between reading and listening?
- Reading and listening are reciprocal activities that present information and ideas to others.
- Reading and listening use different language centers of the brain to process information.
- Reading and listening both involve comprehending and interpreting language receptively.
- Reading and listening skills must be fully developed before introducing writing concepts.
Question 18.
A teacher encourages students to bring to class new words that they come across at home, on television, or while reading, to add to a Mystery Word box in the classroom. The words may be in English or any other language, and the student may write the word or illustrate the word's meaning on the submission to the Mystery Word box. Words are selected from the box each day and the student who wrote or illustrated the word serves as the Word Expert and is tasked with describing the meaning of the word to the class. This activity is particularly beneficial for students who are English learners because it:
- builds on their background knowledge by providing context for learning new words.
- offers opportunities to demonstrate their linguistic experiences and expertise.
- affords repeated practice opportunities to learn novel language structures.
- targets basic, familiar words to support participation in everyday conversations.
Question 19.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A teacher has students complete a reading survey at the beginning of the school year. An excerpt of a student's completed inventory is shown below.

Reading Interest Survey. Section 1: A series of four teacher questions and student answers. Question 1: What is your favorite book? Why? Answer 1: I really like Magic Tree House books. Annie and Jack go back in time for fun adventures. Sometimes the adventures can be scary. Question 2: Where do you like to read? Answer 2: I like to read on my bed with my fat cat Kona. Question 3: How do you feel when you read by yourself? Answer 3: I feel happy when I read by myself. I get really interested in the story. Question 4: How do you feel when you read to someone else? Answer 4: I don't like to read out loud to my class. It can be embarrassing. Section 2: Reading Topics. There are three columns and three rows of reading topics below the directions: Place a check mark beside the topics you enjoy reading about. In the first column, the topics animals/insects, plants, and sports are listed with check boxes to the left of each topic. In the second column, the topics adventure, movies and famous people are listed with check boxes to the left of each topic. The student left a check mark in the box to the left of adventure. In the third column, the topics fairy tales, monsters, and mysteries are listed with check boxes to the left of each topic. The student left a check mark in the boxes to the left of fairy tales, monsters, and mysteries.
Information obtained from the student reading surveys would most appropriately be used for which of the following purposes?
- designing classroom spaces to replicate students' preferred areas to read
- ensuring that students have access to high-interest texts to promote motivation to read
- offering texts that expand students' experiences with different reading genres
- creating learning opportunities to increase students' comfort with turn taking while reading aloud
Question 20.
A teacher displays learning objectives and student work associated with each learning objective around the classroom. Student work includes artifacts such as illustrations, photographs, scribed narratives, mathematics solutions, and questions posed during discussions. The teacher's approach creates a literacy-rich environment that most directly benefits students in which of the following ways?
- designing a space for students to demonstrate their nonacademic talents
- reminding students of expectations by showcasing the exceptional work of others
- integrating a purpose for students to create content and learn from each other
- creating exhibits that students will reference because they are more interesting
Question 21.
Which of the following questions should a teacher consider first when selecting literary and informational texts for students?
- Are there any words in the text that will be unfamiliar to students?
- Will students have background knowledge of or interest in this text?
- How will this text support students' development of problem-solving skills?
- Have students already read this text at home or in another class?
Question 22.
Use the teacher-created rubric below to answer the question that follows.
| Level 4 | Level 3 | Level 2 | Level 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Includes all important details and uses vocabulary from the story | Includes the most important details and uses some vocabulary from the story | Includes some important details but does not include vocabulary from the story | Does not include important details or vocabulary from the story |
| Sequence | Describes all the events in sequence | Describes many events in sequence | Describes some of the events | Describes one or two events |
A kindergarten teacher regularly assesses children's development of oral narrative skills using the rubric. Data from the rubric would most appropriately be used for which of the following purposes?
- creating guidelines to communicate learning expectations
- comparing a child's performance to that of children in the class
- qualifying the effectiveness of instructional approaches
- identifying a child's progress toward specific learning criteria
Question 23.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
After labeling the external body parts of an animal, kindergarten children are asked to describe the animal to a partner. One child's work and an excerpt of their discussion are shown below.
Child's Work Sample
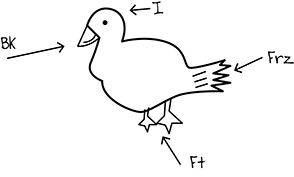
The child illustrated a duck and labeled the duck's beak, feet, eye, and tail feathers. The child wrote the letters B K with an arrow pointing at the duck's beak, I with an arrow pointing at the duck's eye, and F R Z with an arrow pointing at the duck's tail feathers, and F T with an arrow pointing at the duck's feet.
Child's Conversation with Partner
Child 1: Is that a bird?
Child 2: Yes. It's a duck. Here is the beak, eye, feet, and feathers. Do you know why the feet are shaped like this?
Child 1: For swimming?
Child 2: Yes. Ducks have webbed feet for swimming. They use them like paddles.
Child 1: I wish I had paddles on my feet.
Child 2: Me too! Then we could be real fast.
In which of the following ways does this activity demonstrate integration across content areas to support student learning?
- combining play and emergent writing with explicit science instruction
- targeting science vocabulary knowledge to extend oral narratives
- using routines to expand language to express scientific understandings
- connecting discourse with science concepts and emergent writing
Question 24.
A teacher uses weekly one-on-one conferences as an instructional approach to support students' writing skills. When conferring with students, the teacher uses the approach listed below.
- Meet with students individually for five minutes each week.
- Review students' writing samples before each conference.
- Ask students questions that encourage them to reflect on writing strategies they used (e.g., referencing a word wall, stretching out sounds in words).
- Ask students to identify a personal writing strength and an area in which they may need additional support.
- Collaborate with each student to identify a strategy to address their identified need.
The teacher's approach would directly support which of the following outcomes?
- promoting students' positive attitudes toward and motivation to engage in writing activities while taking ownership of their work
- identifying interventions that would support students in applying grade-level grammatical rules and mechanics to their writing
- increasing students' writing stamina by developing a process for editing and revising their writing
- offering direct feedback to students so they can lengthen their writing by expanding their thoughts and ideas
Question 25.
English learners who fluently read and write in their home language are likely to experience successful acquisition of literacy skills in English when given appropriate supports for which of the following reasons?
- Children who speak a home language other than English are primed to acquire reading and writing skills in an additional language.
- Literacy knowledge in a home language provides a foundation for developing reading and writing skills in English.
- Children with literacy skills in a home language have stronger grammatical skills, which is likely to support reading and writing development in English.
- Literacy knowledge in a home language promotes cognitive functioning, which accelerates learning to read and write in English.
Question 26.
Which of the following instructional strategies is most likely to accelerate literacy development of English learners?
- making connections between what students know in their home language and the reading and writing skills they are learning in English
- providing families with reading materials and writing activities that can be used with their child at home
- referring English learners to tiered reading and writing intervention services so that they can receive one-to-one services
- administering benchmark assessments throughout the school year to quantify students' reading and writing progress
Question 27.
After reading a literary text aloud, a second-grade teacher engages students in a discussion to examine the language and technique used by the author. The teacher's approach is likely to promote students' narrative writing development for primarily which of the following reasons?
- Mentor texts provide examples of good writing that can be used as a model when crafting narratives.
- Mentor texts explicitly teach writing skills such as beginning a story with a "hook" to gain the reader's attention.
- Mentor texts show how to accurately use writing mechanics and grammar to produce writing that is coherent.
- Mentor texts identify the steps in the writing process to actively encourage brainstorming, planning, and revising.
Question 28.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
First-grade students work in small groups to conduct research on a major capital or city of their choosing. Student groups are given a variety of reading materials, such as photographs, maps, restaurant menus, and travel guides. In addition, student groups are given the graphic organizer shown below.
City/Capital: blank line
| Popular Foods
|
Climate/Weather
|
| Famous Landmarks
|
Natural Features
|
| Population
|
Fun Facts
|
For which of the following reasons is this graphic organizer an effective strategy for supporting student writing?
- The graphic organizer provides students with a framework to record information about the topic.
- The graphic organizer connects students' background knowledge of the topic with new information.
- The graphic organizer promotes comprehension of the informational texts provided.
- The graphic organizer encourages students to compare and contrast ideas presented.
Question 29.
Which of the following prekindergarten teacher actions would best integrate writing into children's representational play?
- adding notepads and markers to the pretend kitchen area to encourage children to list the daily specials
- providing opportunities for children to form the letters of their first names using sand-letter tracing
- encouraging children to replicate an illustration from a familiar story using paint and crayons
- recording children's oral narrative as they relate a personal experience to their classmates
Question 30.
As part of creating educational portfolios, a kindergarten teacher purposefully collects children's writing samples throughout the school year. The teacher's assessment approach is most likely to yield which of the following sources of information?
- children's grade-level writing skills in comparison to same-age peers
- children's writing strengths, needs, and progress over time
- children's eligibility for special education services for writing
- children's writing growth toward a predetermined set of criteria
Question 31.
Which of the following questions should a prekindergarten teacher consider first when selecting an assessment approach to monitor children's writing progress?
- Will this assessment approach allow me to compare a child's performance to national norms?
- Can this assessment approach be easily embedded into structured and unstructured learning activities?
- What are the different ways that I can modify this assessment so that children can demonstrate their knowledge?
- Can this assessment approach be aligned with the scope and sequence of the curricula to ensure that it measures what I teach?
Question 32.
A second-grade teacher plans a unit in which students will learn about influential scientists who have significantly advanced science and positively contributed to society. In anticipation of this unit, the teacher has strategically selected a variety of reading materials and video clips and is now considering writing activities that would support students' engagement in this topic. Which of the following instructional approaches would best achieve this purpose?
- creating writing experiences that encourage students to reflect on how discoveries have affected their lives
- providing students with opportunities to review and revise the written products of their classmates
- having students reference informational texts to locate key information to answer questions in their daily writing journals
- giving students a model of a written product to reference when generating their own informative texts
Question 33.
Use the checklist below to answer the question that follows.
|
Image of notepad and pencil to the left of the title. The pencil is positioned diagonally to the right over the notepad. |
Editing Checklist |
|---|
blank check box I capitalized the first word in each sentence.
blank check box I capitalized the names of people and places.
blank check box My sentences make sense.
blank check box I wrote complete sentences.
blank check box I ended sentences with a period, exclamation point, or question mark.
blank check box I introduced my topic.
blank check box I ended with a conclusion.
A teacher has second-grade students use the checklist shown to self-edit their informative texts as a step in the writing process. This practice would support student writing development in which of the following ways?
- creating a framework to keep students on task when revising written products
- promoting students' self-awareness to better evaluate specific conventions of writing
- getting students to work collaboratively to strengthen each other's writing
- supporting students in understanding why conventions improve the clarity of writing
Question 34.
Use the arrays below to answer the question that follows.
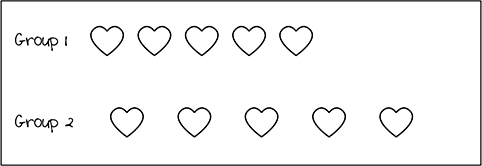
There are two arrays labeled Group 1 and Group 2. Group 1 has five hearts positioned linearly close together. Group 2 has five hearts positioned linearly with about twice the amount of space between each heart as in Group 1.
A kindergarten teacher draws the arrays shown and then asks the class, "Which picture has more hearts?" A child responds, "Group 2 because that picture is bigger." This response indicates that the child has yet to develop which of the following concepts?
- number representation
- conservation of number
- counting on
- one-to-one correspondence
Question 35.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A preschool child is building a structure using magnetic shapes. The teacher engages the child in the following conversation.
Teacher: (holds out two rectangles with different lengths) Tell me what you see here.
Child: I see two rectangles.
Teacher: Yes! There are two rectangles. How are the rectangles different?
Child: (holds up the longer rectangle) This one is more.
Teacher: What does that mean?
Child: It can reach further than the other one.
Based on this conversation, the teacher should address which of the following skills in upcoming instruction?
- using content-specific vocabulary to describe size attributes of objects
- categorizing shapes by number of sides and number of vertices
- measuring the length of objects to compare lengths using quantifiable units
- expressing the areas of equally partitioned shapes as unit fractions
Question 36.
Use the example below of a partitioned number to answer the question that follows.
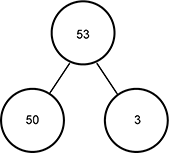
There are three circles with one of the circles on top and two of the circles on the bottom. Each of the two bottom circles are connected to the top circle by a line. In the top circle is the number fifty-three, in the left circle is the number fifty, and in the right circle is the number three.
Students use models like the one shown above to partition whole numbers as part of a lesson about part-part-whole relationships. This activity would most directly support the development of which of the following mathematics skills?
- using numerals to accurately represent an array of objects
- creating strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems
- building an understanding of place value and number sense
- recognizing the relationship between subtraction and addition
Question 37.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
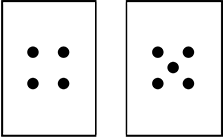
There are two cards positioned side-by-side. The card on the left has four dots arranged in two rows and two columns. The card on the right has four dots arranged in two rows and two columns with a dot in the middle of the four dots.
A kindergarten teacher shows children two cards with arrays based on dice to determine if they can perceive quantities without counting. Which of the following responses from a child shown the cards above best illustrates that the child has acquired this foundational math skill?
- "This one is four and this one is five. I don't have to count them because I can just see how many dots there are."
- "The first card has one, two, three, four. It has four. The second card has one, two, three, four, five. It has five."
- "The second card has one more than the first one. See? One, two, three, four and one, two, three, four, five."
- "There are a lot. Let's see. There are one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine. There are nine dots here."
Question 38.
The first-grade teachers at a school use several instructional strategies to develop and further expand students' conceptual understanding of place value and properties of operations. This approach most directly supports students' access to which of the following upper-elementary topics?
- representing fractions with area models
- estimating time to the nearest minute
- subtracting using the standard algorithm
- multiplying one-digit whole numbers
Question 39.
A first-grade teacher encourages students to use concrete models and drawings when adding and subtracting. Which of the following rationales best supports the teacher's approach?
- Concrete models and drawings increase the accuracy of students' solutions to problems.
- Concrete models and drawings promote students' readiness to learn multiplication and division.
- Concrete models and drawings provide students with opportunities to explore mathematical operations.
- Concrete models and drawings allow students to visualize abstract concepts, which strengthens reasoning.
Question 40.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
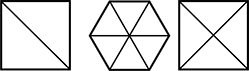
In the diagram, there are three shapes positioned side-by-side that are composed of triangles. The first shape is a square. The square is composed of two large triangles. The second shape is a hexagon composed of six small triangles. The third shape is a square composed of four small triangles.
A kindergarten teacher creates center-based activities in which children compose shapes using different materials, such as tangram pieces, snap cubes, and pattern blocks. One child creates the shapes shown and says, "Look at what I made using all these triangles." Which of the following questions should the teacher ask to expand the child's understanding of composing shapes?
- "What shapes have you created with the triangles?"
- "How many triangles are in each shape?"
- "Can you add one more triangle to each shape?"
- "Do the triangles in each shape make a pattern?"
Question 41.
After preschool children sort shapes, which of the following activities would further expand the children's understanding of definable attributes?
- labeling two-dimensional shapes by figure name
- examining groups of shapes to identify sorting rules
- using shapes to create larger composite shapes
- partitioning shapes equally into halves and fourths
Question 42.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
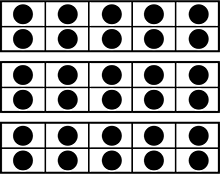
There are three ten frames positioned vertically, one on top of the other. Each ten frame has two rows and five columns with a black circle or counter in each square of the ten frame.
First-grade students are using the ten frames shown to skip-count by fives and tens to thirty. During the activity, a student comments, "Six groups of five make thirty!" The student's observation demonstrates which of the following critical understandings?
- identifying the relationship between addition and subtraction
- recognizing number values without counting
- relating patterns of numbers to the commutative property
- using strategies to add based on place value
Question 43.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A teacher displays an array and asks a student to circle groups of two stars. The teacher then asks the student to count the groups of stars in the array. One student's work is shown below.
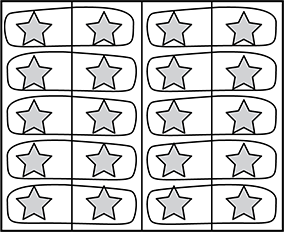
In the array, there are four columns with five stars in each column positioned vertically, one on top of each other. The student has circled stars that are positioned side-by-side in groups of two. The student has circled a total of ten groups of stars.
Which of the following statements best describes the primary purpose of this activity?
- Adding equal groups of stars will support the student's recognition of patterns.
- Organizing stars into pairs will promote the student's use of addition strategies.
- Manipulating the array of stars will introduce the student to the associative property.
- Partitioning stars into groups will promote the student's visualization of division.
Question 44.
While pretending to chop fruit for a salad, a preschool child says, "The cups of fruit salad should have the same number of strawberries. They need to be equal." In this scenario, the child demonstrates development of which of the following skills?
- counting concrete objects
- describing objects in space
- using comparative language
- identifying groups of objects
Question 45.
Use the excerpt below from a second-grade student's quick-write journal to answer the question that follows.
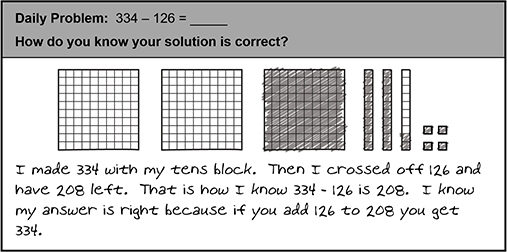
In the quick-write journal, there are three one-hundreds blocks, three tens-blocks, and four ones-blocks. Each one hundred block has ten rows and ten columns, and each tens block has one column and ten rows. The student shaded in a one hundred-block, two tens-blocks, two rows in the third tens-block, and four of the ones blocks. The student wrote: I made 334 with my tens block. Then I crossed off 126 and have 208 left. That is how I know 334 minus 126 is 208. I know my answer is right because if you add 126 to 208 you get 334.
Which of the following strengths is most evident in the student's work sample?
- persevering in solving challenging problems
- observing patterns to reason abstractly about problems
- using tools strategically to accurately solve problems
- justifying a solution to a problem using a viable argument
Question 46.
Use the clock chart below to answer the question that follows.
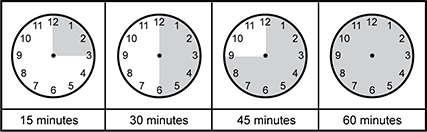
The clock chart has four shaded clocks arranged horizontally side-by-side. The first clock is shaded from twelve to three, the second clock is shaded from twelve to six, the third clock and is shaded from twelve to nine, and the fourth clock is shaded in its entirety.
A second-grade teacher references this chart showing analog clocks with shaded overlays to highlight minutes in an hour. In addition to promoting understanding of time relationships, the teacher's instructional approach would most directly build a foundational understanding of which of the following concepts?
- contextualizing fractions to give meaning to phrases such as "half past"
- recognizing the position of the hour and minute hands to tell time fluently
- solving addition and subtraction problems involving intervals of time
- using words to represent temporal concepts, such as "before" and "after"
Question 47.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Second-grade students complete an exit ticket following a lesson about solving word problems using subtraction. One student's work is shown below.

A word problem is presented: This summer, Jack grew 36 peppers and 7 watermelons. Rosa grew 23 peppers and 17 tomatoes. How many more peppers did Jack grow than Rosa? The student uses a partitioned rectangle to decompose the number thirty-six. The rectangle is divided into two rows and the first row has the number thirty-six. The second row of the rectangle is divided into two sections with the first section being 2 thirds the length of the rectangle and the second section being 1 third the length of the rectangle. In the first section of the second row, is the number twenty-three and in the second section, the number thirteen. Below the partitioned rectangle, the student writes: Jack grew 13 more peppers than Rosa.
In this work sample, the student demonstrates emerging understanding of which of the following mathematics skills?
- communicating addition and subtraction problem-solving strategies
- subtracting whole numbers up to 100 with automaticity
- recognizing the relationship between addition and subtraction
- solving two-step word problems using subtraction
Question 48.
Prekindergarten children work in small groups to construct structures using wooden blocks, craft sticks, paper plates, and magnetic tiles. Which of the following instructional strategies would best connect the children's conceptual understanding of shapes to the composite shapes used in their structures?
- asking the children open-ended questions to encourage discussion of how and why they used certain shapes in their structures
- having the children draw a picture of their structure and color the different shapes they used
- providing the children with assembled structures using the basic shapes for reference
- prompting the children to describe how shapes appear when viewed from different perspectives, including the top and various side views
Question 49.
Which of the following activities would best support prekindergarten children's interest and motivation in representing three-dimensional shapes?
- classifying real-life objects into three-dimensional shape categories
- working with a partner to find three-dimensional shapes around the room
- creating three-dimensional shapes using a variety of materials
- organizing three-dimensional shapes based on their attributes
Question 50.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A second-grade teacher encourages students to reflect on their mathematics learning following a series of learning activities. One student's self-reflection is shown below.

The student's self-reflection includes four rectangles positioned vertically and connected by arrows. The first rectangle reads, This week my learning successes were and the student responded, I learned to measure objects using a ruler, yardstick, and measuring tape. The second rectangle reads, What I don't know yet and the student responded, Sometimes I have a hard time solving word problems involving measurement. The third rectangle reads, What mistakes did I make that helped me learn and the student responded, “I was trying to solve a word problem using addition. I realized I needed to use subtraction to find the difference. The fourth rectangle reads, What will I do to make sure I improve this week? and the student responded, I'm going to slow down and take my time reading word problems. You can add and subtract measurements too!
Encouraging students to engage in self-reflection activities such as this would most directly develop which of the following skills?
- valuing intellectual growth and personal accomplishments
- using observations to develop accurate conjectures
- understanding different approaches for solving problems
- evaluating whether a learning experience is relevant and meaningful
Question 51.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A second-grade student completes two-digit addition problems using manipulatives and a graphic organizer. The student's graphic organizer for the problem 13 + 16 = blank line is shown below.
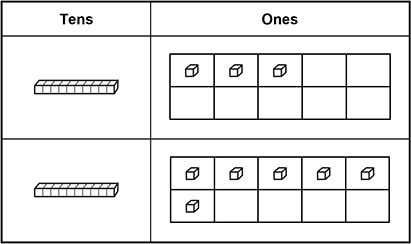
The graphic organizer is divided into two columns and three rows. In the first row are the headers Tens on the left and Ones on the right. Beneath the Tens header in the first column is a tens block in the second and third row. Beneath the Ones column is a tens frame in the second and third row. Each tens frame has two rows and five columns. In the second row of the graphic organizer, the tens frame has three cubes in the first, second, and third columns in the first row. In the third row of the graphic organizer, the tens frame has five cubes in the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth columns of the first row and the first column in the second row.
This problem-solving approach supports the student's understanding of which of the following concepts related to addition?
- how place value relates to regrouping
- the relationship between addition and subtraction
- how addition is the act of increasing one amount by another
- the relationship between regrouping and the standard algorithm
Question 52.
Which of the following instructional strategies would support students in persevering in solving problems that are appropriately challenging?
- giving students the opportunity to redo their work after receiving feedback
- designing activities with multiple entry points based on students' strengths
- grouping students for center-based activities based on their abilities
- modeling strategies for students before they engage in independent work
Question 53.
Use the work sample below from a second-grade student to answer the question that follows.
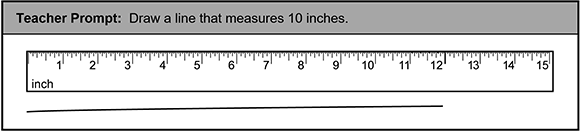
A teacher prompt says Draw a line that measures 10 inches. The work sample shows a ruler that is fifteen inches long with a line drawn below it that is twelve inches long.
Based on this work sample, which of the following instructional strategies should be implemented first to support the student's learning?
- asking the student to explain how they know that the line is 10 inches long
- providing the student with real-life opportunities to measure objects
- delivering explicit instruction to the student before modeling how to measure lengths
- having the student re-draw the line after reviewing written feedback
Question 54.
Use the student work sample below to answer the question that follows.
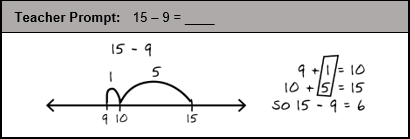
In the work sample, the student responds to the teacher prompt: 15 minus 9 = blank. The student rewrites the teacher's prompt, 15 minus 9, at the top of the work sample. Directly beneath the equation, the student illustrated a line with an arrow on each end. The student has partitioned the line with three numbers, 9, 10, and 15. Above these numbers, the student has connected numbers 9 and 10 and 10 and 15 with arches. Above the arch connecting 9 and 10 the student wrote 1 and above the arch connecting 10 and 15 the student wrote 5. To the right of the number line, the student wrote, one on top of the other, the equations: nine plus one equals ten and ten plus five equals fifteen. In addition, the student connected the equations with a rectangle around the numbers 1 and 5. Beneath these two equations, the student wrote so and the equation fifteen minus nine equals six.
Following a mini-lesson, a student applies the "make-a-ten" strategy to solve a subtraction problem as shown. Supporting the student's understanding and application of this strategy is likely to further promote concept development in which of the following areas?
- representing quantities to solve problems using modeling
- recognizing how operations relate to one another
- recalling basic addition and subtraction math facts fluently
- expanding efficient procedures for using the standard algorithm
Question 55.
A prekindergarten teacher plans learning activities to support children's ability to compare groups of objects in scattered configurations. Before introducing this concept, the teacher should determine if children have acquired which of the following foundational skills?
- composing and decomposing numbers 1 through 10
- representing groups of objects with corresponding number names
- using objects to solve subtraction problems within 10
- understanding the relationship between numbers and quantities
Question 56.
Which of the following activities would best support a prekindergarten child in learning the names of numbers?
- copying numerals on a whiteboard
- matching numerals to corresponding arrays
- counting to tell the number of objects
- singing interactive counting songs routinely
Question 57.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A second-grade teacher asks students to shade hundreds blocks to represent the value of coins and a dollar bill. One student's work is shown below.
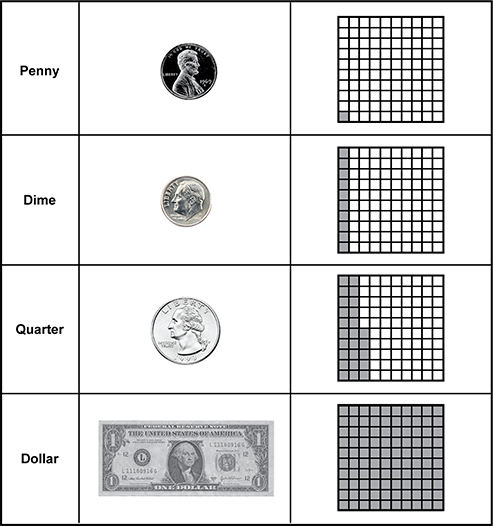
The graphic organizer has three columns and four rows. In the first row, is the word Penny in the first column, a photograph of a penny in the second column, and a hundreds block with one block shaded in the third column. In the second row, is the word Dime in the first column, a photograph of a dime in the second column, and a hundreds block with ten shaded blocks in the third column. In the third row, is the word Quarter in the first column, a photograph of a quarter in the second column, and a hundreds block with twenty-five blocks shaded in the third column. In the fourth row, is the word Dollar in the first column, a photograph of a dollar in the second column, and a hundreds blocks with one hundred blocks shaded in the third column.
This activity is likely to develop students' foundational understanding of concepts needed to perform which of the following skills in later grades?
- estimating money values to the nearest whole unit
- solving real-world problems involving money
- relating money values to fractions and decimals
- comparing two different amounts of money
Question 58.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A teacher has a student complete a math questionnaire at the beginning of the school year. An excerpt from the student's completed questionnaire is shown below.
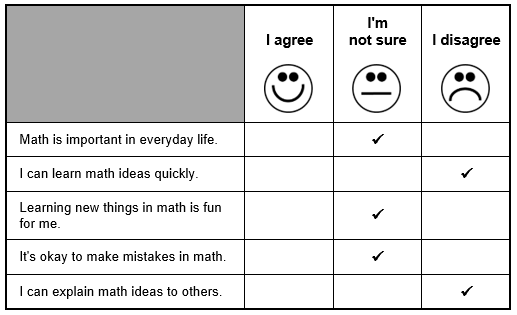
A math questionnaire has a smiling face below the words I agree, a neutral face under the words I�m not sure, and a frowning face beneath the words I disagree. The following statements from the questionnaire have I'm not sure checked: Math is important in everyday life, Learning new things in math is fun for me, It's okay to make mistakes in math. The following statements have I disagree checked: I can learn math ideas quickly and I can explain math ideas to others. No statements have I agree checked.
The teacher's assessment approach is likely to benefit the student's learning in which of the following ways?
- identifying mathematical strengths to assign the student to an appropriate peer group based on academic achievements
- fostering a positive disposition toward mathematics to enable the student to develop good work habits
- identifying learning needs to ensure that the student receives appropriate instruction to develop grade-level mathematics skills
- providing individualized and rigorous intervention based on the student's demonstrated misconceptions
Question 59.
During an activity, a kindergarten teacher observes that many of the children have gender stereotypes associated with community workers. Which of the following teacher actions would best address the students' beliefs?
- asserting to students that individuals of any gender can serve as community workers
- focusing on the duties of each community worker while avoiding gender discussions
- inviting workers into the classroom that represent all genders to discuss their roles within the community
- ensuring that each gender is represented at least once when providing instruction about community workers
Question 60.
Second-grade students read a collection of literary and informational texts about children's experiences of attending schools as part of the national desegregation movement that occurred in the United States in the 19 fifties and 19 sixties . Which of the following discussion topics would best encourage students to understand the perspectives of children who experienced prejudice and racism?
- What steps did teachers and parents take to prepare for children's integration into new schools?
- Would you want to attend a school when teachers and other parents protested your being there?
- How were children affected by teachers and parents who protested their attendance at schools?
- Why would children attend a school where teachers and other parents were not welcoming to them?
Question 61.
Which of the following statements best explains why it is important for teachers to review traditional texts such as nursery rhymes and fables before sharing them with children as a step to support an inclusive classroom environment?
- Traditional texts are sometimes irrelevant in a modern classroom because they are not culturally relevant.
- Traditional texts can be too difficult for children to understand given the outdated language.
- Traditional texts often feature stereotypical gender roles that can perpetuate bigotry.
- Traditional texts frequently have characters and topics that are unrelatable to children.
Question 62.
Which of the following foundational understandings is important for students to develop as part of recognizing the complex relationship between European settlers and Native Peoples in southeastern Massachusetts?
- European settlers migrated to North America to develop fair trade agreements with the Native Peoples.
- European settlers migrated to areas of North America that were already inhabited by Native Peoples.
- European settlers lived harmoniously with the Native Peoples, as demonstrated by their fair bartering.
- European settlers learned new skills from Native Peoples, such as harvesting crops and building shelters.
Question 63.
A teacher overhears a student say to another student, "You are being unfair, and your words are unkind. You can play with us, but you have to share and be nice." This student is demonstrating an emerging understanding of which of the following concepts?
- behaviors that are consistent with good citizenship
- the importance of following agreed-upon classroom rules
- qualities that make for caring and unselfish leaders
- the roles of group members working together
Question 64.
Which of the following questions would most effectively lead students to an inquiry-based learning experience during a unit on geographic landforms?
- "How do the oceans make the world habitable?"
- "Do deserts have a lot of rainfall?"
- "Can you describe the characteristics of a country that interests you?"
- "Are there any plains where we live?"
Question 65.
Use the graphic organizer below to answer the question that follows.
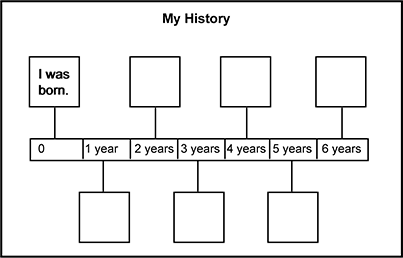
The graphic organizer is titled My History. There is a center rectangle divided into seven sections. The first section is labeled 0, the second section is labeled 1 year, the third section is labeled 2 years, the fourth section is labeled 3 years, the fifth section is labeled 4 years, the sixth section is labeled 5 years, and the seventh section is labeled 6 years. Each section of the rectangle has a box connected to it by a line. These boxes alternate in position from above the rectangle to below the rectangle. The first box is positioned above the section o and reads I was born.
Children use the graphic organizer shown to illustrate and describe major events in their lives as part of a lesson on chronology. Which of the following pieces of information is most critical for children to include in their personal timeline?
- the location where an event occurred
- the causes and consequences of an event
- the individuals who participated in an event
- the sequencing of the events that took place
Question 66.
As part of a research project, second-grade students interview family members, neighbors, or friends to discover where they moved from and why they came to Massachusetts. This activity gives students the opportunity to learn firsthand about:
- how people who migrate enrich their communities.
- the cultural traditions brought by people who migrate.
- push and pull factors that influence why people migrate.
- how the customs of people who migrate influence communities.
Question 67.
Students are asked to work in small groups to collectively construct a timeline of a prominent historical figure using a variety of reading materials, including biographies, maps, and archived newspaper articles. This learning activity would most directly promote students' development of which of the following skills?
- adding visual displays to enhance the meaning of informative writing
- citing evidence from texts to describe key events in history
- understanding how the qualities of a leader affect positive social change
- connecting individual events to larger movements and themes
Question 68.
Use the class bulletin board below to answer the question that follows.
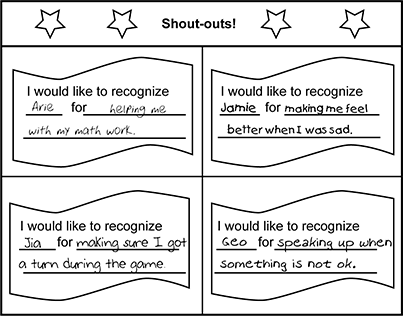
The bulletin board is titled Shout-Outs with four boxes arranged in two rows and two columns beneath the title row. In the upper left-hand corner, the sentence frame, I would like to recognize [blank line] for [blank line] “was completed by a student to read, I would like to recognize Arie for helping me with my math work. In the lower left-hand corner, the sentence frame, I would like to recognize [blank line] for [blank line] was completed by a student to read I would like to recognize Jia for making sure I got a turn during the game. In the upper right-hand corner, the sentence frame I would like to recognize [blank line] for [blank line] was completed by a student to read, I would like to recognize Jamie for making me feel better when I was sad. In the lower right-hand corner, the sentence frame I would like to recognize [blank line] for [blank line] was completed by a student to read I would like to recognize Geo for speaking up when something is not ok.
Second-grade students are encouraged to post notes recognizing the kind acts of their classmates on a class bulletin board. This activity is most likely to support student progress toward which of the following learning objectives?
- Students will identify examples of caring, justice, and fairness within the classroom community.
- Students will uphold democratic principles found within the classroom and community.
- Students will uphold responsibilities to collectively work toward classroom community goals.
- Students will identify the importance of unity and diversity within the context of the classroom.
Question 69.
Use the student group work sample below to answer the question that follows.
| Food | Clothing | Shelter | Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| water | rain jacket | waterproof tent | insect repellent |
| fruit | boots | bug net | sunblock |
| nuts | socks | sleeping bag | bandages |
| energy bars | hat | kindling | toilet paper |
Students work in small groups to generate a list of goods they will bring on an imaginary journey to a tropical rain forest. Which of the following skills must students apply to engage effectively in this activity?
- providing examples of necessary services
- considering basic needs when selecting goods
- determining how scarcity affects choices
- identifying different ways that wants can be met
Question 70.
First-grade students are learning about how individuals participate in elections to vote for community leaders. Which of the following activities would best promote students' understanding of the importance of voting for individuals who demonstrate good leadership qualities?
- reading texts aloud with students that feature leaders who have effected significant change
- engaging students in a whole-group discussion to generate a list of leadership qualities
- staging an election in which students vote for class leaders based on their friendship characteristics
- creating an anchor chart that identifies the leadership qualities demonstrated by each student
Question 71.
Throughout the school year, a kindergarten teacher creates dramatic play centers with a variety of costumes, props, and materials related to jobs that are performed inside and outside of the home. The teacher's instructional approach is likely to promote children's understanding of work by:
- targeting children's development across physical, cognitive, and linguistic domains.
- engaging children in real-world activities that develop planning and organizing.
- providing children with opportunities to construct knowledge through social engagement.
- using explicit teaching to support children's acquisition of specific academic concepts.
Question 72.
A prekindergarten teacher carefully selects books to read aloud that feature citizenship themes, such as being helpful and respectful to others. Which of the following teacher strategies would best support children's recognition of character traits that are consistent with good citizenship during read-aloud activities?
- labeling positive attributes of characters as they occur in stories
- re-reading passages that include character comments that are kind
- creating an anchor chart listing productive behaviors of characters
- encouraging comments about character actions and motivations
Question 73.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Following a read-aloud, a prekindergarten teacher asks students to illustrate events in the story using a graphic organizer. One child's work is shown below.
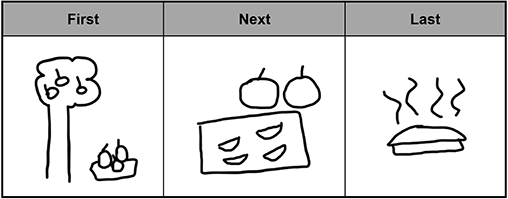
The graphic organizer has three sections positioned side-by-side labeled First, Next, and Last. Under the label First the child illustrated a tree with three apples on the tree and three apples on a cloth next to the tree. Under the label Next the child illustrated a cutting board with four slices of apple below two apples. Under the label Last the child illustrated a pie with steam rising above it.
This activity supports children's understanding of foundational social science concepts primarily by supporting skills related to:
- using words to express cause-and-effect relationships.
- gathering information from texts.
- using phrases to describe personal experiences.
- putting events into sequential order.
Question 74.
A teacher frequently reads historical fiction stories aloud that reinforce grade-level history and social science concepts. The teacher's instructional approach most directly benefits student learning in which of the following ways?
- expanding students' accurate and detailed recall of historical events
- promoting students' interest in history through character experiences
- supporting students' understanding of factors that influenced historical events
- encouraging students to evaluate the credibility and relevance of historical sources
Question 75.
Which of the following activities best utilizes cooperative learning to teach map skills to kindergarten children?
- engaging children in a whole-group discussion about how to use maps to locate important landmarks within the state
- inviting a cartographer to the class as a guest speaker to explain how different maps are created
- having the children work in small groups to locate a treasure using a map and illustrated clues
- reading a story aloud to the class about a character who uses a map to rescue others
Question 76.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A prekindergarten teacher engages two children in conversation after listening to and observing their comments, behaviors, and actions. An excerpt of the conversation is shown below.
Jayla: I don't want to play with you! Go away! [Jayla is attempting to push Leo, another child in the class.]
Teacher: What happened? Why did you say you didn't want to play with him?
Jayla: He keeps screaming. It's loud and hurts my ears.
Teacher: Leo, can you tell Jayla how that makes you feel?
Leo: That makes me feel sad. Jayla doesn't want to play with me.
Teacher: Instead of saying, "I don't want to play with you," you could ask Leo to "please stop screaming."
Jayla: Can you stop screaming please?
Leo: I won't scream.
Teacher: That's good to hear, Leo! I noticed that you asked Leo to stop screaming, Jayla.
The teacher's instructional approach is likely to support a positive classroom community in which of the following ways?
- having children confront other children who are demonstrating inappropriate behavior
- teaching children that it is expected that they treat each other with kindness and respect
- encouraging children to use language to express their feelings when experiencing conflict with others
- getting children to consider their own perspectives when judging others' actions as hurtful
Question 77.
In preparation of planting a class garden, first-grade students work together to determine which tasks must be completed and who should be assigned each task. This activity is most likely to support students' understanding of:
- the importance of being a leader and working hard.
- how to work as a group to achieve a common goal.
- the need to evaluate the contributions of others.
- how to engage in the democratic process.
Question 78.
Use the Classroom Bill of Rights below to answer the question that follows.
Our Classroom Bill of Rights
We have the right to learn.
We have the right to have breakfast and lunch.
We have the right to use the bathroom.
We have the right to feel safe.
We have the right to have an opinion.
At the beginning of the school year, second-grade students work together to create a Classroom Bill of Rights. This activity would most directly support students in making which of the following conclusions?
- Rights are a set of values that bind us together as a nation.
- Good citizens participate in their community and defend the rights of others.
- Rights are a fundamental set of freedoms that belong to everyone.
- Individuals who observe the rights of others respect the rule of law.
Question 79.
As one of the weekly class jobs that second-grade students rotate, the News Anchor is responsible for reporting on the weather and two events happening in the classroom, school, or community. Students are asked to respond to the news in their informational journals following the daily news report. This activity integrates civics content with which of the following literacy learning objectives?
- responding to questions using clearly organized writing
- participating in a shared writing project with classmates
- recounting experiences when writing personal narratives
- including facts in a written summary about a specific topic
Question 80.
Use the vocabulary words below to answer the question that follows.
- water
- ice
- recreation
- lake
- ocean
- river
- commerce
- pond
- stream
- hydrology
Second-grade students work in small groups to define these vocabulary words using illustrations and sentences. Understanding these vocabulary words would most directly support students' progress toward which of the following learning standards?
- Students will give examples of how water is used.
- Students will label bodies of water in defined areas.
- Students will locate water on Earth in all three phases.
- Students will state why water is important to the Earth.
Question 81.
A first-grade teacher uses an interactive whiteboard to engage students in an activity in which they label the parts of different plants, such as a water lily, cactus, and sunflower. When the teacher is describing the purpose of plant parts, which of the following comparisons would best support students in conceptualizing the function of roots?
- "Plant roots are like a rope in a well of water."
- "Plant roots are like a hose attached to a water tap."
- "Plant roots are like a drinking straw in a glass of water."
- "Plant roots are like a river that runs between two cities."
Question 82.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
First-grade students work in small groups to find photographs of cats in books and identify the traits of the cats in photographs. The students place a sticker in the appropriate column of a chart corresponding with each cat's traits. One group's completed chart is shown below.
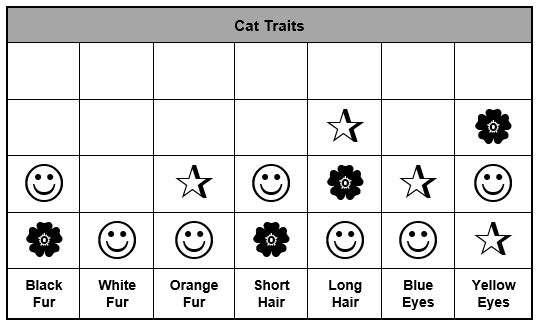
The chart has seven columns and six rows. The first row is titled Cat Traits and in the last row the seven columns are labeled from left to right as Black Fur, White Fur, Orange Fur, Short Hair, Long Hair, Blues Eyes, and Yellow Eyes. The Black Fur column has two stickers, one is a smiley face and the other is a flower. The White Fur column has one smiley face sticker. The Orange Fur column has two stickers, one is a star and the other is a smiley face. The Short Hair column has two stickers, one is a smiley face and the other is a flower. The Long Hair column has three stickers, a star, a flower, and a smiley face. The Blue Eyes column has two stickers, a star and a smiley face. The Yellow Eyes column has three stickers, a star, a smiley face, and a flower.
Which of the following activities should be implemented next to expand students' understanding of inherited traits?
- determining which traits are dominant and which traits are recessive
- distinguishing between traits that are inherited versus those that are acquired
- observing similarities in traits between an animal parent and its offspring
- reading informational texts about traits and how these relate to chromosomes
Question 83.
A kindergarten teacher takes a photograph of each child alongside a classroom plant at the beginning of each month. As an end-of-the-year activity, children organize their photographs in chronological order and display these around the classroom. This activity most directly supports children's development of which of the following science skills?
- describing similarities in the life cycle of plants and animals
- recognizing that plants and animals grow and change over time
- explaining how animals depend on plants to meet their survival needs
- identifying how plants and animals adapt to their environments
Question 84.
A prekindergarten teacher creates discovery tables with a variety of materials, such as pinecones, sand, seashells, bells, cinnamon sticks, maple syrup, and rocks. Small groups of children will rotate between the discovery tables and will be encouraged to explore the materials. Which of the following science concepts is the teacher most likely targeting in this activity?
- distinguishing between living objects and nonliving objects
- using the five senses to gather information about objects
- categorizing objects as either a solid or a liquid
- identifying similarities and differences among objects
Question 85.
A first-grade teacher engages students in a whole-group discussion to design an investigation about the properties of light. Following the discussion, students decide that they will need flashlights, water, bottles, cups, and wooden blocks to conduct their investigation. As students conduct their investigation, the teacher should support them in making which of the following conclusions?
- Light travels through all objects depending on the brightness of the light.
- Light can be used to send signals to communicate with others.
- Light travels in waves and can pass through some but not all objects.
- Light can transfer energy to objects as evidenced by temperature changes.
Question 86.
Small groups of second-grade students were given felt squares, sandpaper sheets, carpet tiles, and blocks and were instructed to investigate what happens when you rub the block with the different materials. Following the investigation, the teacher asks the students, "What did you observe when you rubbed the block with different materials?" Which of the following student responses demonstrates an understanding of the effects of friction on the temperature of objects?
- "You need something like a heater or fire to warm up the block."
- "The block got the warmest when we rubbed it with sandpaper."
- "We rubbed the block with the felt square, but nothing happened."
- "The block wasn't hotter or colder after it was rubbed with the carpet tile."
Question 87.
In response to the class hamster escaping from the cage, students would like to design a solution to better secure the closure of the cage door. Which of the following initial steps would best prepare students to identify an effective solution for this problem?
- gathering qualitative data about cage door prototypes
- constructing model cage doors based on illustrations
- identifying features that would fasten the cage door securely
- observing the cage door for possible design flaws
Question 88.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Second-grade students create double-layered hand mitts using zipper-lock bags containing feathers, fat (i.e., vegetable shortening), cotton balls, or nothing. Students submerge their hands into ice water for a minute while wearing the mitts and are asked to record their findings in their science journals. One student's journal entry is shown below.
| Feathers | Fat | Cotton Balls | Nothing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feathers helped keep my hands stay warm. | Fat helped my hands stay the warmest. | Cotton balls weren't as warm as the feathers and fat. | My hands were really cold! |
After conducting this investigation, students will design a special container to insulate liquids to keep them warm. This sequence of learning activities would best support students' development of which of the following technology/engineering skills?
- applying results of tests to redesign a prototype
- gathering information to build effective models
- recognizing the successes and limitations of materials
- developing solutions to observed design problems
Question 89.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
A prekindergarten teacher designs a "mystery bag" activity in which children use their sense of smell, touch, and hearing to identify objects inside a nontransparent bag. Children are paired with a partner and given a "mystery bag" filled with objects such as the one pictured below.
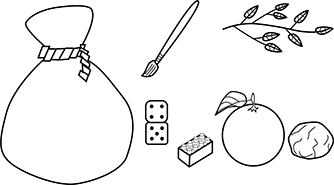
The illustration is of the mystery bag and its contents. Beside the mystery bag is a paint brush, a domino, a building block, an orange, a rock, and a branch with leaves.
While engaging in this activity, a teacher overhears a child say to their partner, "This is something small and plastic with smooth circles on top." In addition to using senses to gather information, the student is developing an emerging understanding of which of the following science concepts?
- using observations to explain how objects are alike
- identifying physical properties to describe objects
- distinguishing between natural and human-made objects
- investigating differences between living and nonliving objects
Question 90.
Kindergarten children establish a goal to reduce waste produced by the class each week. Children identify several steps, such as labeling color-coded bins as "Recycle," "Repurpose," and "Compost," that would support them in achieving this goal. This activity is likely to benefit children's learning in which of the following ways?
- promoting children's critical thinking through observation
- empowering children to develop a plan to overcome a problem
- using hands-on experiences to support children's concept development
- encouraging reflection to grow children's content knowledge
Question 91.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Prekindergarten children are encouraged to use their science journals to illustrate animals in their local environments during weekly nature walks. One child creates the journal entry shown below.
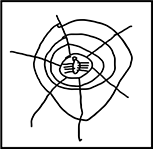
The child has illustrated a spiderweb with a small spider in the middle of the web.
Which of the following statements best explains the primary purpose of this activity?
- Outdoor learning opportunities are more likely to promote children's interest in scientific topics.
- Structuring learning opportunities for children to observe natural scientific phenomena promotes inquiry.
- Embedding sensory exploration into learning opportunities promotes understanding of scientific concepts.
- Integrating motor movement into learning opportunities enhances scientific concept development.
Question 92.
Use the picture cards below to answer the question that follows.
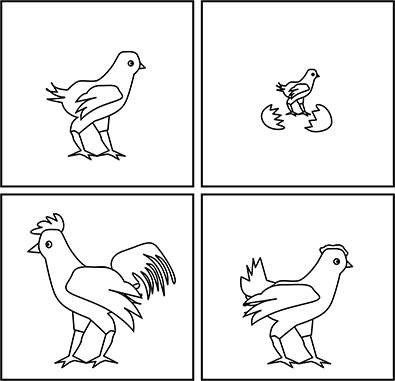
There are four picture cards of chickens arranged in two rows and two columns. In the upper left-hand corner is a young chicken without tail feathers or a comb. In the upper-right hand corner is a chick that has just hatched from an egg. In the lower left-hand corner, there is a chicken with tail feathers, comb, and full wings. In the lower right-hand corner, there is a chicken with a small comb with some tail feathers.
A kindergarten teacher distributes the picture cards shown and instructs children to sequence the cards according to how a chicken grows and changes. Which of the following extension activities would deepen students' understanding of how a chicken grows and changes over time?
- having students use the sequenced cards as a model to illustrate the growth and changes of the chicken in their journals
- engaging students in a one-on-one conversation to assess their knowledge of how a chicken grows and changes
- adding additional picture cards to the activity so that students learn more details about how a chicken grows and changes
- pairing students with a partner to share their knowledge about how a chicken grows and changes over time
Question 93.
Use the student work sample below to answer the question that follows.
| Same | Different |
|---|---|
| four legs | number of spots |
| red nose | fur color on head |
| rounded ears | size |
| furry | eye color |
First-grade students work in small groups to identify similarities and differences between a dog and its puppy and complete a chart listing them. This activity most directly supports children's progress toward which of the following science learning standards?
- Students will recognize the acquired traits of a parent and offspring.
- Students will understand that traits are passed down genetically.
- Students will observe shared traits between offspring and a parent.
- Students will distinguish between dominant and recessive traits.
Question 94.
Which of the following activities would best support prekindergarten children's understanding of the relationship between the size and shape of shadows and a light source?
- using flashlights and transparent and opaque materials to explore while engaging in play
- illustrating pictures showing sunshine and shadows using a variety of art materials
- working in small groups to develop signals to communicate specific messages using a light source
- working in pairs to trace each other's shadow while standing outside at different times on a sunny day
Question 95.
First-grade students would like to develop a rainwater collection system for the school garden to conserve water. Which of the following steps should the students take first in designing a rainwater collection system?
- testing different prototypes of rainwater collection systems
- analyzing data to improve models of rainwater collection systems
- researching rainwater collection systems developed by others
- sketching blueprints for possible rainwater collection systems
Question 96.
A first-grade teacher uses portfolios as an assessment approach to evaluate students' understanding of scientific concepts. Students are responsible for selecting work samples that are included in their portfolios. Including students in the portfolio assessment process is most likely to have which of the following outcomes?
- supporting students' understanding of task expectations
- promoting students' ownership of their accomplishments
- providing students with feedback regarding their performance
- increasing the accuracy and consistency of student scores
Question 97.
In which of the following ways does self-directed play support children's readiness to learn science concepts?
- using children's natural interests to provide explicit instruction about various topics
- creating highly organized activities to model problem-solving skills for children
- providing authentic opportunities for children to investigate the world around them
- grouping materials so that children engage in learning with a specific purpose
Question 98.
Which of the following early learning experiences would most directly support children's readiness to learn about reversible changes to materials?
- exploring the properties, such as texture and hardness, of natural objects
- going to museums with hands-on exhibits that promote interest and curiosity
- engaging in outdoor play, such as swinging and sliding on the playground
- hearing read-alouds of informational texts about influential scientists and their discoveries
Question 99.
A prekindergarten teacher observes a small group of children working together to build a bridge over an imaginary river. The children use a variety of materials, such as linking blocks, paper towel rolls, and interlocking bricks, to construct the bridge. This play experience is most likely to promote the development of which of the following sets of foundational engineering skills?
- thinking creatively, solving problems, and planning
- collecting data, analyzing data, and discussing findings
- conducting research, asking questions, and identifying solutions
- testing prototypes, improving designs, and drawing new designs
Question 100.
A teacher strategically designs learning centers to create opportunities to expand and further support students' understanding of science and technology/engineering concepts. Center materials are rotated throughout the school year to correspond with the learning standards being introduced. When students are provided with discovery-based learning opportunities, such as learning centers, they are more likely to:
- develop practical skills and work habits that are required to acquire adaptive behavior skills.
- use materials, such as carboard boxes and rubber bands, with purpose and creativity.
- connect concepts and apply this knowledge to solve real-world issues and problems.
- plan and carry out tests on models independently to determine which design features need to be improved.
Open-Response Items
The directions shown below represent what you will see on the actual test. For the purposes of this practice test, you will be able to type your written responses in the boxes provided on the answer key.
This section of the test consists of two open-response item assignments. You will be asked to prepare a written response of approximately 150�300 words for each assignment. You should use your time to plan, write, review, and edit your response for each assignment. You must write responses to both of the assignments.
For each assignment, read the topic and directions carefully before you begin to work. Think about how you will organize your response.
As a whole, your response to each assignment must demonstrate an understanding of the knowledge of the field. In your response to each assignment, you are expected to demonstrate the depth of your understanding of the subject area by applying your knowledge rather than by merely reciting factual information.
Your response to each assignment will be evaluated based on the following criteria.
- Purpose: the extent to which the response achieves the purpose of the assignment
- Subject Knowledge: appropriateness and accuracy in the application of subject knowledge
- Support: quality and relevance of supporting evidence
- Rationale: soundness of argument and degree of understanding of the subject area
The open-response item assignments are intended to assess subject knowledge. Your responses must be communicated clearly enough to permit valid judgment of the evaluation criteria by scorers. Your responses should be written for an audience of educators in this field. The final version of each response should conform to the conventions of edited American English. Your responses should be your original work, written in your own words, and not copied or paraphrased from some other work.
Be sure to write about the assigned topics. You may not use any reference materials during the test. Remember to review your work and make any changes you think will improve your responses.
Question 101.
Use the information provided in the exhibits to complete the assignment that follows.
Using your knowledge of foundational history and social science skills and early childhood history and social science content and instruction, write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words in which you:
- identify one academic strength that the child demonstrates related to the history and social science content skill specified;
- identify one academic need that the child demonstrates related to the history and social science content skill specified;
- describe a learning activity that would address the child's identified academic need and promote progress toward the specified history and social science content standard; and
- explain why this learning activity would be effective for the child.
Be sure to cite specific evidence from the exhibits provided to support all parts of your response.
Exhibit: Lesson Plan
As part of a unit on buying goods and services, a kindergarten class is learning to make choices as consumers about the things they need and want. In a previous lesson, children identified the basic human needs of food, clothing, and shelter and distinguished between needs and wants. The following is an excerpt of the teacher's lesson plan.
Learning Objective:
Children will identify how human needs can be met through selling, buying, and trading.
Essential Questions:
- How do we get things that we need?
- How would we get what we need without money?
Vocabulary Words:
- goods
- consumers
- needs
- wants
- income
- selling
- buying
- trading
Activity:
- The concepts of selling, buying, and trading will be introduced using images paired with verbal explanations, such as a grocer selling corn, an individual buying fabric, and two farmers trading milk and apples.
- Children will then engage in a whole-group discussion to share their experiences with selling, buying, or trading. The teacher will record and classify children's discussion contributions on the whiteboard.
- Children will engage in an activity in which they role-play selling, buying, and trading goods at an outdoor market. Children will be given a list of five goods they need to obtain, three coins to purchase three goods, and two goods that they will need to trade for other goods. Children will be instructed to trade their two unneeded goods for needed goods. Children who are not buying and trading goods will be selling goods.
Exhibit: Work Sample
Following the outdoor market activity, the children describe the goods they bought, sold, and traded using illustrations and writing. One child's work is shown below.
Teacher Prompt: Describe the goods you bought, sold, and traded using illustrations and writing.
In the work sample, the child illustrated a child labeled "me", wood, corn, a shirt, a water bottle, and a slice of bread. The child wrote "I bt wud krn srt watr brd" beneath the illustration.
Teacher-Child Conversation:
Teacher: What goods were on your list to buy or trade?
Child: I had to get wood, corn, a shirt, socks, and cheese.
Teacher: In your drawing, it looks like you have wood, corn, a shirt, water, and bread. What goods did you buy?
Child: I used my coins to buy the wood, corn, and shirt.
Teacher: What goods did you trade?
Child: Well, I didn't know what I needed to trade so I kept the water and the bread.
Teacher: You could have traded your water and bread for socks and cheese.
Child: But I didn't have any more coins.
Teacher: When you trade, you exchange goods that you do not need for goods that you do need. You don't need coins to trade goods.
Child: But how do I know other people need bread?
Teacher: You could ask a classmate, "Do you have cheese to trade for bread?"
Child: Well, okay. I liked selling the most.
Teacher: What did you sell in the market?
Child: Apples and oats, which I really like to eat!
Question 102.
Use the information provided in the exhibits to complete the assignment that follows.
Using your knowledge of foundational mathematics skills and mathematics content and pedagogy, write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words in which you:
- identify one area of strength that the student demonstrates related to the mathematics content skill specified;
- identify one area of need that the student demonstrates related to the mathematics content skill specified;
- describe a learning activity that would address the student's identified need and promote progress toward the specified mathematics content standard; and
- explain why this learning activity would be effective for the student.
Be sure to cite specific evidence from the exhibits provided to support all parts of your response.
Exhibit: Lesson Plan
A second-grade teacher plans a lesson in which students will measure and compare lengths using standard units. In a previous lesson, students learned how to measure the lengths of objects using two standard units. An excerpt of the teacher's lesson plan is shown below.
Learning Objective:
Students will use measurement to determine how much longer one object is than another.
Essential Questions:
- What are different ways that measurements are used?
- How can addition and subtraction be used to make comparisons between measurements?
Vocabulary Words:
- measurement
- measurement unit
- ruler
- longer
- longest
- compare
- length
Activity:
- As a review of measuring objects using standard units, students will be paired with a partner for a measurement scavenger hunt activity. Students will be instructed to find and measure the lengths of ten objects using inches on a ruler. Students will record their findings in their math journals.
- Following this activity, students will engage in a whole-group activity in which they share the lengths of some objects found in the classroom. The teacher will record students' findings on the whiteboard.
- The teacher will ask students to identify the longest objects and the shortest objects. Students will be asked to turn-and-talk with a partner to consider how they would determine the difference between the lengths of these objects. Students will be encouraged to share their problem-solving strategies.
- The teacher will then provide explicit instruction on how to determine the difference between two lengths using subtraction. Students will then be asked to use their math journals to respond to a measurement and comparison prompt.
Exhibit: Work Sample
One student's work is shown below.
Teacher Prompt: Measure the pencil and crayon using inches. Is the pencil or the crayon longer? How do you know? What is the difference in length between the pencil and the crayon?
In the work sample, the student measured a pencil and a crayon using a ruler. In the first measurement, the student placed the pencil above a ruler at the one inch mark. The pencil runs the length of the ruler from the one inch mark to the nine inch mark. In the second measurement, the student placed the crayon above a ruler at the one inch mark. The crayon runs the length of the ruler from the one inch mark to the six inch mark.
Math Quick-Write Journal
The pencil is 9 inches long. The crayon is 6 inches long.
I know that the pencil is the longest because I used my ruler. I can compare them with my eyes and hand. My eyes can see that the pencil is the longest. The crayon is as long as my finger. The pencil is longer than my finger. It is as long as 2 of my fingers. The pencil is 3 inches longer than the crayon. I know this because 9 inches minus 6 inches equals 3 inches.
