Practice Test: General Science (64)
Suggested Testing Time: 4 hours
To Take This Practice Test
- Use the answer key to record your responses.
- Prefer to take it offline? You can print the questions and answer key.
Remember:
- The practice test can give you a good indication of how you may perform on an actual test, but there is no guarantee that your results will be the same as on the actual test.
- The actual test looks and operates differently than this practice test. In addition, this test includes one or more assignments that allow you to handwrite and scan your responses. Review the Testing Tutorials and Demonstrations for more information about the actual test platform.
- A periodic table
 is provided on-screen with your actual test.
is provided on-screen with your actual test.
Question 1.
Students are designing a carrying case that can be used for transporting a cat or small dog. The students who have pets share the weight of their pets with the design team. This activity best fits which of the following aspects of the design process?
- researching a design
- modifying a design
- optimizing a design
- evaluating a design
Question 2.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Students conduct an experiment to examine how the materials used to build a levee affect the ability of the levee to prevent flooding. As a first step, they use a water table to examine how quickly running water erodes model levees built out of sand, gravel, or soil.
Which of the following questions should the students consider to help determine which material would be most effective at preventing running water from breaching a levee?
- How does the material used to build the levee affect the shape and dimensions of the levee?
- What are the costs per truckload of each of the materials under consideration for building the levee?
- Which materials are readily available near the site of the levee versus which need to be transported from elsewhere?
- How does the material used to build the levee affect the ability of the levee to support vehicles on a road built along its surface?
Question 3.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Scientists are working to develop an early warning system for volcanic eruptions. The system will rely on the existing seismic network that is already in place to monitor seismic activity surrounding active volcanoes. The seismic stations will automatically communicate their data to the relevant government agencies, where it will be immediately analyzed and formulated into three levels of warnings.
Which component of the engineering design process must be considered to finalize this warning system?
- defining the problem to be solved
- brainstorming and selecting a solution
- modeling and testing prototypes
- researching criteria and constraints
Question 4.
When evaluating an engineering design for a structure such as a bridge, it would be most important to take which of the following actions first?
- comparing the load-bearing strength of a variety of different materials that are being considered for the components
- calculating the necessary strength of components based on extreme, rather than normal, loads
- selecting materials for components based on the mean load expected on each component, rather than the mode or median load
- testing the strength of components by subjecting a physical model to a variety of loads
Question 5.
A team of engineers is designing a new type of air conditioner for home use. The specifications call for the device to be lightweight, energy efficient, and portable. To keep the price of the air conditioner as low as possible, the engineers should ask which of the following questions in evaluating their initial design?
- Will the design continue to meet the specifications during its expected useful life?
- Does the design meet the specifications in the simplest way possible?
- Will the design function normally under a variety of conditions?
- Is the design easy to understand by prospective customers?
Question 6.
Students are designing a single-axis mechanical arm for a simulated Mars rover. The arm should be able to grasp and lift objects. Which of the following tests would appropriately evaluate the effectiveness of each prototype, based on the project's goals?
- determining how large of an object can be raised to a set distance and height
- calculating the durability of the component materials in the arm
- moving the arm to perform various typical tasks
- timing the arm as it holds up one object
Question 7.
Patio furniture that is meant to be left outside can be made from several different types of materials: aluminum, steel, molded plastic resin, wicker, or rot-resistant woods, such as cedar or redwood. Compared with the other options listed, steel possesses which of the following design feature advantages?
- superior resistance to rain and sunlight
- wider range of shapes and colors
- better comfort during all seasons
- greater strength and sturdiness
Question 8.
From an engineering perspective, buildings framed with steel or wood are more resistant to the forces produced by an earthquake than buildings built out of brick or concrete block. This difference in resistance to force is due to the fact that, compared to brick or concrete walls, a wood and steel frame:
- is more resistant to moving.
- can be secured more tightly.
- can support a greater vertical load.
- is more flexible under horizontal stress.
Question 9.
One of the most important advances in the use of concrete as a building material was the incorporation of iron or steel rods, known as rebar, into structural components. The most important advantage of this technological development was that the addition of rebar:
- allowed structural components made of concrete to be cast separately and joined together.
- increased the strength of concrete structural components in resisting shear stresses without increasing weight too much.
- prevented the concrete in structural components from cracking by inhibiting expansion and contraction as the temperature changed.
- inhibited crumbling and fragmentation of the concrete structural components by providing a surface to which the concrete could adhere.
Question 10.
An auto repair shop has a number of tools, including a rivet gun for fastening body parts to the frame and a wrench for removing and replacing lug nuts on a tire. The shop also uses a large block and tackle for raising an engine block out of the engine compartment and a mallet to pound out dents in the car frames. Being able to measure the torque produced when using the tool would be most important when using which of these tools?
- mallet
- wrench
- block and tackle
- rivet gun
Question 11.
Which of the following scientific principles relating to the structure of materials most directly explains why diamond-dust drill bits are used to drill holes in tile, porcelain, glass, or stone?
- The coefficient of friction between two materials depends on the smoothness of the surfaces that are in contact.
- The hardness of a material depends on the structure of its molecular lattice and the type of bonds between its atoms.
- The durability of a material and its resistance to fracture depends on the direction of cleavage planes within the material.
- The melting point of a material depends on the amount of energy needed to break the bonds between the molecules in the material.
Question 12.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
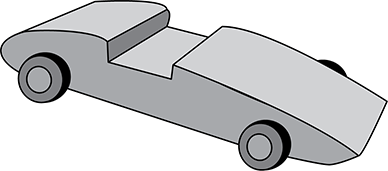
A model car is shown from the side as a roughly flattened tear-drop shape with an area cut out to indicate seating, The car has wheels affixed at the front and back of the seat area.
The diagram shows a traditional derby car, which is a model race car made from wood with plastic wheels, as shown in the diagram. Which of the following methods would be most appropriate for preparing the mounting of the axles of a derby car?
- using a utility knife to carve out a section to place the axles in the body of the car
- using a screwdriver to chisel out slot for the axles in the body of the car
- using a drill to provide holes to insert the axles in the body of the car
- using a hammer to pound the axles into the body of the car
Question 13.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Hot-dip galvanizing is the process of immersing steel in a bath of molten zinc. While the steel is immersed in the zinc, a metallurgical reaction occurs between the iron and the zinc. The end result is a multilayer coating on the surface of the object consisting of zinc and zinc-iron alloy, which is resistant to oxidation and corrosion.
Hot-dip galvanizing is an example of which of the following secondary processes of manufacturing?
- conditioning
- finishing
- assembling
- forming
Question 14.
In manufacturing, the concept of tolerance is critical to ensuring:
- cost containment.
- waste reduction.
- quality control.
- safety.
Question 15.
Ceramics have up to 30% less mass when they come out of the kiln after firing compared to the unfired greenware that went in. This decrease in mass is due primarily to changes in composition of the clay brought about by:
- the rearrangement of the crystal lattice of the natural quartz in clay.
- the melting and fusing of silica particles to form particles of glass in the clay.
- the removal of chemically bound water that was part of the clay's crystal structure.
- the combustion and decomposition of organic carbon compounds that were part of the clay.
Question 16.
When a ferrous metal is heated and hardened during the manufacturing process, this causes the metal to:
- increase in brittleness.
- increase its risk of corrosion.
- become increasingly more malleable.
- become increasingly more magnetized.
Question 17.
Photos from the early twentieth century show rows of insulators for electrical wires on the cross arms of power poles. Insulators must exhibit relatively high hardness, low electrical conductivity, high melting point, low thermal conductivity, and low flammability. Which of the following materials was often used for early insulators because it met these criteria?
- wood
- steel
- glass
- copper
Question 18.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Line | Tool | Safety Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | handheld chisel | Secure loose parts on the tool before using. |
| 2 | handheld wrench | Leave all guards on the tool while in use. |
| 3 | electric belt sander | Make sure that the tool is sharp before use. |
| 4 | air-compression brad nailer | Point the tool away from any person. |
Which line in the table matches a tool with the proper safety procedure to handle it in a workspace?
- Line 1
- Line 2
- Line 3
- Line 4
Question 19.
Advances in which of the following areas have most led to improvements in efficiency and reduction of emissions of internal combustion engines produced since the 19 eighties ?
- thermodynamics
- extraction of fuels
- aerodynamics
- embedded electronic microcontrollers
Question 20.
Which of the following devices is an intermediate form when a radio signal is converted into an audio signal?
- transponder
- decoder
- voltmeter
- thermocouple
Question 21.
Cell-phone technology has spread to many parts of the world that never previously had landline-based telephone service. Which of the following qualities of cell-phone technology is likely most responsible for this phenomenon?
- It provides the combined functionality of televisions, radios, and computers.
- It does not require an extensive on-the-ground infrastructure.
- It is able to transmit text, images, and videos in addition to voice.
- It has interchangeable software components.
Question 22.
In a vehicle suspension system, a shock absorber is an oil-filled cylinder that moves in response to changes in the road. The primary function of the shock absorber is to:
- dampen the oscillation of the springs in the vehicle.
- support the weight of the vehicle and its cargo.
- isolate the passengers and cargo from bumps in the terrain.
- allow the wheels to travel independently with respect to the vehicle body.
Question 23.
Airlines use systems engineering to model the supply of and the demand for flights between various cities at various dates and times. These models require a variety of data inputs to determine what flights will be made available at what dates and times. Which of the following examples of quantitative information would most likely be a type of input data needed for such a model?
- passenger capacities of different airplanes in the fleet
- number of flights to be scheduled on a particular day
- net profits earned each day, broken down by region
- how much to charge for each seat on a flight
Question 24.
A student is programming a robot to stop moving before hitting a wall. This will be accomplished by using a sensor. In this scenario, the sensor functions as the:
- input to the system.
- feedback device in the system.
- output of the system.
- processing device in the system.
Question 25.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
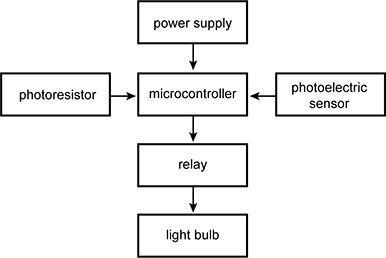
An arrow diagram is shown with a microcontroller in the center. The photo re zis tor, power supply, and photoelectric sensor all point to the microcontroller. From the microcontroller, arrows point to the relay and then from the relay to a light bulb.
A person installs a system in their home that automatically turns certain lights off during the day and on during the night. Which of the following components of this system is a processing device in this system?
- microcontroller
- power supply
- photo re zis tor
- light bulb
Question 26.
Which of the following pieces of evidence has been used to help determine the rate of expansion of the universe?
- the bending of light as it passes through the gravitational field of a galaxy
- the strength of gravity waves as they strike Earth's atmosphere
- the relative motion of the Earth around the Sun
- the red shift of the light from a distant galaxy
Question 27.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Measurement | Earth | Mars | Neptune |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density ( kilograms per meters cubed ) | 5,514 | 3,933 | 1,640 |
| Year (days) | 365 | 687 | 60,190 |
| Orbital Velocity ( kilometers per second ) | 28.8 | 24.1 | 5.4 |
| Orbital Inclination (degrees) | 0.0 | 1.9 | 28.0 |
| Distance from the Sun ( 10 to the 6th kilometers ) | 149.6 | 227.9 | 4,503.4 |
| Gravitational Force ( 10 to the 22nd newtons ) | 3.54 | 0.17 | 0.07 |
Which of the following factors best explains the difference in orbital velocity among the three planets shown in the table?
- the reduction in the density of each planet with increased distance from the Sun
- the decline in the gravitational force between the Sun and the planet with increased distance from the Sun
- the greater tilt of the orbit of each planet with increased distance from the Sun
- the greater length of the orbit and increased length of the year for each planet with decreased distance from the Sun
Question 28.
Which of the following statements best explains why a lunar eclipse occurs rarely instead of every time that there is a full moon?
- Earth, the Moon, and the Sun are seldom in alignment because the plane of the Moon's orbit is tilted relative to that of Earth.
- Earth, the Moon, and the Sun are usually lined up only during the day when Earth does not cast a shadow on the Moon.
- Earth only casts a shadow on the Moon at the points in its elliptical orbit when it is nearest to the Sun.
- Earth's shadow is usually too small to be seen on the disk of the Moon when it is full.
Question 29.
An Earth scientist is using a computer simulation to determine the likely outcome if an asteroid hits Earth with so much force that it changes the tilt of the Earth. If the scientist uses an increase in the tilt of the Earth by 2 degrees as the input, the computer simulation is most likely to report which of the following changes on Earth?
- colder summers and warmer winters
- warmer summers and colder winters
- colder summers and colder winters
- warmer summers and warmer winters
Question 30.
Stars known as blue giants are likely to have a much shorter life cycle than yellow main-sequence stars primarily because they:
- burn much faster and hotter and use up their nuclear fuel quickly.
- are not hot enough to fuse elements heavier than hydrogen.
- rely on nuclear fission instead of fusion to produce their energy.
- possess less nuclear fuel at the start of their lives.
Question 31.
Which of the following planets has a thick atmosphere that consists primarily of carbon dioxide gas?
- Mars
- Neptune
- Venus
- Mercury
Question 32.
Which of the following statements most accurately describes why there are few fossils present in the fossil record from the Archean and Proterozoic eons?
- Populations of organisms in the Archean and Proterozoic eons were too small to be preserved in groups.
- Organisms in the Archean and Proterozoic eons inhabited environments that did not favor preservation.
- Individual organisms in the Archean and Proterozoic eons were too small in size to be preserved.
- Organisms in the Archean and Proterozoic eons generally lacked easily preserved hard body parts.
Question 33.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
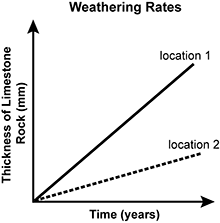
A graph of weathering rates is shown with the thickness of limestone rock in millimeters plotted over time in years. Two locations are plotted. At location 1, the thickness increases very fast in a linear manner. At location 2, the thickness increases much slower in a linear manner.
Which of the following factors was most likely responsible for the different weathering rates between these two limestone locations?
- differences in direction and force of prevailing winds
- differences in regional precipitation rates
- differences in plant species present
- differences in latitude
Question 34.
Growing salt crystals in a middle school earth science laboratory exercise would best help students understand the formation of which of the following types of rock?
- inorganic limestone
- sandstone
- metamorphic granite
- basalt
Question 35.
The upper portion of oceanic crust is primarily composed of which of the following types of rock?
- basalt
- granite
- quartzite
- shale
Question 36.
The theory of plate tectonics has demonstrated that the formation of the majority of ocean crust occurs at:
- convergent plate boundaries.
- spreading centers.
- transform fault boundaries.
- volcanic hot spots.
Question 37.
A geologist working in a cave discovers some very large crystals of quartz. The large size of the crystals is most likely due to their having been formed:
- near the surface, where cooling occurs rapidly.
- in a confined high-pressure magma chamber.
- from a magma rich in silicate minerals.
- in a magma that cooled very slowly deep underground.
Question 38.
Which of the following provides the best example of chemical weathering?
- the slumping of unconsolidated sediments during a rainstorm
- the breakup of a granite outcrop from temperature changes
- the dissolution of limestone by groundwater
- the formation of talus slopes from frost wedging
Question 39.
The deflection of winds and the formation of ocean gyres are primarily caused by:
- the transfer of heat from the tropics to the poles.
- the back-and-forth movement of tides.
- the evaporation of surface water.
- the Coriolis effect.
Question 40.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
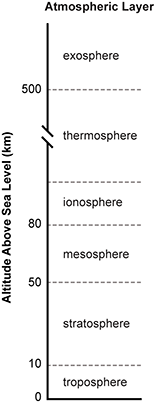
A diagram entitled “Atmospheric layer” shows a stacked bar graph with a y-axis of altitude above sea level in kilometers. At the bottom of the bar graph, from 0 to 10 is the troposphere. Next, from 10 to 50 is the stratosphere and from 50 to 80 is the mesosphere. Above this from 80 to an undefined point is the ionosphere. Then, from the undefined point to 500 is the thermosphere. At the very top, from 500 until the top of the chart is the exosphere.
A scientist collects air samples to determine the degree to which the ozone layer has recovered from the damage caused by chlorofluorocarbon aerosols in the past. The altitude from which a scientist needs to collect the samples is approximately:
- 5 kilometers above sea level.
- 25 kilometers above sea level.
- 70 kilometers above sea level.
- 85 kilometers above sea level.
Question 41.
A geologist is trying to locate groundwater for a community in New England and plans to drill test wells in several locations. In which of the following locations would the geologist be most likely to find an adequate source of groundwater for the community?
- sand and gravel deposits along the edges of a river valley
- a deeply buried layer of fine-grained glacial till
- a bedrock formation composed primarily of shale
- silt and clay deposits from an ancient glacial lake
Question 42.
Which of the following is most directly caused by differential heating of the land surface and ocean surface?
- the changing strength of the trade winds in different seasons
- the early spring tornadoes that occur along the Gulf Coast
- the varying speeds of the jet stream over the course of the year
- the onshore breezes that develop on warm summer afternoons
Question 43.
During late February in southern New England, a warm precipitation-producing air mass moves into the region. Although the temperature of air aloft is well above average for the time of year, a thin layer of extremely cold air remains trapped at the bottom of valleys in the interior. Under these conditions, it is most likely that if steady precipitation falls in these valleys, it will be in the form of:
- snow pellets.
- wet snow that accumulates rapidly.
- heavy sleet.
- rain that freezes on impact.
Question 44.
During the 19 nineties , Doppler radar replaced the radar systems that had been in place for many decades. One of the primary advantages of Doppler radar over conventional radar is that it can be used to:
- estimate the water equivalent of falling frozen precipitation.
- measure the horizontal velocity of falling precipitation.
- calculate the total precipitation that falls over an area.
- measure precipitation intensity over a particular area.
Question 45.
Which of the following statements best explains why most potential sites for development of geothermal power plants in the United States are in the western part of the country, such as Nevada, Colorado, Arizona, and California?
- The western states have higher groundwater temperatures due to their drier and hotter climate.
- The western states have higher groundwater temperatures due to the greater tectonic activity there.
- Locating sites and drilling wells is easier and less costly in the western states because the crust is thinner there.
- Locating sites and drilling wells is easier and less costly in the western states because they lack thick vegetation covering the land.
Question 46.
Most of the kiln-dried lumber used in the building trades is stamped S-P-F, which stands for spruce-pine-fir. Canada is by far the biggest supplier of S-P-F lumber to the U.S. market. Which of the following statements best explains why this is the case?
- A harsh climate unsuitable for deciduous hardwoods means that coniferous softwoods predominate in Canada and their supply is much greater than in the United States.
- The large rivers that flow to the sea in Canada allow Canadian timber companies to cheaply move their S-P-F lumber as whole logs to sawmills before shipping the lumber to U.S. markets.
- Timber harvesting is a common and respected occupation in Canada and provides a skilled workforce that is able to more efficiently exploit forest resources than is possible in the United States.
- Rich soil and abundant precipitation in Canada allow for more rapid growth and quicker maturation of large plantations of young coniferous softwood trees than is possible in the United States.
Question 47.
Which of the following effects of global climate change is the best example of a "positive feedback loop" in the global climate system?
- Increased Antarctic Ocean temperatures lead to local increases in atmospheric water vapor, which falls as snow in the interior of the continent.
- Higher levels of carbon dioxide increase the rate of growth of forests, which increases the sequestering of carbon dioxide in wood.
- Warming temperatures melt Arctic permafrost, which releases methane and carbon dioxide from decomposing vegetation.
- Melting of the Greenland glacier causes fresh water to flow into the North Atlantic, which slows thermohaline circulation.
Question 48.
In a unit about natural disasters and their effects on communities, students are learning how to build a water purification filtration system using common materials. Which of the following strategies would be most effective in removing toxic compounds from the water?
- boiling the water
- bubbling the water with oxygen
- exposing the water to strong sunlight
- percolating the water through activated charcoal
Question 49.
A scientist is studying the effects of climate change on coral reefs over the last five years. The scientist identifies several factors that may be important. Which of the following formats would be most appropriate to demonstrate the influence of each of these factors on coral growth?
- line graph
- pie chart
- scatterplot
- flowchart
Question 50.
A researcher is conducting an experiment to determine whether there is a relationship between acidic precipitation and the decreasing calcium ion concentration of boreal lakes. To ensure that the results of the scientific experiment are valid, the researcher must:
- evaluate the full range of factors that may affect the chemistry of freshwater systems.
- manipulate only one variable while holding the other variables constant.
- explain the causal mechanism that drives the relationship between the two variables.
- exclude data that contradict the expected outcome.
Question 51.
Which of the following statements best describes one difference between the end result of meiosis and the end result of mitosis?
- Mitosis produces four daughter cells, while meiosis produces two daughter cells.
- Mitosis produces daughter cells that are considerably larger in size than the daughter cells produced by meiosis.
- Daughter cells produced by mitosis have both sets of chromosomes, while those produced by meiosis have only one set of chromosomes.
- Daughter cells produced by mitosis contain all the organelles of the parent cell, while those produced by meiosis only contain the parent cell's nucleus.
Question 52.
Which of the following structures represents the lowest level of organization in a plant?
- chloroplast
- sclereid
- xylem
- leaf
Question 53.
Which of the following characteristics of an unknown object would provide the best evidence that the object is a living organism?
- It possesses carbon-containing molecules.
- It is able to reproduce.
- Its temperature is higher than that of the surrounding air or water.
- It has a highly ordered structure.
Question 54.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
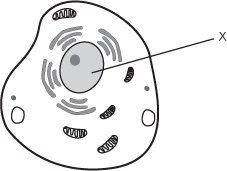
A diagram of a cell is shown. The cell has a number of different membrane-bound compartments. One of these is a structure labeled X. X is roughly egg-shaped, sits in the center of the cell, and is much larger than any of the other structures. X also has a small dark circle within it.
One of the primary roles of the structure labeled X in the generalized cell shown in the diagram above is to:
- control the concentration of ions in the cellular fluids.
- store nutrients necessary for cell functioning.
- contain the genetic material between cell divisions.
- provide a site for the breakdown of cellular waste products.
Question 55.
Whether the products of glycolysis undergo fermentation or cellular respiration during glucose metabolism is dependent on which of the following factors?
- the surface area of the cell
- the cell's immediate energy needs
- the presence or absence of oxygen
- the availability of light
Question 56.
As the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood of a mammal begins to rise, the body maintains homeostasis through which of the following physiological responses?
- decreased cellular respiration
- increased breathing rate
- decreased cardiac output
- increased hemoglobin production
Question 57.
Students culture bacteria collected from water fountains and doorknobs in petri dishes. Following the activity, the petri dishes should be:
- cleaned with soap and hot water and recycled for later use.
- soaked in a mild bleach solution and allowed to air-dry before reuse.
- put in sealed plastic bags and thrown in the trash.
- sterilized and treated as a biohazard to be disposed of properly.
Question 58.
Which of the following factors most limits the amount of energy and matter produced on the forest floor of a coniferous forest in Massachusetts, compared with a deciduous forest in the same area?
- water
- soil nutrients
- sunlight
- winter temperatures
Question 59.
Which of the following characteristics is typical of early successional categories of plants, as compared to later successional plants of the same category?
- small size
- deep roots
- rapid growth
- delayed maturation
Question 60.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Day | Bird Sightings |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 5 |
| 4 | 10 |
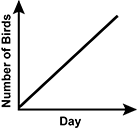
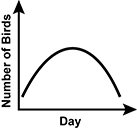
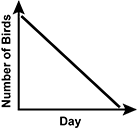
A teacher watches for different species of birds with their class outside their classroom window and records the number of bird sightings each day in the table shown. Which of the following graphs best represents the trend in the data over time?
- A graph of the number of birds sited for each day on the x-axis is shown. The slope appears exponential.
- A graph of the number of birds sited for each day on the x-axis is shown. The slope has a positive linear trend.
- A graph of the number of birds sited for each day on the x-axis is shown. The slope goes up, curves and turns back down.
- A graph of the number of birds sited for each day on the x-axis is shown. The slope has a negative linear trend.
Question 61.
The type of biome that characterizes a particular region is most significantly influenced by which of the following pairs of factors?
- soil type and depth
- day length and prevailing wind direction
- temperature and rainfall
- nutrient availability and food web complexity
Question 62.
A sagebrush plant releases chemical compounds into the soil around it. These compounds inhibit the germination and growth of other plants in the area immediately surrounding the sagebrush plant. This strategy most likely serves to:
- reduce competition for resources in short supply.
- make the plant less appealing to herbivores.
- limit cross-pollination with other sagebrush plants.
- slow the spread of diseases and insect pests.
Question 63.
Use the passage below to answer the question that follows.
A field in central New England where corn was grown is abandoned and left undisturbed. Initially grasses and weed species take over the field. Gradually, woody shrubs and species such as sumac and poplar become established, followed by white pines. After several decades, the area is characterized by a stable community of mixed hardwood trees dominated by oaks.
Which of the following processes is described in the passage?
- evolution
- biological magnification
- exponential growth
- succession
Question 64.
Which of the following structures in a flowering plant is best adapted for the function of receiving pollen?
- petal
- anther
- stigma
- ovary
Question 65.
Monerans are a type of prokaryotic cell that reproduces asexually through fission. The resulting offspring of one reproductive event should be:
- a single genetically distinct daughter cell.
- two genetically identical daughter cells.
- two genetically distinct daughter cells.
- four genetically identical daughter cells.
Question 66.
A certain type of big cat preys on large bovids similar to Cape buffalo. The bovids are difficult to take down by a single cat, so the cats live and hunt in packs. A mutation that allows faster growth and larger body size in the cat proves to increase their success in capturing prey and spreads through successive generations. Which of the following changes in environmental conditions would make this mutation for larger body size disadvantageous for the cats' survival in the future?
- cooling of the environment that results in the bovids growing larger to retain body heat
- increased rainfall that leads to more grass growth and allows the bovids to forage in larger groups
- drying of the environment that favors smaller herbivores that are more efficient grazers than the large bovids
- increased seasonality that allows the open country habitat to spread at the expense of the surrounding forests
Question 67.
Which of the following types of analyses would be most useful in tracing a genetic disorder in a family?
- cohort analysis
- case control analysis
- pedigree analysis
- double-blind analysis
Question 68.
The fur color of a rodent species is determined by a single gene with two possible alleles. The allele for black fur, big B , is dominant, and the white fur allele, little B , is recessive. A rodent with genotype big B little b is bred with a rodent with genotype little B little B . What is the expected phenotypic ratio of the offspring from this cross?
-
25% black fur
75% white fur -
50% black fur
50% white fur -
75% black fur
25% white fur -
100% black fur
0% white fur
Question 69.
A DNA molecule is about to undergo replication. The base sequence of a small section of one of the original DNA strands is shown below.
A–A–G–C–G–T–A
What will be the base sequence of the corresponding section of the new complementary DNA strand that is formed?
- A–A–G–C–G–T–A
- T–T–C–G–C–A–T
- U–U–C–G–C–A–U
- C–C–T–A–T–G–C
Question 70.
Which of the following statements best explains how a given variant gene can be maintained in a large portion of a population, even if that gene does not directly confer an advantage?
- Genetic drift leads to the maintenance of variant genes through chance alone.
- Mutations can occur over and over at the same site and constantly feed new variation into a population.
- Recessive genes are not expressed in the phenotype of heterozygous individuals.
- Natural selection facilitates the spread of some genes in a population at the expense of others.
Question 71.
A large population of mosquitoes is exposed to the pesticide DDT over time and quickly evolves resistance. This change in the mosquito population was most likely caused by:
- recombination of several genes into a new configuration that confers resistance.
- adaptation of individual mosquitoes due to exposure early in their lifetimes.
- genetic drift that concentrates variation already present in the population.
- natural selection acting on variation already present in the population.
Question 72.
Which of the following statements best describes one difference between multicellular protists, such as giant kelp, and other multicellular eukaryotes?
- The cells of multicellular protists are all descended from a single parent cell.
- Multicellular protists can regenerate tissues that are damaged and new individuals can grow from separated parts.
- The cells of multicellular protists are not specialized or differentiated into tissues.
- Multicellular protists can switch back and forth between sexual and asexual reproduction depending on environmental conditions.
Question 73.
The fact that mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA provides the strongest support for which of the following hypotheses?
- Organic molecules formed spontaneously under the conditions found on the early Earth.
- Aerobic organisms evolved after anaerobic organisms.
- Eukaryotes evolved as a result of endosymbiotic relationships among prokaryotes.
- Life on Earth first arose in the oceans rather than on land.
Question 74.
Which of the following observations provides support for the theory of evolution?
- A snowshoe hare's coat turns from brown to white as the winter approaches.
- A young lion becomes a more skilled hunter during its first years of life.
- A tree seedling develops a root system that allows it to cling to the rocky hillside where it germinated.
- A population of insects develops resistance to a particular pesticide over several generations.
Question 75.
A scientist who wants to conduct an investigation of the effects of natural selection on the evolution of a population would most likely select a type of organism characterized by:
- a short generation time.
- high mutation rates.
- asexual reproduction.
- a large genome.
Question 76.
In 1911 Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment in which he directed alpha particles from a radioactive source at gold foil. He discovered that the vast majority of the alpha particles were passing through the thin gold foil, but very rarely one of the particles would bounce off the gold foil. The results of the experiment suggested to Rutherford that the mass of an atom was:
- scattered in pockets outside of the nucleus of the atom.
- concentrated in concentric shells surrounding the center of the atom.
- evenly dispersed throughout the entire atom.
- concentrated in a very small nucleus at the center of the atom.
Question 77.
Which of the following is an example of a pure substance as opposed to a mixture?
- alcohol
- milk
- gasoline
- blood
Question 78.
Water has a significantly higher surface tension than most other substances. Which of the following factors is directly responsible for this characteristic of water?
- the size of atoms in a water molecule
- the solvent properties of water
- the hydrogen bonding between water molecules
- the specific heat capacity of water
Question 79.
An outdoor iron railing rusts after several years. The rust on the railing is composed of:
- the elemental iron that has separated from the railing as the result of temperature fluctuations.
- an oxide of iron produced during the chemical reaction of the railing with the atmosphere.
- the product of broken chemical bonds between the iron and oxygen atoms that make up the railing.
- a reduced form of iron produced by the chemical reaction of water in the atmosphere with the railing.
Question 80.
Use the reaction equation below to answer the question that follows.
H C L aqueous plus N A O H aqueous yields H 2 O liquid plus X
According to the principle of conservation of matter, which of the following is the chemical formula for the reaction product X in the equation shown?
- N A O H aqueous
- H C L aqueous
- N A C L aqueous
- O 2 gas
Question 81.
Which of the following processes in the water cycle transfers heat into the environment?
- ice melting
- water boiling
- ice sublimating
- water freezing
Question 82.
Foams, wools, and fibers can act as thermal insulation. Many types of thermal insulation trap air in small pockets of gas. Which of the following statements best explains how the transfer of heat is reduced by these types of insulation?
- The insulation functions as a radiant barrier, reflecting heat and light from the Sun.
- Convection within the insulating material increases, decreasing heat transfer by conduction.
- Thermal conductivity is much lower in the insulation than in pure solids, and convection cell size is much smaller.
- Heat transfer by radiation is eliminated, specifically through multiple layers of materials with various densities.
Question 83.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Several materials are selected to test as thermal insulators in an investigation, whose steps are as follows:
- Boiling water is poured into a flask, which is then closed with a rubber stopper that holds a thermometer.
- The flask is placed into a box containing the first material.
- A timer is set and measurements are recorded every minute for ten minutes.
This procedure is repeated for the other materials being tested. The same flask, box, and amount of water are used for each trial.
In this investigation, the dependent variable is the:
- insulated material.
- time each trial takes.
- volume of heated water.
- amount of heat conserved.
Question 84.
Rock salt is often sprinkled on frozen roads and walkways to melt ice. This practice is effective primarily because the salt:
- decreases the freezing point of the water.
- breaks the covalent bonds within the water molecules.
- increases the temperature of the water.
- eliminates the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules.
Question 85.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
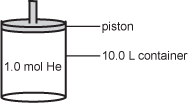
When 1.0 mol of helium at 298 kelvins is placed in the 10.0 liters container shown above, it exerts a pressure of 2.4 atmospheres . Which of the following changes to this system would lead to a decrease in pressure?
- increasing the temperature of the system
- adding additional helium to the container
- moving the piston to a lower position within the container
- removing some of the helium from the container
Question 86.
Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
| Object | Mass ( kilograms ) | Height Above Ground ( meters ) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 7.0 |
| B | 5 | 3.0 |
| C | 10 | 1.0 |
| D | 20 | 0.25 |
The table shows the results of an experiment when four objects are dropped from different heights. Which object has the greatest gravitational potential energy when dropped? ( P E = m g h , where g is the acceleration due to gravity at Earth's surface and g = 9.8 meters per second squared )
- object A
- object B
- object C
- object D
Question 87.
Which of the following classroom activities would be most appropriate for demonstrating the use of mechanical energy?
- illuminating a surface with black lights
- powering a device using batteries
- dropping a ball from a set height
- adding ice to a glass of water
Question 88.
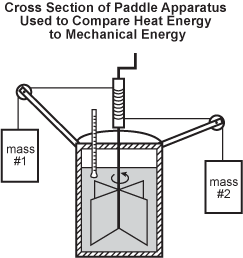
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
A cross section of a paddle apparatus used to compare heat energy to mechanical energy is shown. There are two arms extending from the apparatus, one higher than the other. The taller arm has mass #1, which is connected by a string that winds around a central pole to connect to the shorter arm of mass #2. It is connected in such a way so that when one mass moves, the other mass may move. The central pole extends down into a closed chamber with a paddle wheel in a liquid that turns in a counter-clockwise manner. There is a thermometer in the liquid that extends up into the space above the liquid within the chamber and then farther up out of the closed container.
The device shown in the diagram above was developed to compare heat energy and mechanical energy. As the two masses fall, they turn the paddle wheel inside the sealed container, causing the temperature of the water to rise. The operation of this device shows that:
- the change in the work done on the system is equal to the kinetic energy lost by the system.
- the increase in the mechanical energy of the system reduces the internal energy of the water.
- the change in the potential energy of the weight is equal to the change in the internal energy of the water.
- the entropy of the water is reduced as mechanical energy is expended to do work on the system.
Question 89.
As an air mass near Earth's surface rises and expands, which of the following energy changes occurs within the rising air mass?
- The potential energy of the air mass is expended as water vapor condenses.
- The thermal energy of the air mass is converted into chemical energy.
- The mechanical energy of the rising air mass is converted into heat energy.
- The kinetic energy of the air mass decreases as it cools.
Question 90.
In which of the following systems is entropy decreasing?
- A tree produces sugar during photosynthesis.
- Salt dissolves in a pot of boiling water.
- Coastal cliffs erode during a winter storm.
- The metal frame of a bicycle rusts when left outside.
Question 91.
Use the graph below to answer the question that follows.
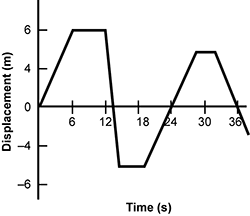
A graph of displacement in meters on the y-axis is shown versus time in seconds on the x-axis. The trend line starts at (0, 0), goes up in a linear manner to (6, 6), flattens out until (12, 6), then decreases in a linear manner until (14, negative 5), where it flattens out to (20, negative 5) and increases in a linear manner until (28, 5). From there it flattens out to (32, 5) and decreases linearly past (36, negative 2) and off the graph.
The graph represents the displacement of a truck at a construction site. Which of the following statements about the truck's movement is true?
- The truck stops moving at 24 seconds.
- The truck starts moving forward at 36 seconds.
- The truck has a constant acceleration at 6 seconds.
- The truck starts moving in a reverse direction at 12 seconds.
Question 92.
Which of the following dogs would be expected to put in the most amount of work to climb a flight of stairs?
- the largest dog
- the fastest dog
- the smallest dog
- the slowest dog
Question 93.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
Two students hold a rope taut between them such that it appears to be a straight line. Above their heads, there is an arrow pointing towards each of the students.
The classroom activity shown in the diagram would be most appropriate for demonstrating which of the following physical science concepts?
- entropy
- net forces
- energy transfers
- conservation of matter
Question 94.
A scientist in outer space measures the acceleration of an object after a known force is applied to the object. Using only the acceleration measurements and the magnitude of the applied force, the scientist can calculate the object's:
- mass.
- volume.
- density.
- weight.
Question 95.
Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
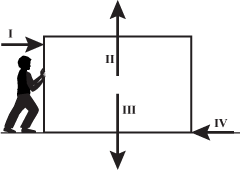
A free-body diagram of a person pushing on a box along the ground is shown. The person is on the left of the box. Arrow 1 points from the left toward the right of the box. Arrow 2 points from the center to above the box. Arrow 3 points from the center to below the box. Arrow 4 points from the right to the left of the box.
In the free-body diagram shown above, a person applies a force to a box in order to slide it across the floor. If the box is sliding at a constant velocity, which of the following forces in the free-body diagram must be equal in magnitude?
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
Question 96.
In which of the following scenarios will transverse waves produce longitudinal waves?
- A wind gust blows across the surface of a lake.
- A person claps their hands.
- A supersonic jet breaks the sound barrier.
- A musician plucks a guitar string.
Question 97.
Which of the following explains why white light separates into the different colors of the spectrum as it travels through a prism?
- Different frequencies of light move through a prism at different speeds, causing them to refract differently as they cross air-glass boundaries.
- The prism magnifies the amplitude of high-frequency wavelengths more than low-frequency wavelengths.
- Variable reflection of light entering the prism at different angles splits the light into different wavelengths.
- The prism polarizes the light waves as they travel through the glass, dividing them into distinct wavelengths.
Question 98.
A person turns on a light switch and almost instantaneously the light goes on. The rapid response of the light to the turning of the switch results from the transfer of:
- electrons through the circuit at the speed of light.
- charged ions through the electric circuit.
- an electric field through the circuit at close to the speed of light.
- kinetic energy of the atoms making up the electric circuit.
Question 99.
Several lights are connected in a parallel circuit and one of the lights burns out. Which of the following statements best describes how the burning out of the light affects the other lights in the parallel circuit?
- Charge still flows through the burned-out light, providing the lights in the other branches of the circuit with electricity.
- The other lights continue to draw the same current since neither resistance nor voltage is affected in those branches of the circuit.
- Current is increased in the other branches of the circuit, so the lights will brighten as a result of the increased flow of charge.
- The branches of the circuit draw less charge overall because the burned-out light no longer draws a charge, reducing the brightness of the lights.
Question 100.
The magnetism of a common bar magnet results from:
- the oscillating polarization of atoms in the magnet.
- the alignment of magnetic fields generated by spinning electrons in the magnet.
- the vibration of the atomic nuclei in the magnet.
- the magnetic field produced by electrons orbiting the nucleus in opposite directions.
Open-Response Items
The directions shown below represent what you will see on the actual test. For the purposes of this practice test, you will be able to type your written responses in the boxes provided on the answer key.
This section of the test consists of two open-response item assignments. You will be asked to prepare a written response of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, for each assignment.
Read the assignments carefully before you begin your responses. Think about how you will organize your responses. You may use the erasable sheet(s) to make notes, write an outline, or otherwise prepare your responses. However, your final response to each assignment must be either:
- typed into the on-screen response box,
- written on a response sheet and scanned using the scanner provided at your workstation, or
- provided using both the on-screen response box (for typed text) and a response sheet (for calculations or drawings) that you will scan using the scanner provided at your workstation.
Instructions for scanning your response sheet(s) are available by clicking the "Scanning Help" button at the top of the screen.
As a whole, your response to each assignment must demonstrate an understanding of the knowledge of the field. In your response to each assignment, you are expected to demonstrate the depth of your understanding of the subject area by applying your knowledge rather than by merely reciting factual information.
Your responses to the assignments will be evaluated based on the following criteria.
- Purpose: the extent to which the response achieves the purpose of the assignment
- Subject Knowledge: appropriateness and accuracy in the application of subject knowledge
- Support: quality and relevance of supporting evidence
- Rationale: soundness of argument and degree of understanding of the subject area
The open-response item assignments are intended to assess subject knowledge. Your responses must be communicated clearly enough to permit valid judgment of the evaluation criteria by scorers. Your responses should be written for an audience of educators in this field. The final version of each response should conform to the conventions of edited American English. Your responses should be your original work, written in your own words, and not copied or paraphrased from some other work.
Be sure to write about the assigned topics. Remember to review your work and make any changes you think will improve your responses.
Any time spent responding to an assignment, including scanning the response sheet(s), is part of your testing time. Monitor your time carefully. When your testing time expires, a pop-up message will appear on-screen indicating the conclusion of your test session. Only response sheets that are scanned before you end your test or before time has expired will be scored. Any response sheet that is not scanned before testing ends will NOT be scored.
Question 101.
Use the information below to complete the exercise that follows.
Environmental and genetic factors can affect the size and growth of a pea plant.
Use your knowledge of life science to write an essay of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- explain two key scientific concepts related to environmental and genetic factors that influence the growth of the pea plant;
- use a representative graph, formula, and/or diagram with all proper labels to model factors that influence the growth of the pea plant; and
- discuss the cause-and-effect relationship between environmental and/or genetic factors and the growth of the pea plant.
Question 102.
Use the information below to complete the exercise that follows.
Design an investigation that addresses the concept of electrostatic forces.
Use your knowledge of physical science to write an essay of approximately 150 to 300 words, or 1 to 2 pages, in which you:
- form and describe a testable scientific claim that addresses the concept of electrostatic forces;
- outline a specific scientific procedure to investigate the proposed claim, including identifying variables and possible controls;
- describe a possible result provided by the data; and
- explain how the data could support or refute the tested claim.