Practice Test: Biology (66)
Suggested Testing Time: 4 hours
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. In addition, this test includes one or more assignments that allow you to handwrite and scan your responses. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
Question 1.
Which of the following properties of carbon primarily contributes to carbon's versatility to develop large, complex molecules?
- the ability to exist in multiple forms in one state of matter
- the capacity to form different types of solids
- the ability to create four covalent bonds with other atoms
- having low reactivity
Question 2.
Which of the following statements best describes the primary role that sulfur plays in the human body?
- Sulfur is a major component of all molecules in the mammalian body.
- Sulfur is a major component of two essential amino acids in the human body.
- Sulfur is responsible for transmitting electrical impulses across all nerve synapses.
- Sulfur is a necessary part of the reaction that metabolizes ATP and releases free energy.
Question 3.
Enzymes function best at an optimal pH level because changes in pH can:
- change the shape of the enzyme.
- increase the kinetic energy of the enzyme.
- alter the amino acid sequence of the enzyme.
- increase the numbers of active sites in the enzyme.
Question 4.
A student is doing an experiment to determine how change in acidity affects enzyme activity. The time it takes for a disk soaked with catalase at different acidities to rise to the top of a vial containing 1% hydrogen peroxide will be measured. If the student presents the findings in a line graph, which of the following conditions will be represented on the x-axis of the graph?
- pH values
- catalase concentrations
- disk rise times
- percent hydrogen peroxide
Question 5.
The ability of plants to transport water and dissolved nutrients against the force of gravity is directly attributable to the:
- cohesion of water molecules.
- breaking of hydrogen bonds in liquid water.
- temperature-induced changes in water density.
- high specific heat of liquid water.
Question 6.
Biologically important properties of water such as its cohesion, high specific heat, anomalous phase densities, and role as a solvent can be attributed primarily to the:
- tendency of water molecules to form double bonds.
- hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules.
- relatively low molecular weight of water compared to other liquids.
- ability of water to dissociate into hydrogen and hydroxide ions.
Question 7.
Saturated fats are best distinguished from unsaturated fats by the fact that saturated fats:
- are more likely to be solid at room temperature.
- contain more cholesterol.
- are more common in plants than in animals.
- contain more double bonds.
Question 8.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
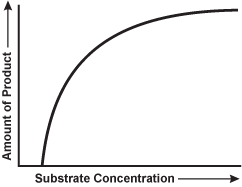
A graph of the amount of product versus substrate concentration is shown. As substrate concentration increases, there is first a sharp increase in the amount of product, which gradually slows down more and more until it levels off.
The graph shows the relationship between the amount of product of a reaction and the substrate concentration for a reaction that is catalyzed by an enzyme. Which of the following is the best explanation for the flattening of the curve at higher concentrations of the substrate?
- There is a competitive inhibitor present.
- The enzyme is being denatured.
- The substrate has been used up.
- The active site of the enzyme is saturated.
Question 9.
Which of the following cell membrane transport processes is dependent on energy supplied by the hydrolysis of ATP?
- simple diffusion of dissolved oxygen into a cell
- movement of small ions through channel proteins
- exchange of ions by way of a sodium-potassium pump
- osmotic uptake of water in a cell in a hypotonic environment
Question 10.
During cellular respiration, some of the energy stored in the glucose molecule is captured by ATP and some is released as:
- thermal energy.
- electromagnetic energy.
- radiant energy.
- mechanical energy.
Question 11.
Which of the following molecules is released as a by-product of cellular respiration?
- O 2
- H 2
- H 2 O
- C 6 H 12 O 6
Question 12.
The process of photosynthesis involves which of the following transformations?
- thermal energy into mechanical energy
- electromagnetic energy into chemical energy
- potential energy into kinetic energy
- radiant energy into electromagnetic energy
Question 13.
During the production of glucose in most plants, the hydrogen in the glucose molecule comes from:
- splitting of the chlorophyll molecule present in the chloroplasts.
- splitting of water molecules from water vapor absorbed through the stoma.
- absorption of free hydrogen molecules through the stoma.
- splitting of water molecules from liquid water absorbed through the roots.
Question 14.
Which of the following statements describes a similarity between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
- Oxygen is required.
- Glucose is a reactant.
- Reactions occur in mitochondria.
- Lactic acid and ethanol are produced.
Question 15.
A science class builds a compost heap, adds water, and turns the heap regularly. When the compost is finished, the heap will be greatly diminished in size because microorganisms will have:
- partially converted carbon compounds in the organic matter into carbon dioxide during respiration.
- heated the heap as a by-product of their metabolism and converted liquid water into water vapor.
- partially converted nitrogenous compounds in the organic matter into nitrogen gas.
- used oxygen contained within the spaces of the heap to metabolize glucose.
Question 16.
Which of the following processes is most likely to cause an increase in the level of lactic acid within a cell?
- hydrolysis
- respiration
- glycolysis
- fermentation
Question 17.
The Calvin cycle is the process by which:
- carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into carbohydrates.
- hydrogen ions are generated and used to make N A D P H .
- electrons become excited and are used to produce ATP.
- oxygen is removed from water molecules and released as a gas.
Question 18.
The mechanism by which ATP provides energy for the metabolic processes of a cell involves the:
- generation of heat by hydrolysis of a phosphate group.
- transfer of a phosphate group to other molecules.
- lowering of the activation energy required for phosphorylation.
- absorption of light by pigments during phosphorylation.
Question 19.
Which of the following statements describes a characteristic shared by all living organisms?
- All organisms sexually reproduce during their life cycle.
- All organisms make all of the protein that they use.
- All organisms metabolize during all or part of their life cycle.
- All organisms are structurally similar with membrane-bound organelles.
Question 20.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
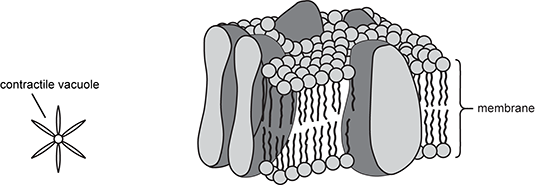
Two cell structure diagrams are shown. In the first, labeled contractile vacuole, a circle is surrounded by leaf-like arms in a star shape. The second, labeled membrane, shows two layers of molecules that are circles with two wavy arms each, all with the wavy arms pointed toward one another and with the circles on the top and bottom. Spanning these are large ovals that crest out of either side of the circle layers.
How do the two cell structures shown work together to maintain homeostasis?
- Nutrients entering through the membrane are stored in a contractile vacuole to meet the cell's energy needs.
- Excess water in the cytoplasm is pumped out of a contractile vacuole through the membrane to preserve water balance.
- Foreign matter passing through the membrane is engulfed and destroyed by a contractile vacuole to protect the organism.
- Steroid hormones pass through the membrane and stimulate a contractile vacuole, a secondary messenger, to regulate blood sugar.
Question 21.
Some aquatic organisms can adjust physiologically to cold environments by altering the proportions of the components in their cell membranes. A higher concentration of which of the following components of a cell membrane would allow an organism to withstand coldness well?
- integral proteins
- unsaturated fatty acids
- phosphate groups
- carbohydrates
Question 22.
Which of the following statements best describes how the structure of the cell membrane would affect the response of an animal cell if the cell were moved from an isotonic solution into a 50% saltwater solution?
- Tiny pores within the membrane would allow water to pass from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
- The hydrophobic nature of the lipids in the membrane would allow for the passage of ions directly through the bilayer.
- Water molecules would attach themselves to proteins that regularly move back and forth across the membrane.
- Protein channels in the membrane would increase the passage of charged particles.
Question 23.
Which of the following statements best explains how limiting factors affect the growth of multicellular organisms?
- Cells cannot grow in size indefinitely because they have a limited life span and die if they do not continually divide.
- Cells cannot grow above a certain size because the maximum size to which they can grow is limited by metabolic constraints.
- Growth in the size of an organism is limited by the space between cells because cells must constantly communicate with their neighbors.
- Growth in the size of an organism requires that cells differentiate into different types, which only occurs during embryonic development.
Question 24.
In which of the following phases will a human cell mostly reside during the cell cycle?
- G1 phase
- S phase
- G2 phase
- M phase
Question 25.
Which of the following statements describes a result of the asymmetric cell division of stem cells?
- One of the daughter cells has a finite capacity for cell division and the other daughter cell continues to have an unlimited proliferative ability.
- Both daughter cells have a finite capacity for cell division.
- One of the daughter cells has a finite capacity for cell division and the other daughter cell becomes programmed to begin the apoptosis phase.
- Both daughter cells have an unlimited ability to proliferate.
Question 26.
Which of the following statements best explains why ordinary light microscopes must be used, rather than scanning or transmission electron microscopes, to watch the process of cell division occur?
- The high magnification of an electron microscope speeds up the movement of specimens, making it difficult to observe each phase of cell division.
- Electron microscopes create distortion in the image of the object being viewed that prevents the user from observing the fine details of cell division.
- Preparation of specimens for viewing under an electron microscope results in the death of the specimen, so living cells cannot be viewed.
- The magnification of an electron microscope is too great to allow it to be focused on a whole cell.
Question 27.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum is particularly well developed in cells that:
- secrete proteins or glycoproteins.
- detoxify drugs or poisons.
- support chemiosmosis.
- hydrolyze macromolecules.
Question 28.
Which of the following structures are typically found in both plant and animal cells?
- cell walls
- Golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- central vacuoles
Question 29.
Which of the following plant structures is most closely associated with temperature regulation in green plants?
- phloem
- stomata
- root hairs
- sclerenchyma cells
Question 30.
Which of the following statements best describes one difference between synaptic paracrine signaling and endocrine cell signaling?
- Synaptic paracrine signaling ligands use receptor sites to cross the target cell membrane, while endocrine signaling ligands cross the membrane by simple diffusion.
- Synaptic paracrine signaling relies on ligands to carry the signal, while endocrine signaling relies on specialized messenger cells to carry the signal.
- In synaptic paracrine signaling, target cells and signaling cells are the same type, while in endocrine signaling they are different types of cells.
- In synaptic paracrine signaling, target cells are near the signaling cell, while the two cells are usually far apart in endocrine signaling.
Question 31.
Which of the following procedures would best illustrate transport through the xylem of a plant?
- exposing lettuce leaves to saline solution
- separating pigments using chromatography paper
- channeling a seedling to grow in a downward direction
- exposing the cut stem of a carnation to colored food dye
Question 32.
A germinating fern spore will develop into:
- a rhizoid.
- a gametophyte.
- an archegonium.
- a sporophyte.
Question 33.
Closure of stomata immediately affects a plant's:
- root pressure.
- transport of glucose.
- rate of water loss.
- frost resistance.
Question 34.
Which of the following describes the triple response of seedlings that allows them to push up through the soil to the surface?
- phototropism; ethylene emission; programmed cell deaths
- slowing of stem elongation; thickening of stem; horizontal growth of stem
- changes in turgor pressure; phytochromes; blue-light receptors
- variation in auxin concentrations; production of growth inhibitors; abscission layers
Question 35.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
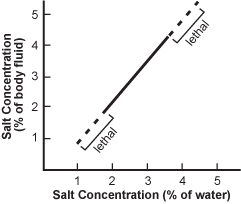
A graph of salt concentration in percent of body fluid is shown versus salt concentration in percent of water on the x-axis. A roughly linear trend line extends from about (1.8, 1.8) to (3.5, 4.3). On either side of this, there are two lines continuing from the main trend line and they are both marked lethal.
The graph above shows the change in salt concentration in the cells of a spider crab as the salt concentration of the surrounding water changes. The data suggest that with respect to salt concentration the spider crab is:
- regulating its internal environment.
- using a positive feedback mechanism to maintain homeostasis.
- conforming to the external environment.
- using a negative feedback mechanism to maintain homeostasis.
Question 36.
Which of the following constituents of the musculoskeletal system plays a direct role in the function of the circulatory system?
- joint
- collagen
- cartilage
- red marrow
Question 37.
Which of the following is a function performed by the liver?
- regulation of blood flow to the stomach during digestion
- generation of new red and white blood cells
- removal of wastes and toxins from the blood
- control of peristalsis in the digestive tract
Question 38.
Which of the following statements best describes the role of clonal selection in the development of acquired immunity to a pathogen?
- Leukocytes that are stimulated as a result of increased body temperature during an infection differentiate from their precursor stem cells more rapidly.
- Lymphocytes that possess receptors that can bind to the pathogen's antigens rapidly divide to produce many cells capable of recognizing and attacking the pathogen.
- Natural killer cells that produce antibodies capable of attacking the pathogen are stimulated to produce more antibodies than cells that do not produce such antibodies.
- Phagocytes that ingest many pathogens over a short period of time grow and divide more rapidly than those that have not ingested many pathogens.
Question 39.
Evidence suggests that fever is a mechanism of homeostasis that can help fight infection by:
- reducing the permeability of plasma membranes to pathogens.
- increasing the concentration of oxygen in the blood.
- lowering blood pressure and heart rate.
- enhancing production and mobility of leukocytes.
Question 40.
Which of the following best describes the function of the cilia that are attached to the epithelial lining of the bronchi and bronchioles of the lungs?
- producing mucus and other secretions that trap pathogens
- insulating delicate lung tissue from exposure to cold inhaled air
- moving particulate contaminants upward to the pharynx
- trapping inhaled oxygen molecules for transfer to the blood
Question 41.
Which of the following best describes the mechanism by which hemoglobin loads and unloads oxygen?
- Production of C O 2 during cellular respiration lowers blood pH, which decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen and facilitates the unloading of oxygen to cells.
- Oxygen molecules binding to one subunit of a hemoglobin molecule change its shape, and the other three subunits also change shape and accept oxygen more readily.
- Blood arriving at the lungs has a lower P O 2 pressure than the air inside the lungs, which favors the diffusion of oxygen into the blood from the lungs.
- Carbon dioxide in the blood as a result of increased cellular respiration causes the heart's pacemaker to speed up and increase the transport of oxygen to cells.
Question 42.
The sensation of thirst is produced by the brain primarily in response to signals from the body indicating:
- decreased heart rate and blood pressure.
- increased internal temperatures.
- decreased urinary output by the kidneys.
- increased osmolarity of the blood.
Question 43.
Which of the following best describes a difference between the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system?
- Axons within the peripheral nervous system are longer since they must stretch from cell bodies in the ganglia located along the spine to their destinations in the tissues.
- Nerve cells that are located within the peripheral nervous system have many more dendrites than those that are located within the central nervous system.
- Synapses within the peripheral nervous system are electrical rather than chemical and so do not require the use of neurotransmitters to transmit information.
- Impulses in the peripheral nervous system carry information from the body to the brain, while those in the central nervous system carry it from the brain to the body.
Question 44.
Which of the following best describes the role played by the hormone oxytocin in human reproduction?
- inducing and regulating uterine contractions during the various stages of labor
- stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovary and maturation of the oocytes
- inducing and regulating the disintegration of the uterine lining during menstruation
- stimulating the development of the endometrium in preparation for pregnancy
Question 45.
Which of the following is a major difference between cartilage and other types of connective tissues?
- The extracellular matrix in cartilage lacks collagen.
- Cartilage does not contain blood vessels.
- The primary mineral in cartilage is phosphorus rather than calcium.
- Cartilage cells do not possess nuclei.
Question 46.
A group of 14 students is monitoring the acidity level in a nearby stream over a period of two weeks. At the same time every day, a student will take one of four available digital pH meters to measure the pH of the stream and record the result in a laboratory notebook. Which of the following factors represents a systematic error associated with the design of the experiment?
- the rounding of the pH readings in the digital displays
- the measurements being made by different students
- the use by the students of four different pH meters
- the sampling being done at the same time every day
Question 47.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
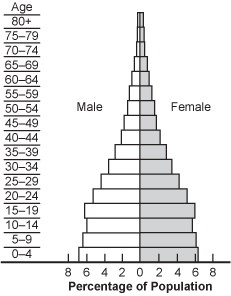
A diagram that is a roughly inverted V is split down the middle vertically by the baseline percentage of the population of an age group equaling 0. On the y-axis are groups of ages from 0 at the base to 80 plus on the top and thinnest part of the diagram. One half of the inverted V is labeled male and the other half of the inverted V is labeled female.
Based on the age structure table above, the human population that is represented will probably:
- continue to grow rapidly.
- increase slowly and steadily at a constant rate.
- grow for another generation and then stabilize.
- remain at its current size.
Question 48.
Which of the following is an example of a mutualistic relationship between two organisms?
- hawks hunting mice during the day and owls hunting mice at night
- ants obtaining food from aphids and protecting them from predators
- ticks feeding on a moose's blood and dispersing at the same time
- bees feeding on thistle nectar and siskins feeding on thistle seeds
Question 49.
Thermoclines are related to which of the following characteristics of ecosystems?
- the ecotones that exist between grasslands and forests
- the inverse correlation of temperature and elevation
- the zonation of organisms in intertidal habitats
- the vertical stratification of freshwater lakes
Question 50.
Which of the following conditions is a particular problem for organisms living in estuaries?
- availability of light
- leaching of nutrients
- erosion of substrate
- variation in salinity
Question 51.
Which of the following pairs of environmental factors together represents the primary determinant of the distribution of terrestrial biomes worldwide?
- mean temperature and precipitation
- elevation and mean precipitation
- mean temperature and soil type
- elevation and soil type
Question 52.
When existing species in a habitat alter environmental conditions in such a way that they inhibit their own reproduction in relation to other species, which of the following events is likely to occur?
- density-independent selection
- habitat fragmentation
- boom-and-bust population cycles
- secondary succession
Question 53.
Which of the following statements best explains why wildflowers on the forest floor in temperate deciduous forests often bloom between late March and early May in Massachusetts?
- Higher temperatures are more prevalent later in the summer.
- Pollinators are more available in early spring.
- Light is a limiting factor later in the summer.
- Fewer insect herbivores are active in the early spring.
Question 54.
The productivity of fisheries over areas of regular oceanic upwellings is evidence that which of the following conditions is often limiting in open-ocean ecosystems?
- nutrient availability
- light intensity
- salinity level
- water temperature
Question 55.
Which of the following statements best explains why the biomass of each trophic level is less than the biomass of the level immediately below?
- Detritivores and decomposers form a large part of the biomass of lower trophic levels but are not found at higher levels.
- Species diversity is much greater for lower trophic levels than it is for higher trophic levels.
- Energy is lost as heat within each trophic level and is also used to sustain physiological processes of animals and plants.
- Animals at each trophic level are larger and more active than animals at the trophic level below.
Question 56.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
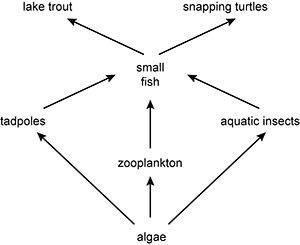
A diagram is shown with algae at the base and having three arrows point out from it: one to tadpoles, one to zooplankton, and one to aquatic insects. Each of these organisms has an arrow pointing from it to small fish. Small fish then has two arrows pointing from it: one to lake trout and one to snapping turtles.
Quagga mussels are an introduced species of freshwater mussel. These organisms are very efficient filter feeders that feed on algae. Which of the following changes in the freshwater food web shown would result directly from the presence of quagga mussels?
- an increase in aquatic insects
- a decrease in zooplankton
- an increase in tadpoles
- a decrease in lake trout
Question 57.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
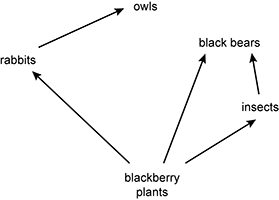
A food web is shown. At the base, blackberry plants have three arrows going out from them: one to rabbits, one to black bears, and one to insects. There is an arrow from rabbits to owls and another arrow from insects to black bears.
Which of the following organisms occupies multiple trophic levels within the food web shown?
- owl
- rabbit
- insect
- black bear
Question 58.
Grasses have deep roots and grow from buds located below the surface of the soil. These traits are adaptations that allow rapid regrowth in response to which of the following limiting factors?
- limited nutrients
- blizzards
- periodic floods
- wildfires
Question 59.
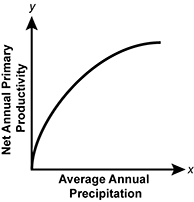
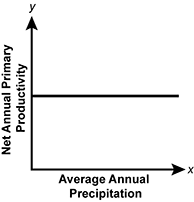
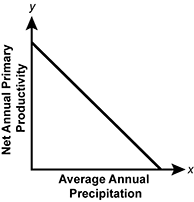
Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between annual primary productivity and precipitation in terrestrial ecosystems?
- A graph of net annual primary productivity versus average annual precipitation on the x-axis is shown. A trend line that starts off rising quickly and eventually levels off is depicted.
- A graph of net annual primary productivity versus average annual precipitation on the x-axis is shown. A trend line that is flat hallway up the net annual primary productivity is depicted.
- A graph of net annual primary productivity versus average annual precipitation on the x-axis is shown. A trend line that starts off increasingly slowly and then increases exponentially is depicted.
- A graph of net annual primary productivity versus average annual precipitation on the x-axis is shown. A downward linear trend line is depicted.
Question 60.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
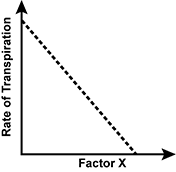
A graph of the rate of transpiration on the y-axis is shown versus factor X. A downward linear trend line is depicted.
An increase in which of the following independent environmental factors (Factor X) is most likely to result in the change in the rate of transpiration shown in the graph?
- temperature
- wind speed
- humidity
- light intensity
Question 61.
A line graph would be most appropriate for displaying which of the following types of data about an ecosystem?
- a change in the number of detritivores in four different habitats of the ecosystem over the course of a year
- a comparison of the number of individuals of three different keystone species across the four types of habitat in the ecosystem
- contributions of seven different plant families to the total mean annual biomass of primary producers in forest habitats of the ecosystem
- relationships between the soil type and soil moisture in the ecosystem with the percentage distribution of several plant species across the ecosystem
Question 62.
Students are examining data showing the level of mercury found in a variety of marine organisms and trying to correlate these levels with the role of these organisms in a marine food web. This activity is most likely being used as part of a unit about which of the following ecological concepts?
- secondary succession
- biodiversity
- carrying capacity
- biomagnification
Question 63.
Marine organisms are affected by the commercial fishing industry's practice of dragging fishing nets along the ocean floor. This practice primarily results in which of the following consequences?
- distinct differences in the size of male and female fish
- eutrophication of coastal waters
- destruction of underwater habitats
- transmission of fish parasites
Question 64.
Which of the following processes is a direct cause of the rise in global sea levels?
- warming of ocean waters
- increasing runoff from rivers
- changing of oceanic currents
- increasing dissolved carbon dioxide
Question 65.
The primary concern about the impact of the introduction of exotic species on natural systems is that exotic species:
- interfere with native species' growth by altering an area's chemical balance.
- serve as a food source that attracts other consumer species to an area.
- interbreed with native species, resulting in reduced genetic diversity.
- undergo population growth in the absence of most limiting factors.
Question 66.
The increase in kinetic energy that results when radiant energy is absorbed by molecules and atoms is a direct contributor to which of the following phenomena?
- acid rain
- sea level rise
- ocean dead zones
- biomagnification
Question 67.
Winter bird feeder observations from citizen scientists in North America indicate that the wintering range of a species of hummingbird has shifted approximately 200 miles northward. This piece of data is most closely associated with which of the following trends?
- increasing fragmentation of wildlife habitat
- increasingly widespread use of wind turbines
- rising global temperatures
- rising number of invasive species
Question 68.
The primary benefit of contour plowing on a farm is that it:
- increases organic matter and helps maintain soil structure.
- reduces the need for irrigation and cultivation.
- increases the angle and availability of incident light.
- reduces soil erosion due to water runoff.
Question 69.
Aquatic ecosystems tend to be dead zones near points at which nuclear power plants discharge water because of:
- high levels of acidity.
- elevated background radiation.
- decreased light penetration.
- low dissolved oxygen content.
Question 70.
The presence of increased levels of nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere is an environmental concern because this can result in:
- a decrease in soil fertility as minerals are leached away.
- a decrease in the populations of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
- an increase in the rate of ozone depletion in the atmosphere.
- an increase in the eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems.
Question 71.
The draining of wetlands for development leads directly to increases in which of the following environmental problems?
- accumulation of pollutants
- flooding in adjacent habitats
- pressure on nearby landfills
- establishment of exotic species
Question 72.
Which of the following practices is the best way to reduce the environmental consequences associated with logging forests in mountainous areas?
- applying nitrogen and potash fertilizers after logging the site
- closing the logged area to recreational uses until trees are reestablished
- leaving some trees standing on the site when it is logged
- cultivating the soil immediately after logging and planting tree seedlings
Question 73.
Use the DNA sequence below to answer the question that follows.
G A C T G A
Which of the following base sequences of mRNA is complementary to the given sequence of DNA?
- A G T C A G
- C T G A C T
- A G U C A G
- C U G A C U
Question 74.
Which of the following events occurs first during DNA replication?
- DNA polymerase attaches free-floating nucleotides to each complementary strand.
- The number of chromosomes is reduced by half through the activation of DNA ligase.
- Primers that allow for RNA attachment are deposited along the template strand by DNA primase.
- DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds located between the strands.
Question 75.
Which of the following phenomena is an example of a change in gene expression due to factors in the external environment without a corresponding change in the structure of the genes involved?
- rapid vegetative growth in food crops
- tetraploidy in some species of flowers
- gender changes in some species of fish
- darkening of the skin from Sun exposure
Question 76.
Ionizing radiation, such as ultraviolet light, can cause cancer primarily by:
- interfering with gene expression by damaging the DNA strand.
- blocking DNA replication by preventing the separation of the complementary chromosomes.
- interfering with normal tissue replacement by causing apoptosis of large numbers of cells.
- facilitating the entrance of viruses to cells by creating small holes in the cell membranes.
Question 77.
The codons GGT, GGC, GGA, and GGG all code for the amino acid glycine. A substitution mutation that changes the third codon in the triplet would result in which of the following outcomes?
- a stop signal to end the coding
- a shift in the coding frame
- no effect on the expression
- inversion of the triplet
Question 78.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
To create a model of DNA replication, a student uses a zipper to represent the DNA, with each of the teeth of the zipper painted a different color to represent one of the nucleotides of the DNA. The zipper's slider, which opens the zipper when the slider is moved downward, represents the enzyme that opens the DNA.
Which of the following modifications should the student make to this model to represent the movement of DNA polymerase?
- adding one object to move down the middle between the two sides of the opened zipper
- adding two objects to move along in opposite directions on each side of the opened zipper
- adding one object to move up one side then down the other side of the opened zipper
- adding two objects to move along in the same direction on each side of the opened zipper
Question 79.
Scientists have developed plants that contain genes from microbes to help them kill insects. Some people are concerned that transgenic agricultural crops might transfer genes to other species. Which of the following is the basis for this concern?
- Plant genes have promoter sequences that are similar to those of microbes.
- Transgenic plants may be unusually susceptible to native diseases.
- Most microbes are known to exchange DNA through conjugation.
- Transgenic DNA is designed to be incorporated into new genomes.
Question 80.
Upon reaching a ribosome, a tRNA molecule will:
- match an anticodon to the complementary mRNA codon.
- attach an amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain.
- eliminate introns from the mRNA sequence.
- terminate the growing polypeptide chain.
Question 81.
One consequence of the redundancy of the genetic code is that:
- somatic mutations do not affect the germ line.
- nucleotide base deletions may lead to frameshift mutations.
- some point mutations have no effect on phenotypic expression.
- missense mutations may result in translocations.
Question 82.
Which of the following techniques is used to increase the quantity of DNA in a sample to be analyzed?
- DNA sequencing
- polymerase chain reaction
- restriction fragment analysis
- DNA hybridization
Question 83.
Which of the following types of diagrams is used to calculate and display the range of genotypes that are possible in the offspring of two sexually reproducing organisms?
- pedigree
- gene sequence
- gene histogram
- Punnett square
Question 84.
A species has two alleles and three phenotypes for fur color—brown, white, and tan. Which of the following expressions represents the expected ratio of phenotypes of the offspring produced by a cross between two parents who are both heterozygous for fur color?
- 0 brown to 4 tan to 0 white
- 1 brown to 3 tan to 0 white
- 1 brown to 2 tan to 1 white
- 2 brown to 0 tan to 2 white
Question 85.
Which of the following statements best describes one advantage of reproducing asexually by mitosis, rather than sexually by meiosis and fertilization?
- Populations that reproduce asexually have higher survivorship because mitosis produces fewer poorly adapted individuals than meiosis.
- Asexual reproduction produces fewer mutations in the population because genes are less likely to mutate during mitosis than during meiosis.
- Asexual reproduction by mitosis is more energy efficient since sex cells are not produced by meiosis and there is no need to find a mate.
- Populations that reproduce asexually are self-limiting and not as likely to exceed carrying capacity since clones produced by mitosis do not compete with one another.
Question 86.
Alleles present in which of the following types of loci are more likely to vary due to the process of crossing over during meiosis?
- loci that are located near the ends of the chromosomes
- loci that are part of a translocation of a gene sequence
- loci that are located near the centromeres of chromosomes
- loci that are part of an inversion of a gene sequence
Question 87.
Which of the following statements best explains how the linkage of genes on a chromosome decreases genetic variation in a population?
- Linked genes are protected from the effects of crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis.
- Linked genes, because they code for multiple traits, are likely to be important to physiological processes and undergo strong stabilizing selection.
- Linked genes cannot vary independently, so there is a greater percentage of parental than recombinant phenotypes.
- Linked genes are less likely to undergo neutral mutations than genes that are not linked.
Question 88.
If both parents are heterozygous for a trait such as tongue rolling, what is the probability of one of their children being homozygous recessive for this trait?
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Question 89.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Number of Offspring | Phenotype of Offspring |
|---|---|
| 9,771 | white and smooth |
| 3,266 | white and wrinkled |
| 3,249 | purple and smooth |
| 1,088 | purple and wrinkled |
In pea plants, white flowers and smooth pods are dominant traits, while purple flowers and wrinkled pods are recessive traits. While investigating the inheritance patterns of flower color and pod texture in pea plants, a scientist makes the observations recorded in the table. Which of the following conclusions is supported by the reported results?
- Both parents are homozygous recessive for both traits.
- Both parents are heterozygous and show both dominant traits.
- One parent is homozygous recessive for color but homozygous dominant for texture.
- One parent is heterozygous for texture but homozygous dominant for color.
Question 90.
In humans, the allele for red-green colorblindness is sex-linked and recessive. For a colorblind female, which of the following statements must be true?
- Her mother is colorblind.
- Both parents carry the allele for colorblindness.
- Her father has normal vision.
- Her mother has normal vision but is a carrier for colorblindness.
Question 91.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
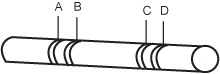
A chromosome is shown with four genes on it: A, B, C, and D. A is the furthest left, followed by B close to it, then a long space until C. D is on the far side of C but close to it.
The diagram above shows a chromosome map of four genes relative to each other. Which pair of genes would have the highest recombination frequency?
- B and A
- A and C
- B and C
- A and D
Question 92.
In mice, black coat color allele ( big B ) is dominant to brown coat color allele ( little B ). However, a gene on a different chromosome determines whether or not color will be deposited in the coat at all. The dominant allele big C represents color deposition while the recessive allele little C represents lack of pigment. If two mice heterozygous for both genes are crossed, what is the probability that any one of their offspring will be brown?
- one sixteenth
- three sixteenths
- one quarter
- nine sixteenths
Question 93.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| blank | Bill Length: Species 1 | Bill Length: Species 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Forest A | 6 to 10 mm | -- |
| Forest B | -- | 8 to 12 mm |
| Zone of Sympatry | 6 to 8 mm | 10 to 12 mm |
Two insect-eating species of bird live in two different forests separated by agricultural fields. Eventually, agriculture is abandoned in the region and the fields become forests. Each species moves into this new forest, where they coexist. However, over time, birds living in this zone of sympatry diverge in bill length from birds of the same species that are living in the original forest habitats. Which of the following processes best explains this divergence in bill length as shown in the table?
- hybridization between the two species in the zone of sympatry
- competition between individuals of the two species in the zone of sympatry
- consumption of a different set of insect prey species in the zone of sympatry
- increased predator pressure on each of the two species in the zone of sympatry
Question 94.
Which of the following statements best describes the role that gene duplication mutations play in the evolution of a species?
- Since gene duplication does not lead to a change in function, it can spread through a species and provide new genetic variation for selection to act on.
- Since gene duplication leads to incompatibility during crossing over, it may interfere with recombination and lead to a reduction of variation in a species.
- Since gene duplication can result in overproduction of a protein, it may either increase or decrease the adaptation of a species depending on the protein.
- Since gene duplication can prevent individuals with duplicated genes from reproducing with individuals without duplicated genes, it can serve as a species-isolating mechanism.
Question 95.
The draining and filling of intervening swamps has led to a small population of frogs becoming isolated from the rest of the species. In this population of frogs, some of the individuals are green in coloration, while some are yellow. By chance, the frequency of the green allele, which is recessive, is 50%, and that of the dominant yellow allele is also 50%. Neither color has any adaptive significance. Due to limitations on the available resources in their isolated habitat, the frog population stays small. After a period of time, it is discovered that all of the frogs are green. Which of the following processes is most likely responsible for this allele change in the frog population?
- genetic drift
- founder effect
- recombination
- stabilizing selection
Question 96.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Toward the end of the Miocene, about 6 to 7 million years ago, environments in North America became cooler and drier. Forests dwindled and were replaced with savannas dominated by C4 grasses. Perissodactyl lineages went extinct, eventually leaving only the horse, rhinoceros, and tapir lineages, which were each represented by only a few species. In contrast, the artiodactyls radiated into a large number of lineages, each of which was represented by numerous species.
Which of the following interpretations of the relationship between extinction and adaptive radiation as a result of environmental change is best illustrated by the information provided?
- One lineage can rapidly evolve into another and radiate as the species in the older group of lineages go extinct.
- Lineages that cannot adapt to environmental change go extinct and better adapted lineages evolve to occupy the empty ecological niches.
- Lineages that can adapt their behavior to a changed environment can rapidly expand and replace lineages that require genetic change to adapt.
- One lineage that possesses traits allowing more effective adaptation to a changed environment can outcompete another lineage and replace it in the ecosystem.
Question 97.
Which of the following statements best describes a characteristic of viruses that allows them to act like mutations in the genetic code of the host?
- Viruses can remain hidden in the body in small numbers without affecting their hosts and can be passed down to infect the next generation.
- Viruses can remain dormant for long periods of time in the external environment, only to reemerge when new generations of susceptible organisms are born.
- Viruses reproduce so quickly that they can be spread throughout a population before their hosts can mount an effective immune response.
- Viruses that lose their virulence due to natural selection can become embedded in the genetic code and passed down to subsequent generations.
Question 98.
A plant biologist is testing the effect of four different mutagens on a species of flowering plant. The biologist plants a sample of ten seeds collected from each of ten different plants. After growing the plants to maturity under identical conditions, the biologist divides them into five groups of twenty plants each. The biologist exposes four of the groups to a different mutagen, leaving one group as a control. The biologist then collects seeds from each group and the control, plants them, and analyzes the resulting offspring for evidence of deleterious and beneficial mutations. Which of the following changes to the experiment is necessary for the results to be considered valid?
- The plants should be observed before they reach maturity.
- The number of mutagens compared in the experiment should be limited to two.
- The original set of ten plants should be propagated vegetatively from the same mother plant.
- The biologist should continue the experiment for another generation and plant F 2 , rather than F 1 , offspring.
Question 99.
Researchers trying to date speciation events in the past for which fossils are not available sometimes rely on evidence that assumes the:
- occurrence of convergent evolution.
- validity of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
- existence of a molecular clock.
- applicability of the biological species concept.
Question 100.
Which of the following pairs is a result of convergent evolution?
- a turtle's egg and a frog's egg
- a bird's wing and a bat's wing
- a housefly's leg and a bee's leg
- a human hand and a monkey hand
Open-Response Items
The directions shown below represent what you will see on the actual test. For the purposes of this practice test, you will be able to type your written responses in the boxes provided on the answer key.
This section of the test consists of two open-response item assignments. You will be asked to prepare a written response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, for each assignment.
Read the assignments carefully before you begin your responses. Think about how you will organize your responses. You may use the erasable sheet(s) to make notes, write an outline, or otherwise prepare your responses. However, your final response to each assignment must be either:
- typed into the on-screen response box,
- written on a response sheet and scanned using the scanner provided at your workstation, or
- provided using both the on-screen response box (for typed text) and a response sheet (for calculations or drawings) that you will scan using the scanner provided at your workstation.
Instructions for scanning your response sheet(s) are available by clicking the "Scanning Help" button at the top of the screen.
As a whole, your response to each assignment must demonstrate an understanding of the knowledge of the field. In your response to each assignment, you are expected to demonstrate the depth of your understanding of the subject area by applying your knowledge rather than by merely reciting factual information.
Your response to each assignment will be evaluated based on the following criteria.
- Purpose: the extent to which the response achieves the purpose of the assignment
- Subject Knowledge: appropriateness and accuracy in the application of subject knowledge
- Support: quality and relevance of supporting evidence
- Rationale: soundness of argument and degree of understanding of the subject area
The open-response item assignments are intended to assess subject knowledge. Your responses must be communicated clearly enough to permit valid judgment of the evaluation criteria by scorers. Your responses should be written for an audience of educators in this field. The final version of each response should conform to the conventions of edited American English. Your responses should be your original work, written in your own words, and not copied or paraphrased from some other work.
Be sure to write about the assigned topics. Remember to review your work and make any changes you think will improve your responses.
Any time spent responding to an assignment, including scanning the response sheet(s), is part of your testing time. Monitor your time carefully. When your testing time expires, a pop-up message will appear on-screen indicating the conclusion of your test session. Only response sheets that are scanned before you end your test or before time has expired will be scored. Any response sheet that is not scanned before testing ends will NOT be scored.
Question 101.
Use the information below to complete the exercise that follows.
As part of a lesson on transcription and translation, students are provided with beads in 21 different colors to build a necklace. All of the beads are the same shape and size. Students are given a key to use that tells them the sequence of beads to thread, based on a three-digit code.
Use your knowledge of the concept introduced in the scenario—the process of transcription and translation of DNA and RNA—to write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- describe the key scientific concepts related to the phenomenon presented to the depth of knowledge a student would need to master the concept introduced in the scenario;
- include a representative graph, formula, and/or diagram with all proper labels to model the concept introduced in the scenario; and
- discuss how a biology teacher could use the specific science and engineering practice of "engaging in argument from evidence" to help students understand phenomena related to the concept introduced in the scenario.
Question 102.
Use the information below to complete the exercise that follows.
The inefficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels affects the number of organisms supported at each trophic level, as well as the approximate amount of energy available at a given trophic level in an ecosystem.
Use your knowledge of life science to write a response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- form a testable scientific claim that addresses energy transfer between trophic levels;
- design an investigation, including any safety considerations, to test the proposed claim, including identifying variables and controls;
- explain how any collected data may provide evidence that supports or refutes the proposed claim; and
- discuss how a biology teacher could use the science and engineering practice "planning and carrying out an investigation" to help students make sense of phenomena related to energy transfer between trophic levels.